The Causes of Female Infertility
This article takes look into the causes of female infertility. Experiencing difficulties in conceiving can transform an exciting and hopeful time into one marked by stress and uncertainty. Infertility is defined by several criteria:
- If you are under the age of 35 and have been trying to get pregnant for a year without success.
- If you are over the age of 35 and have not conceived after six months of trying.
- If you have experienced two or more miscarriages.
- If you have undergone fertility treatments without achieving pregnancy.
When to Seek Help
It is advisable to seek medical assistance sooner if you have:
- Irregular menstrual cycles, which can indicate ovulatory issues.
- A history of gynecological problems such as endometriosis, pelvic surgery, ectopic (tubal) pregnancies, or pelvic infections.
Understanding the Pregnancy Process
The process of becoming pregnant involves several critical steps, and difficulties can arise at any stage, including:
- Egg Production: The ovaries must release a healthy, mature egg during ovulation.
- Fertilization: Sperm must successfully meet and fertilize the egg in the fallopian tube.
- Implantation: The fertilized egg must then travel to the uterus and attach to the uterine lining to begin development.
Issues in any of these steps can hinder the ability to conceive, and understanding where the problem lies is essential for seeking appropriate treatment and support.
YOU MAY LIKE: What do Antioxidants do?
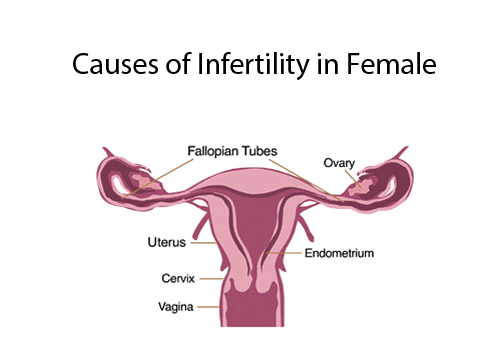
Causes of Female Infertility
Female infertility can result from a range of factors that disrupt essential biological processes. These processes include:
- Ovulation: This is the phase where a mature egg is released from the ovary. Disruptions in this process can prevent the egg from being available for fertilization.
- Fertilization: This occurs when sperm successfully meets and merges with the egg in the fallopian tube after traveling through the cervix and uterus. Any interference in this journey can hinder fertilization.
- Implantation: After fertilization, the fertilized egg must attach to the lining of the uterus to grow and develop into a baby. Any issues with the uterine lining or the fertilized egg can prevent successful implantation.
Diagnosis of Female Infertility
Diagnostic Procedures
Identifying the causes of infertility involves a series of diagnostic procedures. The complexity of the diagnosis can vary:
- Simple Cases: In some instances, a few straightforward tests can identify the cause.
- Complex Cases: Other times, determining the cause requires extensive testing and patience.
- Unexplained Infertility: Occasionally, no definitive cause can be found despite thorough evaluation.
Initial Evaluation
The diagnostic process typically starts with:
- Physical Examination: A comprehensive physical exam to assess overall health and reproductive organs.
- Health History: A detailed review of the patient’s medical, sexual, and reproductive history.
Diagnostic Methods
To further evaluate the cause of infertility, physicians may employ one or more of the following methods:
- Confirming Ovulation:
-
- Blood Test: This test checks for normal ovulation physiology. Issues with ovulation can stem from hormonal deficiencies, congenital defects, or age-related factors.
- Assessing Ovarian Reserve:
-
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Test: A blood test measures FSH levels to evaluate the quantity and quality of eggs remaining in the ovaries.
- Measuring Hormone Levels:
-
- Hormonal Analysis: Common causes like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is linked to hormonal imbalances, can prevent ovulation.
- Post-Coital Test:
-
- Cervical Mucus Analysis: After intercourse, this test analyzes cervical mucus to determine how well sperm survive in the reproductive tract.
- Endometrial Biopsy:
-
- Uterine Lining Biopsy: This test examines the endometrium to investigate potential issues with ovulation or hormone levels.
Additional Testing
Depending on the initial findings, additional detailed tests may be necessary to pinpoint the cause of infertility.
Emotional Considerations
Some Fertility Care recognizes that the diagnostic and treatment process can be emotionally challenging. They emphasize a compassionate approach, focusing on the emotional well-being of the couple throughout their journey.
Conditions Leading to Infertility
Several common conditions can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle and cause hormonal imbalances, significantly affecting female fertility. Key conditions include:
- Anovulation (Absence of Ovulation):
-
- According to studies by MSD Health, anovulation is diagnosed in 20% to 25% of female infertility cases.
- Hyperprolactinemia (Excessive Production of Prolactin):
-
- This condition reduces the activity of the hypothalamus, impacting ovulation and leading to anovulation.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
-
- In PCOS, the ovaries release very few or no eggs, resulting in insufficient levels of estrogen and the formation of small cysts on the ovaries.
SEE ALSO: Itching in Private Part
Additionally, medical conditions affecting the fallopian tubes or uterus can impair fertility:
- Obstruction of the Fallopian Tubes:
-
- Blockages prevent the egg from traveling from the ovary to the uterus.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
-
- PID, a major risk factor, increases the likelihood of ectopic pregnancies and infertility.
- Congenital Abnormalities of the Uterus and Vagina (Müllerian Abnormalities):
-
- These abnormalities reduce a woman’s ability to achieve pregnancy.
Another gynecological issue affecting fertility involves changes in cervical mucus. Reduced quality or quantity of cervical mucus hampers the sperm’s ability to reach and fertilize the egg.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Fertility
A woman’s lifestyle and habits play a crucial role in fertility. Notable factors include:
- Stress:
-
- Stress can lead to depression, immune system changes, sleep disorders, and female infertility. It reduces hormone concentrations, causes irregular ovulation, and can induce spasms in the fallopian tubes.
- Weight and Body Mass Index (BMI):
-
- Being overweight or obese can cause hormonal changes that negatively impact fertility. According to MSD Health, 12% of primary infertility cases are attributed to weight-related issues.
- Alcohol Consumption:
-
- Drinking alcohol can contribute to infertility problems.
- Pollution and Environmental Contaminants:
-
- Exposure to these factors can also negatively affect fertility.
Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions can impair the female reproductive system, leading to infertility. Some notable examples include:
- Ovulation Disorders: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hormonal imbalances can prevent regular ovulation.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): This infection can damage the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus.
- Endometriosis: This condition involves the growth of uterine tissue outside the uterus, which can cause blockages and scarring.
- Uterine Fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus can interfere with implantation or block the fallopian tubes.
- Premature Ovarian Failure: This condition causes the ovaries to stop functioning properly before the age of 40.
- Scarring from Surgery: Previous surgeries on the reproductive organs can lead to scar tissue that affects fertility.
Medications and Drugs
Certain medications and drugs can also impact female fertility, such as:
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: These cancer treatments can damage the reproductive organs.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Long-term use of high doses of NSAIDs like aspirin and ibuprofen can affect ovulation.
- Antipsychotic Medications: Some medications used to treat mental health conditions can impact hormonal balance and ovulation.
- Recreational Drugs: The use of drugs like marijuana and cocaine can impair fertility.
The Bottom Line
According to the Mayo Clinic, issues with ovulation are responsible for about one-quarter of infertility cases in couples. Indicators that a woman may not be ovulating include irregular or absent menstrual periods.
These signs suggest the need for further evaluation and potential treatment to address underlying fertility issues.
How Can I Assess My Fertility?
At Ovoclinic assisted reproduction centers, we perform comprehensive infertility evaluations to determine if a woman has fertility issues. The assessment process includes the following steps:
- Initial Consultation:
-
- An infertility specialist will conduct a thorough interview with the patient to gather detailed medical and reproductive history.
- Physical Examination and Transvaginal Ultrasound:
-
- A physical exam and transvaginal ultrasound are performed to check for any pathologies or abnormalities in the reproductive organs.
- Blood Tests:
-
- Blood tests are conducted to measure hormone levels and assess ovulation status.
- Hysterosalpingography:
-
- This procedure examines the fallopian tubes to ensure they are open and can allow the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus without blockage.
What Treatments Can Help My Fertility?
Advances in assisted reproduction have made it possible for women with fertility issues to conceive. At Ovoclinic, they offer several treatment options:
- Fertility Preservation:
-
- Egg Vitrification (Egg Freezing): This procedure involves freezing and storing eggs so that a woman can choose to become a mother at a later time. This is beneficial for those who wish to delay motherhood or face health issues that might affect their fertility in the future.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
-
- IVF Treatment: Recommended for women with various fertility problems, especially those with pathological causes. In IVF, eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a lab. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the uterus to achieve pregnancy.
These treatments provide hope and options for women experiencing fertility challenges, allowing them to pursue their dream of becoming mothers even in the face of difficulties.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.