Here are the Reasons for Heart Palpitation
Before delving into what brought about or reasons for heart palpitation, understand that heart palpitations, pronounced as “pal-pih-TAY-shuns,” refer to the sensations of having a heart that is beating rapidly, fluttering, or pounding.
These episodes can be brought on by various factors including stress, physical exercise, certain medications, or, in rare cases, an underlying medical condition.
While experiencing heart palpitations can be concerning, they are typically harmless and do not indicate a serious health issue. However, in rare instances, heart palpitations can signal a more severe heart condition, such as an irregular heartbeat known as arrhythmia, which may necessitate medical intervention.
Symptoms Explained
Heart palpitations can present in several distinct ways, each describing a different sensation:
- Beating too fast: This refers to the feeling that your heart is racing, often significantly faster than usual, which can be alarming.
- Flip-flopping: This sensation is akin to the heart turning over or performing a somersault, creating an unusual and often uncomfortable feeling.
- Fluttering rapidly: This feels like the heart is fluttering quickly, similar to the rapid flapping of a bird’s wings, and can sometimes be felt as a series of rapid, light taps.
- Pounding: This is when the heartbeats are so forceful that they can be felt distinctly and strongly in the chest, and sometimes even in the neck or throat.
- Skipping beats: This occurs when it feels like the heart has missed a beat or paused momentarily, which can be followed by a stronger-than-usual beat.
These sensations might not be restricted to the chest area alone. Heart palpitations can also be felt in the throat or neck, adding to the discomfort and concern they may cause. Additionally, these palpitations can happen at any time—whether you are engaged in physical activity or simply at rest.
Causes
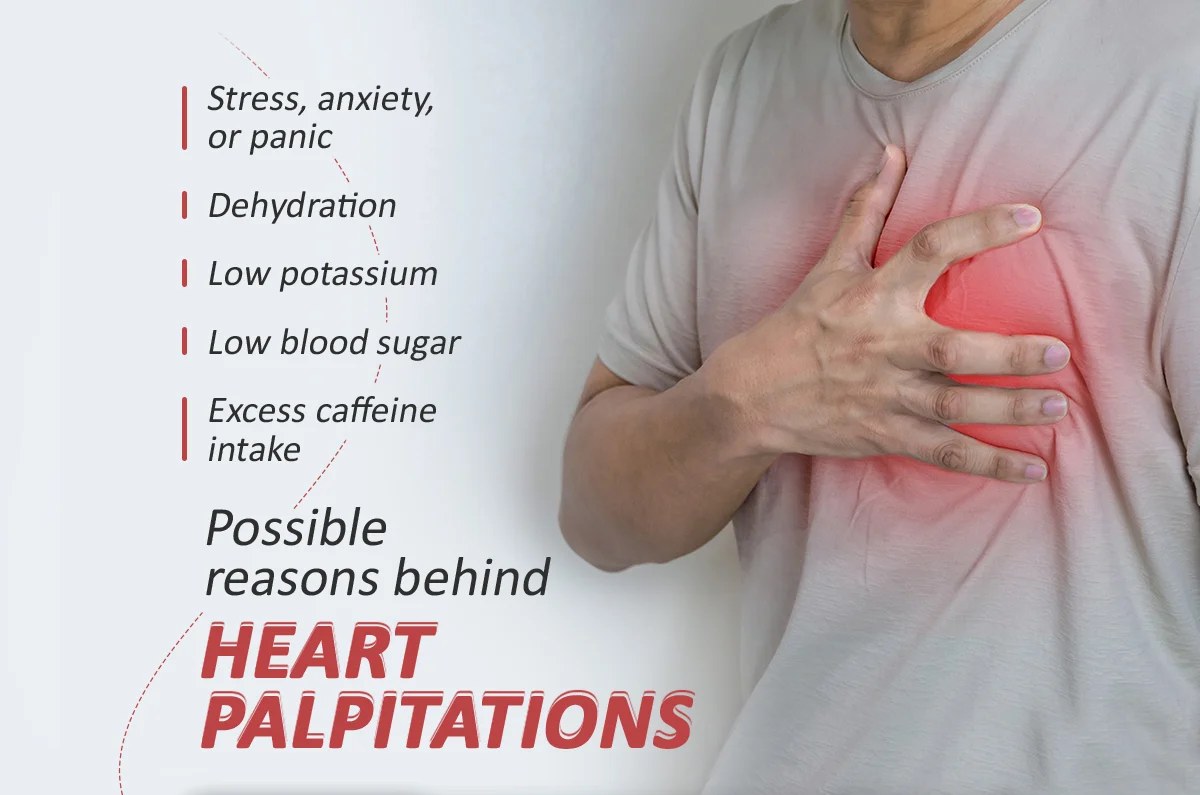
Often, the exact cause of heart palpitations cannot be determined. However, there are several common factors that can trigger them:
- Strong emotional responses: Experiencing intense emotions such as stress, anxiety, or panic attacks can lead to palpitations.
- Depression: Emotional health conditions like depression can also contribute to the occurrence of palpitations.
- Strenuous exercise: Engaging in vigorous physical activity can cause the heart to palpitate.
- Stimulants: Consuming substances such as caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, amphetamines, and certain cold and cough medications containing pseudoephedrine can trigger palpitations.
- Fever: Having a high body temperature can sometimes cause the heart to palpitate.
- Hormone changes: Hormonal fluctuations related to menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can lead to palpitations.
- Thyroid issues: Both hyperthyroidism (too much thyroid hormone) and hypothyroidism (too little thyroid hormone) can result in palpitations.
In some cases, heart palpitations can be indicative of a more serious issue, such as an irregular heart rhythm, known as arrhythmia. Arrhythmias can manifest in various forms:
- Tachycardia: An unusually fast heartbeat.
- Bradycardia: An unusually slow heartbeat.
- Irregular rhythm: A heartbeat that deviates from the typical rhythm.
- Combination: A mixture of these variations, potentially involving both fast and slow heartbeats or an irregular pattern.
When to See a Doctor
Occasional heart palpitations that last only a few seconds and occur infrequently typically do not require medical evaluation.
However, if you have a history of heart disease and experience frequent or worsening palpitations, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider.
In such cases, heart-monitoring tests may be necessary to determine if the palpitations are indicative of a more serious underlying heart condition.

It is crucial to seek emergency medical attention if heart palpitations are accompanied by any of the following symptoms:
- Chest discomfort or pain: This can be a sign of a serious heart condition, such as a heart attack.
- Fainting: Losing consciousness can indicate a significant issue with heart function or blood flow.
- Severe shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially if sudden and intense, can be a symptom of a critical heart or lung issue.
- Severe dizziness: Feeling extremely lightheaded or dizzy may suggest an urgent cardiovascular problem that needs immediate medical intervention.
SEE ALSO: Turmeric Milk Benefits
Reasons for Heart Palpitation (Risk Factors)
Several factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing heart palpitations. These risk factors include:
- Stress: High levels of stress can contribute to the occurrence of palpitations.
- Anxiety disorder or panic attacks: Individuals with anxiety disorders or those prone to panic attacks are more susceptible to palpitations.
- Pregnancy: The hormonal changes and increased blood volume during pregnancy can lead to palpitations in some women.
- Certain medications: Some medications, particularly those containing stimulants like certain cold or asthma medications, can trigger palpitations.
- Overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism): An overactive thyroid can disrupt normal heart function, leading to palpitations.
- Other heart conditions: Individuals with pre-existing heart problems, such as irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), structural heart changes, a history of heart attack, or previous heart surgery, are at higher risk of experiencing palpitations.
Identifying these risk factors can help individuals take proactive measures to manage and potentially reduce their likelihood of experiencing heart palpitations.
Complications Regarding the Reasons for Heart Palpitation
When heart palpitations are caused by an underlying heart condition, several potential complications may arise:
- Fainting: Rapid heartbeats can lead to a drop in blood pressure, causing syncope (fainting). This risk is heightened in individuals with existing heart issues, such as congenital heart disease or specific valve problems.
- Cardiac arrest: Although rare, palpitations stemming from life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances can result in the heart ceasing to beat effectively, leading to cardiac arrest.
- Stroke: Palpitations associated with conditions like atrial fibrillation, where the upper chambers of the heart quiver instead of beating properly, can lead to the formation of blood clots. These clots may then travel to the brain arteries, causing a stroke.
- Heart failure: Certain arrhythmias can impair the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. In some cases, managing the rate of an arrhythmia contributing to heart failure can help improve the heart’s function.
Understanding these potential complications underscores the importance of promptly addressing heart palpitations, especially if they are recurrent or accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Seeking medical attention and appropriate management can mitigate these risks and safeguard heart health.
Recommended Treatments
The treatment for heart palpitations depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common approaches:
- Lifestyle modifications: Making lifestyle changes can often help reduce or eliminate palpitations. This may include reducing stress through relaxation techniques, avoiding triggers such as caffeine or nicotine, getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and ensuring adequate hydration.
- Medications: In cases where palpitations are caused by an underlying heart condition such as arrhythmia, medications may be prescribed to regulate the heart rate or rhythm. These may include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, anti-arrhythmic drugs, or other medications to address specific issues.
- Treatment of underlying conditions: If palpitations are a symptom of an underlying medical condition such as hyperthyroidism or anxiety disorder, treating the underlying condition may alleviate the palpitations.
- Cardioversion: In certain cases of severe or persistent arrhythmias, cardioversion may be recommended. This procedure involves restoring the heart’s normal rhythm using electrical shocks or medications.
- Catheter ablation: For certain types of arrhythmias that do not respond well to medication, catheter ablation may be considered. This procedure involves using radiofrequency energy or cold therapy to destroy small areas of heart tissue that are causing the abnormal electrical signals responsible for the arrhythmia.
- Implantable devices: In some cases, implantable devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be recommended to regulate the heart’s rhythm and prevent dangerous arrhythmias.
- Lifestyle counseling: Counseling or therapy may be beneficial for individuals whose palpitations are triggered or exacerbated by stress, anxiety, or other emotional factors.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances and the underlying cause of the palpitations. Treatment may involve a combination of approaches tailored to address specific symptoms and risk factors.
More Insights
Here are some additional insights and a concluding note on heart palpitations:
Insights
- Holistic Approach: Addressing heart palpitations often requires a comprehensive, holistic approach that considers both physical and emotional factors. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or yoga, can complement medical treatments by helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
- Regular Monitoring: Individuals experiencing palpitations should maintain regular communication with their healthcare provider to monitor symptoms and adjust treatment as needed. Keeping a symptom journal can be helpful in tracking the frequency, duration, and triggers of palpitations.
- Awareness of Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers can play a significant role in managing palpitations. Common triggers include caffeine, alcohol, certain medications, intense physical exertion, and emotional stress. By minimizing exposure to these triggers, individuals may experience fewer episodes of palpitations.
- Education and Support: Education about heart health and palpitations can empower individuals to take an active role in managing their condition. Support groups or online forums can provide valuable peer support and a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies.
Conclusion on The Reasons for Heart Palpitation
Heart palpitations can be alarming, but in many cases, they are harmless and can be managed effectively with lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medical interventions.
However, it’s essential not to ignore palpitations, especially if they are accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as chest pain, fainting, or shortness of breath.
Seeking prompt medical attention and working closely with a healthcare provider are crucial steps in diagnosing and treating palpitations.
By taking proactive measures to address underlying causes and minimize risk factors, individuals can often reduce the frequency and severity of palpitations, leading to improved overall heart health and quality of life.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.