Fatty Liver Disease Facts
Fatty liver disease is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and it’s becoming increasingly common due to our sedentary lifestyles and unhealthy diets.
The disease can cause severe liver damage if left untreated, making it essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into FLD and explore everything you need to know about this condition.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
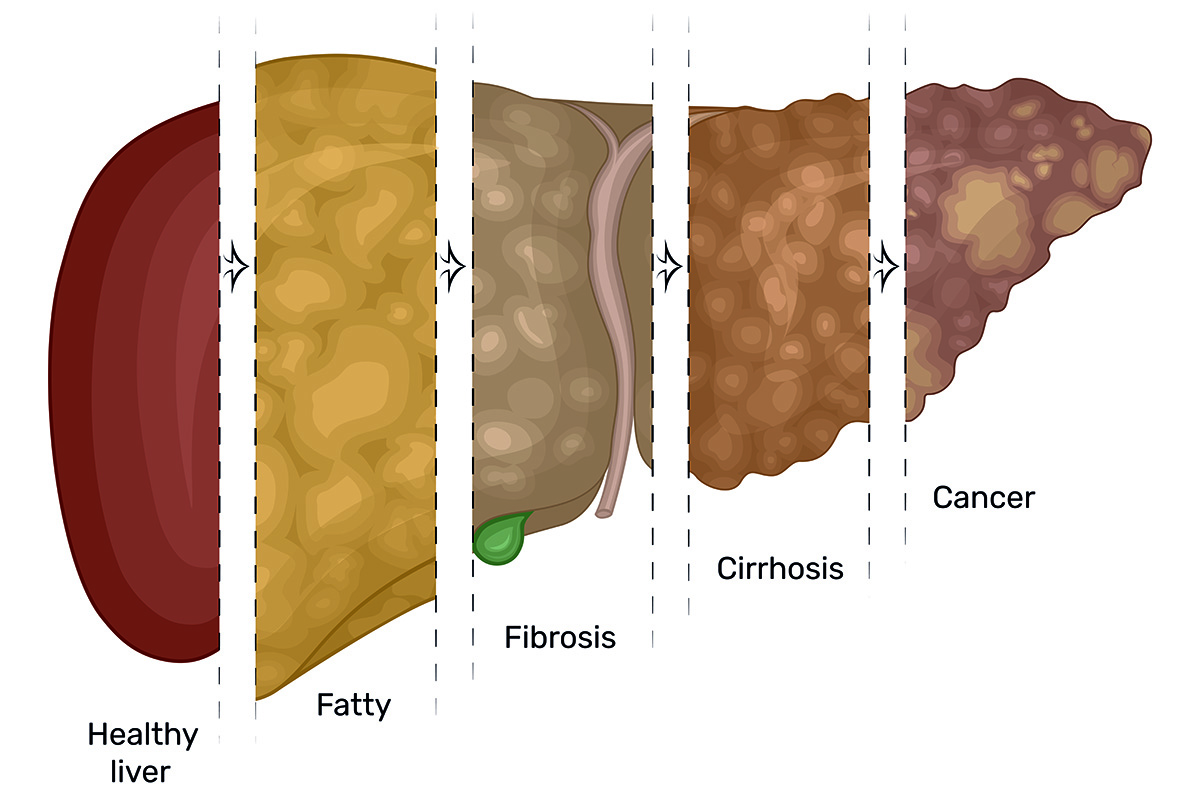
Fatty liver disease occurs when too much fat accumulates in the liver, leading to inflammation and damage to liver cells. The disease is also known as hepatic steatosis and can be categorized into two types, alcoholic fatty liver disease (ALD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
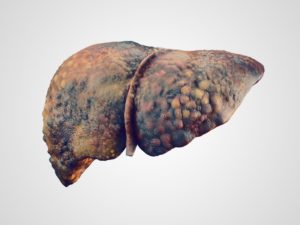
ALD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, which causes fat to accumulate in the liver.
It’s the most common form of this disease and can lead to liver cirrhosis, a severe liver disease that can be fatal.
NAFLD, on the other hand, is caused by a buildup of fat in the liver due to factors other than alcohol consumption.
These factors include obesity, insulin resistance, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome.
NAFLD is the most common liver disorder in the western world and is estimated to affect up to 25% of the global population.
Symptoms of FLD
Fatty liver disease often does not cause any noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, as the disease progresses, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Enlarged liver
- Spider-like blood vessels on the skin
It’s essential to see a doctor if you experience any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent severe liver damage.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Diagnosing this disease usually involves a combination of blood tests, imaging tests, and a liver biopsy.
Blood tests are used to check for elevated levels of liver enzymes, which can indicate liver damage. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can reveal fat accumulation in the liver.
In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small piece of liver tissue is removed and examined under a microscope.
Here are some additional insights on fatty liver disease:
Risk Factors:
Certain factors increase the risk of developing FLD. The primary risk factors include:
Obesity: People who are overweight or obese are at a higher risk of developing FLD, especially NAFLD.
Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance is a condition where the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance is a risk factor for NAFLD.
High blood pressure: High blood pressure can cause damage to the liver and increase the risk of developing fatty liver disease.
High cholesterol and triglycerides: Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can increase the risk of developing this disease.
Type 2 diabetes: People with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of developing NAFLD.
Complications
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can lead to severe liver damage, including:
Liver cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a severe liver disease that occurs when liver cells are damaged and replaced by scar tissue. Cirrhosis can lead to liver failure and can be fatal.
Liver cancer: People with fatty liver disease are at an increased risk of developing liver cancer.
Liver failure: In severe cases, this disease can cause liver failure, a life-threatening condition that requires urgent medical attention.
Cardiovascular disease: Liver disease is associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke.
Treatment of Fatty Liver Disease
The treatment of fatty liver disease depends on the underlying cause. If alcohol consumption is the cause, you will need to quit drinking alcohol immediately.
You may also need to make dietary changes, such as reducing your intake of saturated fats and increasing your intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Weight loss is also an essential aspect of treating fatty liver disease, especially in cases of NAFLD. Losing weight can reduce the amount of fat in the liver and improve liver function.
Exercise and physical activity are also crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and improving liver health.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to treat fatty liver disease. For example, insulin-sensitizing agents may be used to treat NAFLD, and medications may be prescribed to manage complications such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Prevention of Fatty Liver Disease
Preventing this disease involves making healthy lifestyle choices. Limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can all reduce your risk of developing the disease.
It’s also essential to manage any underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
Preventing fatty liver disease involves making healthy lifestyle choices. Here are some tips for preventing the disease:
Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can cause ALD, a type of fatty liver disease. Limiting alcohol consumption is an essential step in preventing ALD.
Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for developing this disease. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can reduce your risk.
Eat a balanced diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources can reduce your risk of developing fatty liver disease.
Manage underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol can increase the risk of developing fatty liver disease. Managing these conditions through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups can help prevent the disease.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce insulin resistance, and improve liver health.
Conclusion
By making healthy lifestyle choices and managing underlying medical conditions, you can reduce your risk of developing the disease and improve your overall health and well-being.
If you suspect you may have FLD, consult with your doctor for diagnosis and treatment options.
This disease is a prevalent condition that can lead to severe liver damage if left untreated. The disease is often asymptomatic in the early stages, making it essential to get regular check-ups with your doctor to detect any signs of liver damage.
Diagnosis and treatment in the early stages can prevent the progression of the disease and improve liver function.
Lifestyle changes such as reducing alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical activity can prevent the development of FLD.
It’s also essential to manage underlying medical conditions that increase your risk of developing the disease.
Summarily, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for FLD is essential for maintaining liver health.
By making healthy lifestyle choices and managing underlying medical conditions, you can reduce your risk of developing this condition and improve your overall health and well-being.
If you suspect you may have FLD, consult with your doctor for diagnosis and treatment options.
Impact of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Health Benefits of Blueberries

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.