Impact of Nutrition on Brain Health
The intricate relationship between nutrition and brain health has become increasingly evident in recent years. What we consume profoundly influences cognitive function, mood, and overall brain well-being.
This article delves into the science behind this connection, exploring how different nutrients impact the brain, offering practical dietary recommendations to optimize brain health.
The Brain: A Nutrient-Hungry Organ
The brain, despite constituting only 2% of the body’s weight, consumes a disproportionate amount of energy. It relies heavily on a steady supply of glucose for fuel, but it also requires a diverse array of micronutrients to function optimally.
These nutrients play crucial roles in neurotransmitter synthesis, brain cell repair, and protection against oxidative stress.
SEE ALSO: Lack of Appetite Causes
Key Nutrients for Brain Health
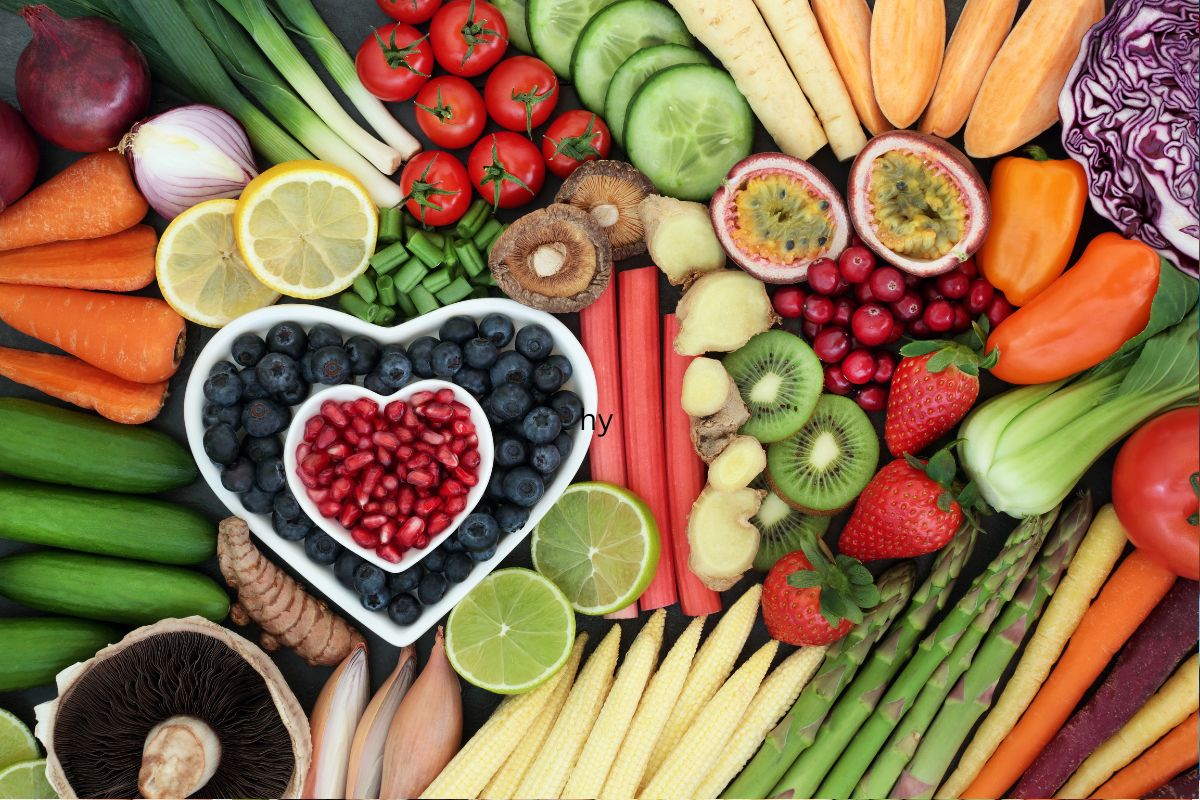
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Essential for brain structure and function, omega-3s are found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in plant-based sources such as flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts. These fats help build brain cells, improve communication between neurons, and reduce inflammation.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, found in abundance in fruits, vegetables, and nuts, protect brain cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can contribute to aging and disease.
- B vitamins: Crucial for energy production and neurotransmitter synthesis, B vitamins (B1, B2, B6, B12, and folate) are found in whole grains, legumes, leafy green vegetables, and poultry. Deficiencies in these vitamins can lead to cognitive impairment and mood disorders.
- Vitamin D: Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and bone health, but it also plays a role in brain function. It is found in fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products, and the body can produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
- Magnesium: Involved in numerous brain functions, including learning, memory, and mood regulation, magnesium is found in whole grains, nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables.
The Impact of Diet on Brain Health
A diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins provides the necessary nutrients to support optimal brain function. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars can negatively impact brain health.
- Mediterranean diet: Emphasizing whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, olive oil, and fish, the Mediterranean diet has been consistently linked to a reduced risk of cognitive decline, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
- DASH diet: Originally designed to lower blood pressure, the DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is also beneficial for brain health due to its emphasis on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, and lean protein.
- Mind diet: A combination of the Mediterranean and DASH diets, the Mind diet focuses on brain-healthy foods and lifestyle factors. It emphasizes whole grains, leafy green vegetables, berries, nuts, beans, fish, poultry, olive oil, and wine in moderation.
Nutrition and Cognitive Decline
As we age, our brains undergo changes that can affect cognitive function. A nutrient-rich diet can help mitigate these changes and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
- Alzheimer’s disease: While the exact causes of Alzheimer’s disease are complex, research suggests that diet plays a role. A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and B vitamins may help reduce the risk or slow the progression of the disease.
- Dementia: Similar to Alzheimer’s disease, dementia is linked to various factors, including diet. A healthy diet can support cognitive function and potentially delay the onset of dementia symptoms.
The Role of Nutrition in Alzheimer’s Care Services
For individuals with Alzheimer’s disease or dementia, nutrition is a critical component of care. Alzheimer’s care services often incorporate dietary guidelines to support patients’ overall well-being. Specialized diets, meal planning, and assistance with eating may be necessary to ensure adequate nutrition and hydration.
Alzheimer’s care services play a crucial role in managing the nutritional needs of individuals with dementia. These services offer tailored meal plans, dietary modifications, and support for caregivers to ensure patients receive the appropriate nutrients.
Practical Dietary Recommendations
To optimize brain health, consider the following dietary recommendations:
- Prioritize whole foods: Focus on consuming whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Limit processed foods: Reduce your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of saturated and unhealthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can impair cognitive function, so drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consider supplements: While a balanced diet should provide most essential nutrients, some individuals may benefit from supplements. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
- Regular meals: Maintain consistent blood sugar levels by eating regular meals and snacks.
The Gut-Brain Connection
Emerging research has highlighted the significant impact of gut health on brain function. The gut-brain axis refers to the communication between the digestive system and the central nervous system. A healthy gut microbiome, populated with beneficial bacteria, is associated with improved mood, cognitive function, and reduced inflammation.
- Probiotics: Found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods, probiotics support gut health and may positively impact brain function.
- Prebiotics: These indigestible fibers act as food for beneficial gut bacteria. They are found in whole grains, bananas, garlic, and onions.
Nutrition and Mental Health
Beyond cognitive function, nutrition plays a vital role in mental health. Certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and B vitamins, have been linked to reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety. A balanced diet can help regulate mood and promote emotional well-being.
The connection between nutrition and brain health is undeniable. By making conscious dietary choices and prioritizing brain-healthy foods, individuals can significantly enhance cognitive function, reduce the risk of cognitive decline, and improve overall well-being.
It’s important to remember that while diet plays a crucial role, other lifestyle factors such as physical activity, sleep, and mental stimulation also contribute to brain health.
Benefits of Cloves to The Vagina

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.