A Guide on Symptoms and Signs of Prostate Cancer
This article explores the symptoms and signs of prostate cancer, empowering you to recognize potential risks and seek medical attention promptly. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer diagnosed in men after skin cancer [American Cancer Society].
Prostate cancer is a common type of cancer that affects men. The prostate is a small gland located just below the bladder. It produces a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. Prostate cancer develops when cells in the prostate gland grow abnormally and spread.
Early detection of prostate cancer is crucial because it is often highly treatable in its early stages.
It’s a condition where cells in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped gland below the bladder, multiply abnormally and have the potential to spread.
The good news? Prostate cancer, especially when detected early, often responds well to treatment. The key lies in recognizing the warning signs your body might be sending. This article empowers you with knowledge about prostate cancer symptoms and signs, risk factors, and the importance of early detection.
Prostate and Its Role in Men’s Health
Before diving into symptoms and signs of prostate cancer, let’s understand the prostate’s function. The prostate gland is a vital part of the male reproductive system. It produces seminal fluid, a milky white fluid that nourishes and transports sperm during ejaculation.
This fluid also contains substances that help sperm remain motile (able to swim) and survive in the woman’s reproductive tract.
Prostate Cancer: A Silent Threat in the Early Stages
Prostate cancer is often a silent disease in its early stages, meaning there might not be any noticeable symptoms. This is why regular checkups with your doctor are crucial for early detection.
Symptoms and Signs of Prostate Cancer
As prostate cancer progresses, some men may experience a range of symptoms. It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so a proper diagnosis from your doctor is essential.
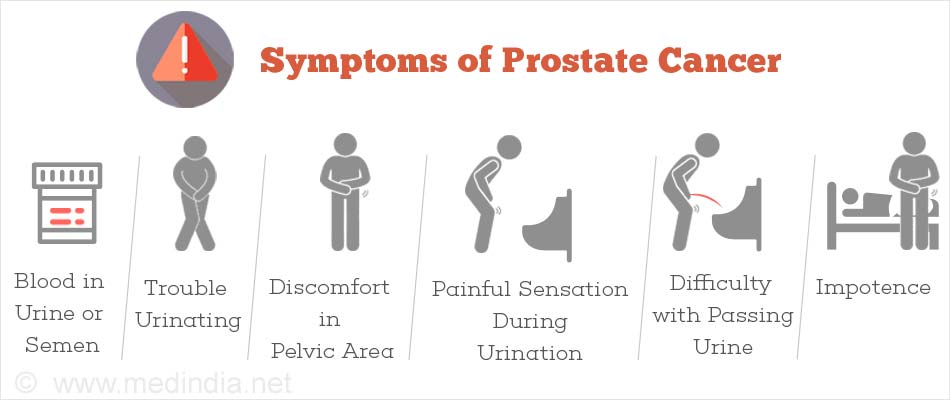
Here’s a breakdown of some common symptoms and signs of prostate cancer:
- Urinary Issues:
- Difficulty starting urination (hesitancy)
- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Weak urine stream or dribbling
- Feeling like your bladder isn’t emptying completely (urinary retention)
- Pain or burning sensation during urination (dysuria)
- Blood in Urine or Semen (Less Common): While less frequent, the presence of blood in either urine (hematuria) or semen (hematospermia) can be a sign of prostate cancer and warrants immediate medical attention.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Erectile dysfunction (difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection) can be a symptom of prostate cancer, especially in advanced stages.
- Pain: You might experience pain in the lower back, pelvis, upper thighs, or even testicles. This pain can be constant or occur intermittently.
Don’t Ignore Subtle Changes: Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is paramount in prostate cancer because treatment options are most successful when the cancer is confined to the prostate. Here’s why early detection matters:
- Improved Treatment Outcomes: Early detection allows for a wider range of treatment options with higher success rates and better preservation of quality of life.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Early-stage prostate cancer might be treated with minimally invasive procedures like surgery or radiation therapy with fewer side effects.
- Reduced Risk of Spread: Early detection helps prevent the cancer from spreading to other parts of the body, where treatment becomes more complex.
Who Should Get Screened for Prostate Cancer?
The decision to get screened for prostate cancer involves a conversation with your doctor, considering your age, family history, and overall health. Here are some factors that might influence your doctor’s recommendation for screening:
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer significantly increases with age. Most cases are diagnosed in men over 50. Men with a high risk, like those with a family history, might be advised to start screening earlier.
- Family History: Having a father, brother, or son diagnosed with prostate cancer increases your risk.
- African American Ethnicity: African American men are at a higher risk of developing and dying from prostate cancer compared to other races.
- Overall Health: Your doctor will consider your overall health and life expectancy when recommending screening.
Understanding Prostate Cancer’s Progression and Potential Side Effects
While prostate cancer itself can be a concern, it’s also important to understand how the cancer might progress and the potential side effects associated with treatment. Here’s a breakdown of some key points:
- The Risk of Spread (Metastasis): Prostate cancer can spread beyond the prostate gland to nearby organs like the bladder. In some cases, it can travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to reach bones or even other organs. Spreading to the bones is a particular concern, as it can cause significant pain and increase the risk of fractures. While treatment options exist for advanced prostate cancer, the chance of a complete cure becomes less likely.
- Urinary Incontinence: Both prostate cancer itself and its treatment can lead to urinary incontinence, the inability to fully control your bladder. The type and severity of incontinence will influence the treatment approach. There are various options available, including medications, catheters, and surgery, to help manage this issue.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Erectile dysfunction, the difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, can be a consequence of prostate cancer or its treatment. This could be due to surgery, radiation therapy, or hormone therapy. Fortunately, there are treatment options available for erectile dysfunction, including medications, vacuum devices, and even surgery.
By understanding these potential consequences, men facing a prostate cancer diagnosis can make more informed decisions about their treatment plan and be prepared for potential side effects.
Screening Options for Prostate Cancer
Two main screening options are available for prostate cancer:
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): During a DRE, your doctor inserts a gloved finger into your rectum to feel the prostate gland for any lumps or abnormalities.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate. Elevated PSA levels can indicate prostate cancer, but other factors can also cause a rise in PSA.
It’s important to discuss the pros and cons of both screening options with your doctor to determine if they are right for you. While screening can detect cancer early, it’s not foolproof. Sometimes, a high PSA level might not indicate cancer, and a low level doesn’t guarantee absence of cancer.
It’s important to discuss the pros and cons of both screening options with your doctor to determine if they are right for you. While screening can detect cancer early, it’s not foolproof. Here’s a closer look:
- Advantages of Screening:
- Early detection allows for a wider range of treatment options with higher success rates and better preservation of quality of life.
- The ability to monitor slow-growing cancers through active surveillance if detected early.
- Potential for peace of mind knowing your cancer status.
- Disadvantages of Screening:
- False-positive results: An elevated PSA level or abnormality on a DRE might not always indicate cancer, leading to unnecessary anxiety and potentially invasive biopsies.
- Overdiagnosis: Screening can sometimes detect slow-growing cancers that might not have caused any problems during a man’s lifetime, leading to unnecessary treatment and its side effects.
- Psychological impact: The process of screening and waiting for results can cause stress and anxiety.
Weighing the Options:
The decision to undergo prostate cancer screening is a personal one. There’s no single right answer, and it depends on various factors like your age, overall health, family history, and risk tolerance. By openly discussing the pros and cons with your doctor, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your individual needs and preferences.
Remember: Even if you choose not to undergo regular screening, maintaining open communication with your doctor and being aware of potential symptoms is crucial for early detection.
Prostate Cancer: Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Living Well
Diagnosis: Taking the Next Step
If you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your risk factors, your doctor will likely recommend further evaluation. Here’s what to expect:
- Detailed Medical History: Your doctor will discuss your symptoms, family history, and overall health.
- Physical Exam: This may include a DRE to assess the prostate for abnormalities.
- PSA Test: A blood test to measure PSA levels.
- Biopsy: If a DRE or PSA test raises suspicion, a biopsy might be necessary. This involves taking a small tissue sample from the prostate for examination under a microscope to confirm the presence or absence of cancer cells.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
The course of treatment for prostate cancer depends on various factors, including the stage and grade of the cancer, your overall health, and your preferences. Here’s an overview of some common treatment options:
- Active Surveillance: In some early-stage, slow-growing cancers, your doctor might recommend active surveillance. This involves monitoring the cancer through regular PSA tests, biopsies, and physical exams to intervene only if the cancer shows signs of progression.
- Surgery: Radical prostatectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the entire prostate gland. This is an option for some men with early-stage prostate cancer. Robotic-assisted surgery is a minimally invasive variation of this procedure.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It can be delivered externally, through a machine, or internally, through radioactive implants placed near the prostate.
- Hormone Therapy: This therapy aims to lower testosterone levels, which can fuel the growth of some prostate cancers. Hormone therapy can be used in conjunction with other treatments or alone in advanced stages.
- Cryotherapy: This procedure freezes and destroys prostate tissue using extreme cold. It’s a minimally invasive option for some men with early-stage prostate cancer.
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU): HIFU uses focused ultrasound waves to heat and destroy prostate tissue. It’s a relatively new treatment option with ongoing research.
Living Well After Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but remember, you’re not alone. Many men successfully navigate treatment and live fulfilling lives. Here are some tips for living well after a prostate cancer diagnosis:
- Maintain Open Communication with Your Doctor: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor your health and manage any side effects from treatment.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with other men who have been through similar experiences can provide emotional support and valuable information.
- Focus on a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep can all contribute to your overall well-being.
- Manage Stress: Stress can take a toll on your physical and emotional health. Explore relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to manage stress effectively.
- Maintain a Healthy Sex Life: Talk to your doctor about potential sexual side effects of treatment and explore options for maintaining a healthy sex life.
The Future of Prostate Cancer Treatment
Research on prostate cancer is constantly evolving, leading to the development of new and more targeted treatment options. Here are some promising areas of research:
- Precision Medicine: Tailoring treatment based on the specific genetic makeup of the cancer cells for a more personalized approach.
- Immunotherapy: Harnessing the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Developing even less invasive surgical and radiation therapy procedures with fewer side effects.
A Look at Prostate Cancer Prevention Strategies
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk. Here’s a detailed exploration of some key strategies:
Dietary Choices for a Reduced Risk:
- Embrace a Rainbow on Your Plate: Fill your diet with a vibrant array of fruits and vegetables. These are powerhouses of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall health and potentially offer some protection against prostate cancer.
- Whole Grains for a Balanced Approach: Incorporate whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread into your meals. These complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and dietary fiber, which can help with weight management, a crucial factor in prostate health.
- Focus on Food, Not Supplements: While research on the direct link between dietary supplements and prostate cancer prevention is ongoing, the current evidence suggests prioritizing whole foods over supplements. By consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, you naturally obtain a spectrum of essential nutrients for optimal health.
Exercise: A Powerful Ally for Men’s Health:
- Move Your Body Most Days: Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle and offers numerous benefits for prostate health. Aim for most days of the week to engage in some form of exercise, even if it’s just brisk walking. If you’re new to exercise, start gradually and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts as your fitness improves.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese is a known risk factor for prostate cancer. Exercise, combined with a healthy diet, can help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Consult your doctor for personalized guidance on creating a safe and effective weight management plan.
Open Communication with Your Doctor:
- Understanding Your Risk Profile: If you have a family history of prostate cancer or other factors that elevate your risk, discussing this with your doctor is crucial. Early detection and potentially even preventative measures might be recommended based on your individual risk assessment.
- Exploring Potential Medications: Studies suggest that 5-alpha reductase inhibitors like finasteride and dutasteride, used for treating enlarged prostate and hair loss, might also offer some reduction in the overall risk of developing prostate cancer. However, there’s also some evidence indicating a possible increased risk of a more aggressive form of prostate cancer with these medications. Discussing the pros and cons of these medications with your doctor is vital to make informed decisions for your specific situation.
Remember, a healthy lifestyle is an investment in your overall well-being. By incorporating these strategies, you can take charge of your prostate health and empower yourself to reduce your risk.
Taking Charge of Your Health
Prostate cancer is a serious condition, but with early detection and proper treatment, the outlook is often positive. By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and screening options, you can take an active role in your health. Schedule regular checkups with your doctor, discuss your concerns openly, and make informed decisions about your healthcare journey.
Remember, knowledge is power. With the right information and proactive approach, you can manage your risk and live a long, healthy life.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Sources:
- American Cancer Society: https://www.cancer.org/
- National Cancer Institute: https://www.cancer.gov/
- Prostate Cancer Foundation: https://www.pcf.org/

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.