Using Ginger for Stomach Ulcer
In this article, you’ll learn about how using ginger for stomach ulcer can be quite helpful. Ginger’s gastroprotective properties make it a potentially valuable herb for treating ulcers. Widely utilized in Asian cuisine and desserts like gingersnaps, ginger is a staple spice. It forms the foundation of popular beverages like ginger ale and ginger beer.
Ginger, the rhizomes of Zingiber officinale Roscoe (from the Zingiberaceae family), is not just a common kitchen spice but also holds numerous health benefits.
Throughout history, its rhizomes have been utilized in traditional medicine systems to address a wide array of ailments such as arthritis, rheumatism, muscular pains, sore throats, hypertension, fever, and even diabetes.
Its versatile uses extend to treating gastric issues like constipation, dyspepsia, gastritis, and nausea.
Scientific studies have validated these traditional uses, confirming ginger’s efficacy in treating gastric ulcers induced by various factors including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
Moreover, ginger has been proven effective in preventing gastric ulcers induced by NSAIDs, stress, and other factors in laboratory animals.
It also exhibits anti-emetic properties against nausea caused by different triggers, though there are conflicting reports on its effectiveness in preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and motion sickness.
Further research is needed to fully understand ginger’s mechanisms of action and its potential as a gastroprotective agent in humans.
Studies have shown ginger to possess antioxidant properties, which may contribute to its gastroprotective effects by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting lipid peroxidation.
This review outlines the various gastroprotective effects of ginger and underscores the need for future research to establish its effectiveness and utility in human health.
Nutritional Value of Ginger
Ginger is not only a flavorful addition to various dishes but also packs a punch in terms of nutrition. According to the USDA, a ¼ cup of 1-inch ginger slices contains:
- 19 calories
- ½ gram of protein
- 0 grams of fat
- 4 grams of carbohydrates
- ½ gram of fiber
- Less than half a gram of sugar
- 4 milligrams of calcium
- 10 milligrams of magnesium
- 8 milligrams of phosphorus
- 100 milligrams of potassium
- 3 milligrams of sodium
- 1.2 milligrams of vitamin C
If you’re not keen on the taste of plain water, you can infuse it with ginger for a refreshing twist. Ground ginger is also readily available in the spice section of most grocery stores, and pickled ginger can be found in the international foods section.
For those who prefer convenience, ginger capsules are sold in many health food stores. However, it’s crucial to read the label carefully, as these are dietary supplements and not regulated by the FDA. The appropriate dosage varies depending on the health condition you’re addressing.
In addition to aiding with ulcers, ginger has been noted for its anti-inflammatory properties and potential benefits for heart health and cancer prevention, as highlighted in an October 2014 review published in the Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Services.
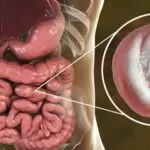
Peptic ulcers, defined by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), are sores that form in the lining of the stomach or duodenum.
They are often caused by prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin, or by an infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
A June 2013 review published in the Journal of Functional Foods highlighted the gastroprotective effects of ginger. It emphasized ginger’s significant role in treating various gastric issues, including nausea, vomiting, indigestion, gastritis, and bloating.
The review also indicated that ginger is effective in preventing gastric ulcers induced by NSAIDs and H. pylori infection. However, it’s important to note that these studies were conducted on laboratory animals, and further research is needed to confirm these effects in humans.
The underlying principle is that using ginger may offer anti-inflammatory effects similar to NSAIDs, thereby reducing the need for NSAIDs and lowering the risk of developing ulcers. While ginger may not provide immediate relief from ulcer pain, it could aid in preventing recurrent ulcers.
Ginger, a common kitchen spice, possesses notable healing properties attributed to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory qualities.
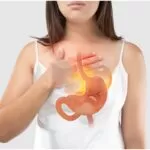
When it comes to stomach ulcers, incorporating ginger into your routine can help prevent oxidative reactions, thus alleviating uncomfortable symptoms like burning pain in the epigastrium.
Here are two simple recipes utilizing ginger for stomach ulcer relief
Recipe 1: Fresh Ginger Tea
- Add a few slices of fresh ginger to a cup of hot tea.
- Drink this concoction both in the morning and evening.
- Ginger and tea together work to reduce inflammation, curb oxidative reactions, and improve ulcer symptoms.
- Consistent and regular consumption is key to experiencing the desired effects.
Recipe 2: Ginger Juice
- Peel and crush fresh ginger to extract its juice.
- Mix the ginger juice with a cup of warm water.
- Optionally, add a few tablespoons of honey and a squeeze of lemon to enhance the flavor.
- Consume this ginger juice concoction in the morning on an empty stomach for best results.
Incorporating these ginger-based recipes into your daily routine can provide effective relief from stomach ulcer symptoms.
Insights on Ginger for Stomach Ulcer
Ginger shows promise as a natural remedy for stomach ulcers due to its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Here are some insights and useful points regarding the use of ginger for stomach ulcers:
- Healing Properties: Ginger possesses antibacterial and anti-inflammatory qualities, making it effective in preventing oxidative reactions and reducing symptoms associated with stomach ulcers.
- Simple Recipes: Ginger can be easily incorporated into one’s diet through simple recipes such as ginger tea or ginger juice. These recipes involve adding fresh ginger to hot tea or warm water, respectively, and can be consumed regularly for relief.
- Reducing Inflammation: Both ginger and tea have demonstrated the ability to reduce inflammation, which can alleviate discomfort caused by stomach ulcers.
- Regular Consumption: Consistent and regular consumption of ginger-based remedies is key to experiencing the desired effects. Patients should aim to incorporate ginger into their daily routine to effectively manage ulcer symptoms.
- Precautions: While ginger is generally safe for consumption, individuals should consult with a healthcare professional before using ginger as a remedy for stomach ulcers, especially if they have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
- Additional Enhancements: Adding honey and lemon to ginger-based concoctions not only enhances the flavor but also provides additional health benefits. Honey has antibacterial properties, while lemon is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants.
- Morning Consumption: Consuming ginger-based remedies in the morning, preferably on an empty stomach, may enhance their effectiveness in providing relief from stomach ulcer symptoms.
Ginger offers a natural and effective approach to managing stomach ulcers. By incorporating ginger into one’s diet through simple recipes and regular consumption, individuals can potentially alleviate discomfort and improve their overall gastrointestinal health.
However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using ginger as a remedy for stomach ulcers to ensure safety and efficacy.
Ulcers can cause significant discomfort, prompting many to seek quick relief. Over-the-counter medications like ranitidine (Zantac) or famotidine (Pepcid) can help by reducing stomach acid. Acid-neutralizing medications such as Rolaids or Tums offer temporary relief, but the pain may return as the stomach produces more acid, typically within an hour or two.
It’s essential to avoid antacids containing aspirin, as they pose a risk of serious bleeding, as cautioned by the FDA. Thus, products like Alka-Seltzer should be avoided for ulcer pain relief.
If home remedies and over-the-counter options fail to alleviate your ulcer pain, it’s advisable to consult your doctor for further evaluation and management.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.