Managing Sugar Levels Naturally
In managing sugar levels, understand that elevated blood sugar levels, commonly referred to as hyperglycemia, are closely associated with diabetes and prediabetes.
Prediabetes is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that are not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
The regulation of blood sugar levels in the body is primarily managed through the production and action of insulin, a hormone that facilitates the uptake and utilization of glucose by the body’s cells. Insulin plays a pivotal role as the main regulator of blood sugar levels. However, various factors can disrupt this delicate balance and contribute to hyperglycemia.
Internal Factors Contributing to High Blood Sugar
Internally, several mechanisms can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels:
- Overproduction of Glucose by the Liver: Sometimes, the liver can produce excessive amounts of glucose, contributing to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Insufficient Insulin Production: In some cases, the body may produce inadequate amounts of insulin, leading to impaired glucose regulation.
- Insulin Resistance: This condition occurs when the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, making it challenging for glucose to enter the cells and be utilized effectively.
External Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
External factors can also influence blood sugar levels and contribute to hyperglycemia:
- Dietary Choices: Consuming a diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, diuretics, and some antipsychotic drugs, can impair blood sugar regulation and contribute to hyperglycemia.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity can reduce the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can elevate blood sugar levels.
According to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 13% of U.S. adults are living with diabetes, while an additional 34.5% have prediabetes. This alarming statistic indicates that nearly half of all U.S. adults are either living with diabetes or at risk of developing the condition.
Effective management of blood sugar levels is crucial, especially for individuals with diabetes. Persistent hyperglycemia can lead to severe complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Strategies to Naturally Lower Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and well-being. Here are 14 evidence-based strategies to help naturally lower blood sugar levels:
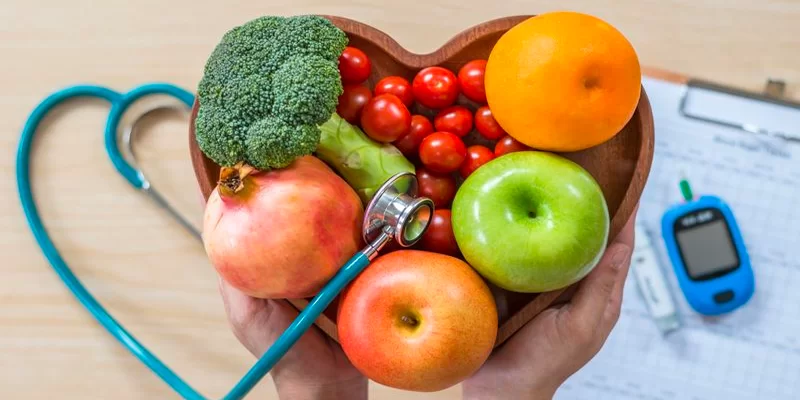
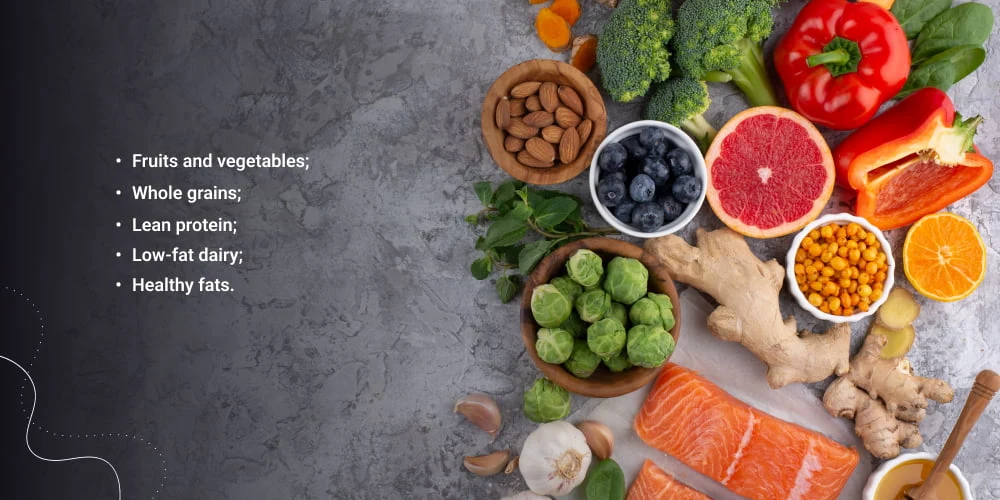
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming a diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit intake of refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, each week.
- Monitor Carbohydrate Intake: Be mindful of your carbohydrate consumption and opt for complex carbohydrates that are digested more slowly.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or tai chi to help lower cortisol levels and regulate blood sugar.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support overall health and blood sugar regulation.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Moderate your alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly: Keep track of your blood sugar levels using a glucometer and consult with a healthcare professional to adjust your treatment plan as needed.
- Avoid Sugary Drinks: Limit or avoid sugary beverages like sodas, fruit juices, and energy drinks, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Include plenty of fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, to help slow down glucose absorption and promote satiety.
- Eat Regular Meals: Stick to a consistent meal schedule and avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
- Limit Processed Foods: Minimize consumption of processed and packaged foods, which often contain hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and additives.
- Consult with a Registered Dietitian: Work with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan tailored to your individual needs and preferences.
- Stay Informed and Educated: Keep yourself informed about diabetes management, blood sugar monitoring, and lifestyle modifications to make informed decisions about your health.
Adopting these evidence-based strategies can help you naturally lower your blood sugar levels, promote overall health, and reduce the risk of developing complications associated with diabetes and hyperglycemia.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.