Genital Warts in Men: A Complete, In-Depth Health Guide
Genital warts in men explained in detail. Learn causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, and lifestyle tips to manage HPV and protect sexual health.
Introduction: Genital warts in men are a common sexually transmitted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite how widespread the condition is, it is often surrounded by stigma, fear, and misinformation. Many men delay seeking help because of embarrassment or lack of proper understanding, which can lead to prolonged symptoms, emotional distress, and transmission to sexual partners.
Genital warts are caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). While the condition is generally not life-threatening, it can significantly affect a man’s physical comfort, sexual health, confidence, and overall quality of life. The good news is that genital warts are manageable, treatable, and in many cases preventable.
This comprehensive health guide explains genital warts in men in clear, simple language. It covers causes, symptoms, stages, diagnosis, treatment options, home care, lifestyle considerations, prevention strategies, and frequently asked questions. The goal is to provide accurate, practical, and reassuring information for men seeking clarity and support.
What Are Genital Warts?
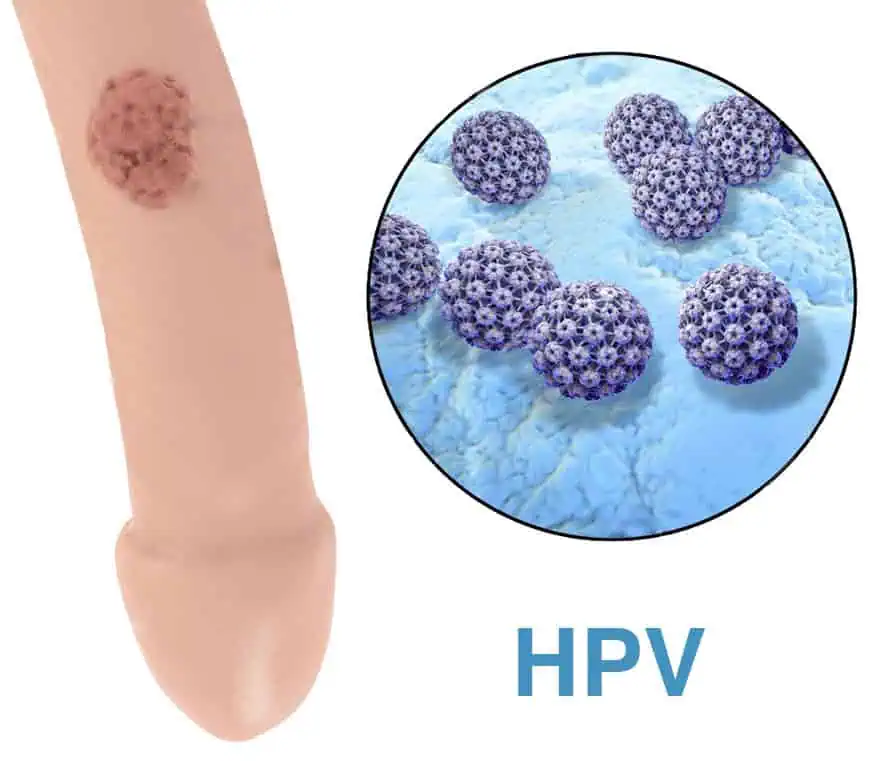
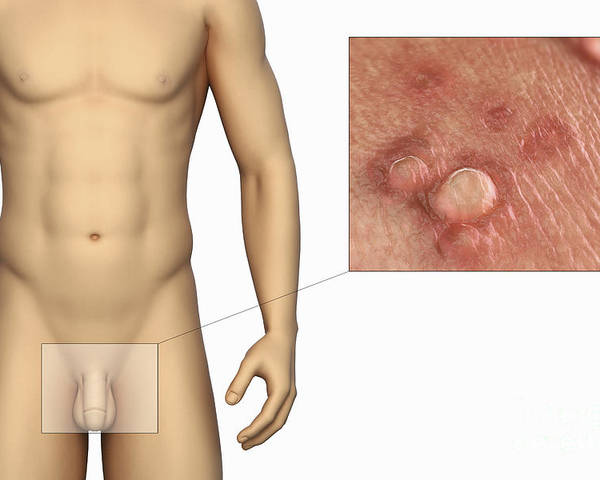
Genital warts are small growths or lesions that appear on or around the genital and anal areas. They are caused by specific low-risk strains of the human papillomavirus, most commonly HPV types 6 and 11. These strains are different from the high-risk HPV types that are associated with cancers.
In men, genital warts may appear on the penis, scrotum, groin, inner thighs, anus, or around the opening of the urethra. They can vary in size, shape, and number. Some warts are small and flat, while others are raised and clustered, sometimes resembling a cauliflower-like texture.
Understanding HPV and Its Role in Genital Warts
Human papillomavirus is one of the most common sexually transmitted viruses globally. There are over 100 different types of HPV, and more than 40 can infect the genital area.
Low-Risk vs High-Risk HPV Types
- Low-risk HPV types (such as HPV 6 and 11) cause genital warts but rarely lead to cancer.
- High-risk HPV types (such as HPV 16 and 18) are linked to cancers of the cervix, anus, penis, and throat.
A man can carry HPV without showing any symptoms, which makes it easy to unknowingly transmit the virus to others.
How Genital Warts Are Transmitted
Genital warts in men are primarily spread through intimate skin-to-skin contact. This includes vaginal, anal, or oral sexual contact with an infected partner.
Important points about transmission include:
- Penetration is not required for transmission
- Condoms reduce risk but do not provide complete protection
- HPV can spread even when warts are not visible
- A person can be contagious months or years after initial infection
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing genital warts in men:
- Unprotected sexual activity
- Multiple sexual partners
- Weakened immune system
- Early sexual activity
- Smoking
- Chronic stress
- Poor overall health
Men with compromised immunity are more likely to develop persistent or recurrent warts.
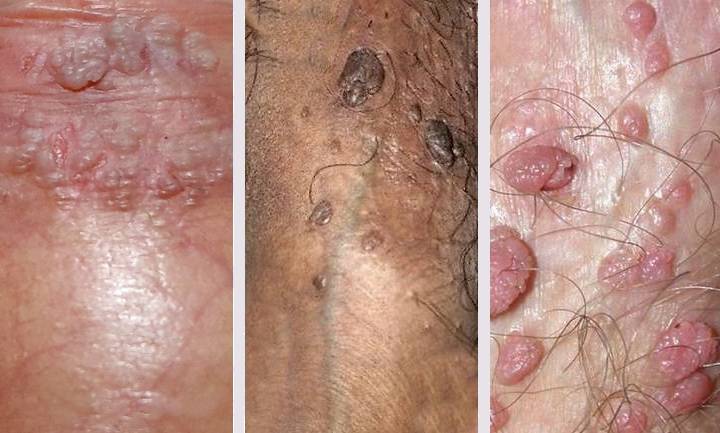
Signs and Symptoms of Genital Warts in Men
Genital warts can vary widely in appearance and symptoms. Some men may not notice them immediately, especially if the warts are small or located internally.
Common Symptoms
- Small bumps or growths in the genital area
- Flesh-colored, gray, or slightly darker lesions
- Flat or raised growths
- Single wart or clusters of warts
- Mild itching or discomfort
- Bleeding during sexual activity (rare)
Genital warts are usually painless, which often delays diagnosis.
Stages of Genital Warts Infection
Initial Exposure
HPV enters the body through microscopic breaks in the skin. At this stage, there are usually no symptoms.
Incubation Period
The incubation period can last from weeks to several months. During this time, the virus remains active in the body but warts may not be visible.
Wart Development
Visible warts appear once the virus multiplies and affects skin cells. The number and size of warts vary among individuals.
Dormant Phase
In some cases, the immune system suppresses the virus, causing warts to disappear. However, the virus may still remain in the body.
Diagnosis of Genital Warts in Men
Diagnosis is usually made through a physical examination by a healthcare professional. In most cases, visual inspection is sufficient.
Diagnostic Methods
- Physical examination
- Application of acetic acid solution to highlight lesions
- Biopsy (rare, used when diagnosis is uncertain)
There is currently no routine HPV test approved for men.
Medical Treatment Options
While there is no cure that completely eliminates HPV from the body, several treatments can remove visible warts and reduce symptoms.
Topical Treatments
- Prescription creams and solutions applied directly to warts
- These treatments destroy wart tissue over time
In-Office Procedures
- Cryotherapy (freezing warts)
- Electrocautery (burning warts)
- Surgical removal
- Laser therapy
The choice of treatment depends on the size, number, and location of warts.
Home Care and Supportive Management
Home care focuses on supporting healing, preventing irritation, and reducing recurrence.
- Keep the affected area clean and dry
- Avoid scratching or picking warts
- Wear loose-fitting clothing
- Avoid sexual contact during active outbreaks
Self-treatment with unapproved products should be avoided.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Genital warts in men can affect mental and emotional well-being. Feelings of shame, anxiety, fear of rejection, and reduced self-esteem are common.
Open communication with partners, professional counseling, and proper education can help reduce emotional distress.
Sexual Health and Relationships
Men diagnosed with genital warts should inform current and recent sexual partners. Honest communication builds trust and reduces transmission risk.
Abstaining from sexual contact during treatment and using protection afterward can help manage the condition responsibly.
Prevention of Genital Warts in Men
HPV Vaccination
The HPV vaccine is one of the most effective preventive measures. It protects against the most common wart-causing and cancer-causing HPV strains.
Safe Sexual Practices
- Consistent condom use
- Limiting number of sexual partners
- Regular sexual health checkups
Lifestyle Measures
- Strengthening immune health
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress
Can Genital Warts Go Away on Their Own?
In many cases, genital warts may disappear without treatment as the immune system suppresses the virus. However, this can take months or years, and warts may return.
Long-Term Outlook
Most men with genital warts lead normal, healthy lives. With proper treatment and preventive care, outbreaks often become less frequent over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are genital warts dangerous?
Genital warts are generally not dangerous, but they require medical evaluation to rule out other conditions.
Can genital warts cause cancer?
The strains that cause genital warts are usually low-risk and not linked to cancer.
Can I still have children?
Yes. Genital warts do not affect fertility in men.
Complications Associated With Genital Warts in Men
Although genital warts are generally considered low-risk, untreated or recurrent cases can lead to several complications. Persistent warts may grow larger, spread to surrounding areas, or become uncomfortable during daily activities. In some cases, warts located near the urethra or anus may interfere with urination or bowel movements.
Another important complication is recurrence. Even after successful treatment, the virus may remain dormant in the body, allowing warts to reappear during periods of stress or weakened immunity. This is why long-term management and immune support are crucial.
Genital Warts vs Other Male Genital Conditions
Many men confuse genital warts with other skin conditions affecting the genital area. Proper identification is essential for correct treatment.
- Genital warts vs pearly penile papules: Pearly penile papules are harmless, non-infectious bumps that appear around the head of the penis and do not require treatment.
- Genital warts vs herpes: Herpes causes painful blisters or sores, while genital warts are usually painless growths.
- Genital warts vs skin tags: Skin tags are benign growths not caused by HPV and are not contagious.
A healthcare professional can accurately distinguish between these conditions through examination.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Healing and Reduce Recurrence
Lifestyle plays a major role in how the body responds to HPV infection. Strengthening overall health can reduce outbreaks and support faster healing.
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet with fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains
- Prioritize quality sleep to support immune function
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques
- Avoid smoking, as it weakens immune defenses
- Limit alcohol intake
Nutrition and Immune Support
A strong immune system helps control HPV and reduce wart recurrence. Nutrients that support immune health include:
- Vitamin C from citrus fruits and berries
- Vitamin A from carrots and leafy greens
- Zinc from nuts, seeds, and legumes
- Antioxidants from colorful fruits and vegetables
Staying well-hydrated also supports skin healing and overall health.
HPV Vaccination and Its Role in Men
The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing the strains of HPV that cause most genital warts. It is recommended for boys and men, even if they are already sexually active. Vaccination reduces the risk of new infections and helps protect sexual partners.
Myths and Facts About Genital Warts in Men
Myth: Only promiscuous men get genital warts
Fact: Any sexually active man can contract HPV.
Myth: Condoms provide complete protection
Fact: Condoms reduce risk but do not fully eliminate it.
Myth: Genital warts mean cancer
Fact: Most genital warts are caused by low-risk HPV strains.
Frequently Asked Questions (Extended)
Can genital warts spread to other parts of the body?
Genital warts usually remain in the genital area but can spread through direct contact.
Can shaving spread genital warts?
Yes. Shaving can cause micro-cuts that spread the virus to nearby skin.
How long do genital warts last in men?
They may last weeks, months, or longer depending on immune strength and treatment.
Final Thoughts
Genital warts in men are common, manageable, and treatable with proper medical care and lifestyle support. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, honest communication with partners, and preventive measures such as vaccination are key to controlling the condition.
By understanding genital warts and taking proactive steps to support immune health, men can reduce recurrence, protect their partners, and maintain a confident, healthy life.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.