STD Prevention and Treatment
Regarding STD prevention and treatment, understand that sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) represent a significant public health challenge caused by the transmission of bacteria, viruses, and other parasites through sexual contact.
While some STDs are treatable with antibiotics, others, like HIV, are incurable and can be fatal. Therefore, prevention plays a crucial role in managing the spread of these infections.
Prevention of STDs
Preventing the spread of STDs involves various strategies influenced by sociocultural factors such as culture, age, employment, education, religion, and gender. These factors shape sexual behavior and consequently affect the transmission rates of STDs. Key prevention methods include:
1. Abstinence
Abstinence, or refraining from sexual contact, is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of STDs. By avoiding sexual activity, individuals can completely eliminate the risk of contracting or spreading infections.
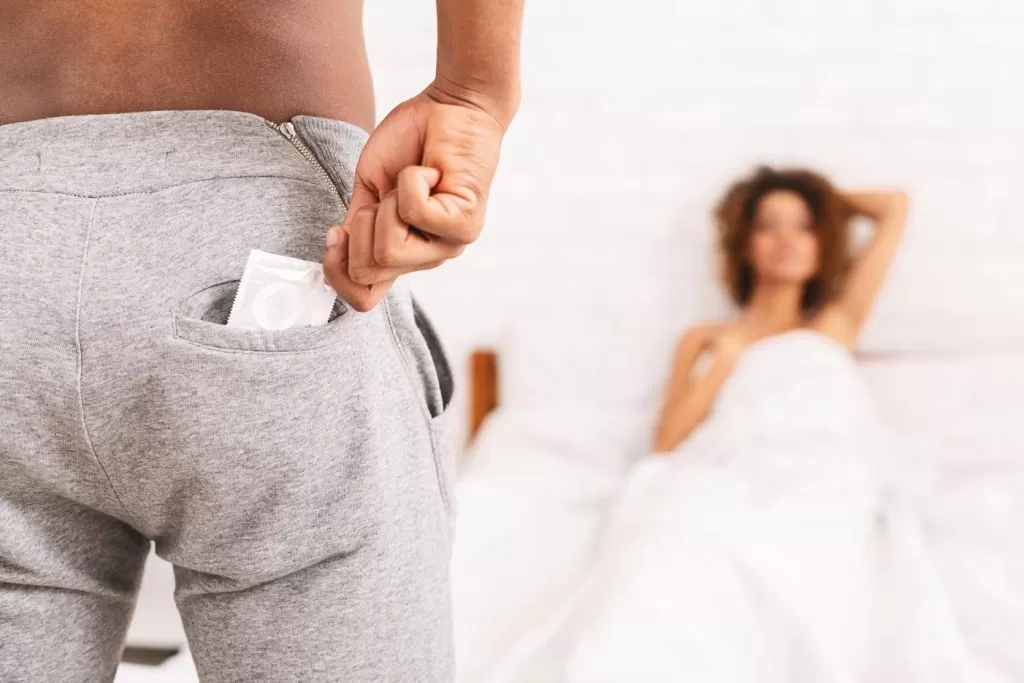
2. Barrier Contraceptives
Barrier contraceptives, such as condoms, offer a physical barrier that helps prevent the transmission of STDs from one individual to another.
For condoms to be effective, they must be used correctly and consistently. Proper use involves ensuring that the condom covers the penis completely during intercourse and is disposed of appropriately after use to prevent any potential spread of infection.
3. Sexual Health Checks
Regular sexual health screenings are vital for preventing the spread of STDs. Attending a sexual health clinic for screening before engaging in sexual activity with a new partner can help detect and treat any existing infections, thereby reducing the risk of transmission.
Additionally, screenings are recommended before resuming sexual relations if a partner has had sexual contact with someone else.
However, it’s important to note that some infections may not be detectable during certain stages, so regular check-ups and honest communication between partners are essential.
Expanding Prevention Efforts
In addition to the primary prevention strategies, there are several other approaches to reduce the spread of STDs:
1. Education and Awareness
Educational programs that provide information about STDs, their transmission, and prevention methods are crucial. These programs should target various populations, including adolescents, adults, and high-risk groups, to ensure widespread awareness and understanding.
2. Access to Healthcare Services
Improving access to healthcare services, including sexual health clinics and testing facilities, is essential. Ensuring that individuals can easily obtain screenings, treatments, and preventive measures like condoms can significantly reduce the spread of STDs.
3. Vaccination
Vaccines are available for some STDs, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B. Promoting vaccination programs, especially among young people, can help prevent these infections and reduce their prevalence.
4. Reducing Stigma
Addressing the stigma associated with STDs is important for encouraging individuals to seek testing and treatment. Creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment can help individuals feel more comfortable discussing their sexual health and taking necessary precautions.
STDs pose a major public health issue due to their potential to cause serious health problems, including incurable and fatal conditions like HIV.
Preventing the transmission of STDs involves a multifaceted approach that includes abstinence, the use of barrier contraceptives, regular sexual health checks, education, improved healthcare access, vaccination, and reducing stigma.
By implementing these strategies, individuals and communities can effectively manage and reduce the spread of STDs.
SEE ALSO:Worst Foods for Erectile Dysfunction
Vaccination and Nonoxynol-9 in STD Prevention
Vaccination Against STDs
Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Key vaccines currently available include those targeting hepatitis B and certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
These vaccines are highly effective in providing immunity against these infections, reducing the risk of transmission and associated health complications.
- Hepatitis B Vaccine: Protects against hepatitis B virus, which can cause liver damage and long-term health issues.
- HPV Vaccine: Provides protection against HPV strains known to cause genital warts and various cancers, including cervical cancer.
Nonoxynol-9: Limitations and Uses
Nonoxynol-9 is a spermicidal and microbicidal agent commonly used to lubricate condoms. While it can kill some local vaginal microbes, it is not fully protective against all STDs. Its effectiveness varies, and it may not provide adequate protection against viral infections like HIV or herpes.
Therefore, additional preventive measures, such as condom use and vaccination, are recommended for comprehensive STD protection.
Treatment of STDs
The treatment of sexually transmitted diseases depends on the specific causative organism and aims to prevent long-term complications and further transmission. Key considerations in the treatment of STDs include:
Comprehensive Screening and Partner Notification
- Screening: All sexual partners of an infected individual should undergo screening for STDs to identify and treat infections promptly, thereby preventing further spread.
- Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics: Individuals at high risk of contracting STDs, such as rape victims, may be prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics like azithromycin and cefixime to prevent infection.
Specific Treatments for Different STDs
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial STDs such as Chlamydia, syphilis, and gonorrhea are typically treated with antibiotics such as cephalosporins, penicillin, and other appropriate agents.
- Antiviral Therapy: Viral infections like herpes simplex virus (HSV) may be managed with antiviral agents to reduce symptoms and viral shedding. Local treatments such as freezing therapy can be used for warts caused by HPV. HIV infection requires lifelong treatment with antiretroviral drugs to suppress the virus and maintain low viral loads.
- Parasitic Infections: STDs caused by parasites such as Trichomonas vaginalis are treated with specific antibiotics. Parasitic infections like lice and scabies are managed with shampoos or creams containing insecticides to eliminate the parasites and prevent reinfestation.
In Summary
Here’s a breakdown on STDs (Sexually Transmitted Diseases) prevention and treatment:
Prevention:
- Abstinence: No sexual contact is the ultimate protection.
- Mutual Monogamy: Being in a long-term, committed relationship with a partner who is also not infected.
- Barrier Methods: Consistent and correct use of condoms and dental dams significantly reduces the risk of transmission. Opt for water-based lubricants with latex condoms.
- Vaccination: Get vaccinated for HPV and Hepatitis B to guard against those specific STDs.
- Testing: Regularly getting tested, especially before having sex with a new partner, helps in early detection and treatment. Encourage your partners to do the same.
- Open Communication: Talking openly and honestly about sexual history with partners allows informed decisions about safer sex practices.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics: Effective for treating bacterial STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
- Antivirals: Manage and suppress viral STDs like herpes, although not a cure.
- Other Medications: Depending on the STD, other medications might be prescribed.
- Partner Notification: If diagnosed with an STD, informing current and recent partners is crucial for their testing and treatment to prevent further spread.
Remember:
- Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent complications from STDs.
- Not all STDs are curable, but most are manageable with proper treatment.
- Many clinics offer confidential and affordable STD testing and treatment.
For detailed information on specific STDs, consult a healthcare provider or visit trusted health websites.
Conclusion
Effective management of sexually transmitted diseases involves a multifaceted approach that includes vaccination, the use of barrier methods like condoms, and prompt treatment with appropriate antibiotics or antiviral agents.
Regular screening, partner notification, and comprehensive healthcare access are essential for preventing the spread of STDs and minimizing their impact on individual and public health.
By integrating preventive measures and timely treatment protocols, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to mitigate the burden of STDs and promote overall well-being.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.