Diabetic Feet
The Importance of Foot Care
Regarding diabetic feet, foot care is crucial, especially if you have diabetes, as it can help prevent serious complications such as nerve damage, circulation problems, and infections. By taking proactive steps, you can maintain healthy feet and overall well-being.
Key Reasons for Foot Care
- Preventing Nerve Damage and Circulation Issues: Diabetes can lead to neuropathy and poor blood flow, which can result in severe foot problems if not managed properly.
- Avoiding Infections: Proper foot care reduces the risk of infections, which can be more difficult to treat in people with diabetes.
Maintaining Healthy Feet
To keep your feet in good condition, it’s important to adopt a comprehensive approach that includes managing your diabetes and leading a healthy lifestyle. Here are some essential practices:
- Regular Medical Exams:
- Schedule yearly foot exams to check for any issues.
- Monitor your ABCs: A1c (blood sugar levels), blood pressure, and cholesterol.
- Daily Blood Sugar Monitoring:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels daily to ensure they are within a healthy range.
- Regular Exercise:
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve circulation and overall health.
- Balanced Diet:
- Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-dense foods to support overall health.
Foot Care Regimen (Diabetic Feet)
Implementing a thorough foot care routine can help prevent serious foot problems:
- Inspect Your Feet Daily: Look for any cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling.
- Wash and Dry Your Feet Properly: Clean your feet daily with mild soap and lukewarm water, then dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Moisturize Your Feet: Apply lotion to prevent dry skin, but avoid the areas between your toes to prevent fungal infections.
- Trim Your Toenails Carefully: Cut nails straight across and file the edges to prevent ingrown toenails.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Choose well-fitting shoes that provide support and protection. Avoid walking barefoot to prevent injuries.
- Avoid Prolonged Pressure: Refrain from standing or sitting in one position for too long to ensure good circulation.
By following these guidelines and maintaining a consistent foot care routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing serious foot problems and enhance your overall quality of life.
SEE ALSO: Heel Crack Treatment
Toenail Care
People with diabetes can often manage routine toenail care, but certain conditions like visual impairments, nerve problems, or circulatory changes in the legs or feet can make it unsafe. It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if you can safely trim your toenails and to learn the proper techniques.
Tips for Proper Toenail Care
- Trim After Washing: Cut your toenails after washing your feet when your nails are soft.
- Cut Straight Across: Avoid a curved cut to help prevent ingrown toenails.
- Avoid Cutting Corners: Use an emery board to smooth the edges instead of cutting into the corners.
- Don’t Cut Too Short: Be careful not to trim your toenails too short to avoid sores.
- Seek Professional Help: If you have difficulty seeing, or if your nails are thick or yellowed, have a foot doctor or healthcare provider trim them.
Footwear
If you have neuropathy or nerve damage affecting foot sensitivity, you might not notice cuts or bumps. To protect your feet, it’s important to wear shoes at all times.
Choosing the Right Shoes
- Comfortable Fit: Select well-fitting shoes with plenty of room, especially in the toe box. Avoid buying tight shoes with the hope that they will stretch.
- Breathable Materials: Choose shoes made from leather, canvas, or suede instead of plastic or other non-breathable materials.
- Avoid Certain Types: Steer clear of thong sandals, flip-flops, pointed-toe and open-toe shoes, and very high heels.
- Adjustable Shoes: Wear shoes that can be adjusted with laces, buckles, or Velcro.
- Daily Inspections: Check the inside of your shoes daily for tears or bumps that could cause pressure or irritation.
- Change Shoes Regularly: If you have nerve damage, switch shoes after five hours to change pressure points on your feet.
- Special Shoes: If you frequently have foot problems, ask your doctor if special shoes would be beneficial.
Sock Care
- Protective Layer: Socks can provide a soft protective layer between your foot and shoe.
- Clean and Dry: Wear clean, dry socks or non-binding pantyhose. Avoid socks or hosiery with seams that can cause additional pressure points or that are too tight on the leg.
- Socks in Bed: Wear socks to bed if your feet are cold.
By following these guidelines, you can maintain healthy toenails and feet, significantly reducing the risk of complications. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and recommendations.
Signs and Symptoms of Foot Problems
It’s crucial to identify early warning signs of foot problems to prevent complications. Be alert for the following symptoms:
- Burning, Tingling, or Painful Feet: These sensations can indicate nerve issues.
- Loss of Sensation: An inability to feel heat, cold, or touch can be a sign of neuropathy.
- Color or Shape Changes: Discoloration or deformities in your feet should be monitored closely.
- Loss of Hair: A decrease in hair growth on the toes, feet, and lower legs can indicate circulation problems.
- Thickening and Yellowing Toenails: This may be a sign of fungal infections or other issues.
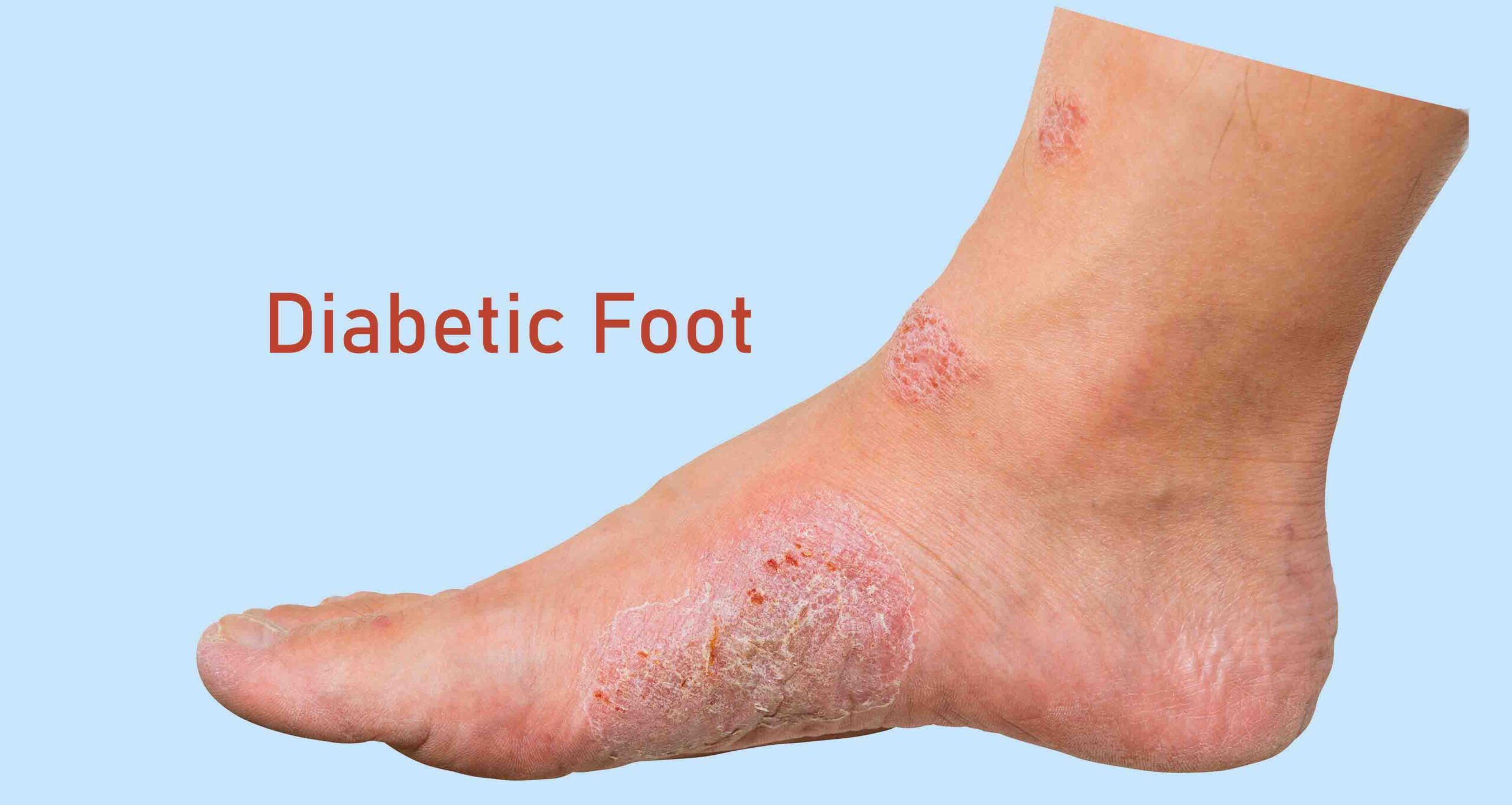
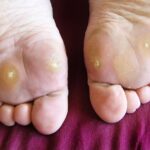
- Appearance of Red Spots, Blisters, Sores, Ulcers: These can quickly become serious if not treated.
- Infected Corns or Ingrown Toenails: These can lead to severe infections.
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately to avoid serious health complications.
Potential Complications
Adhering to proper foot care guidelines can help prevent foot problems. However, high blood sugar levels over time can cause nerve damage and circulation issues, which contribute to foot problems. Untreated sores, ingrown toenails, and other issues can lead to infections. Poor circulation complicates the healing of infections, making prevention critical.
- Gangrene: Infections that do not heal can cause tissue to die and turn black, a condition known as gangrene. Treatment may involve surgical amputation of a toe, foot, or part of a leg.
Visiting the Doctor
Regular check-ups are essential for maintaining foot health:
- Routine Examinations: A doctor should examine your feet at every visit, with a thorough foot exam conducted annually. If you have a history of foot problems, more frequent checks are necessary.
- Foot Care Guidance: Your healthcare provider should offer information on foot care and address any concerns.
- Report Issues Promptly: Inform your doctor about any corns, calluses, sores, cuts, bruises, infections, or foot pain.
If needed, your doctor can refer you to a podiatrist specializing in diabetic foot care or provide information about special shoes that may help.
Importance of Prompt Medical Attention
Diabetes-related foot problems can escalate rapidly and are challenging to treat. Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent severe complications and maintain foot health.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.