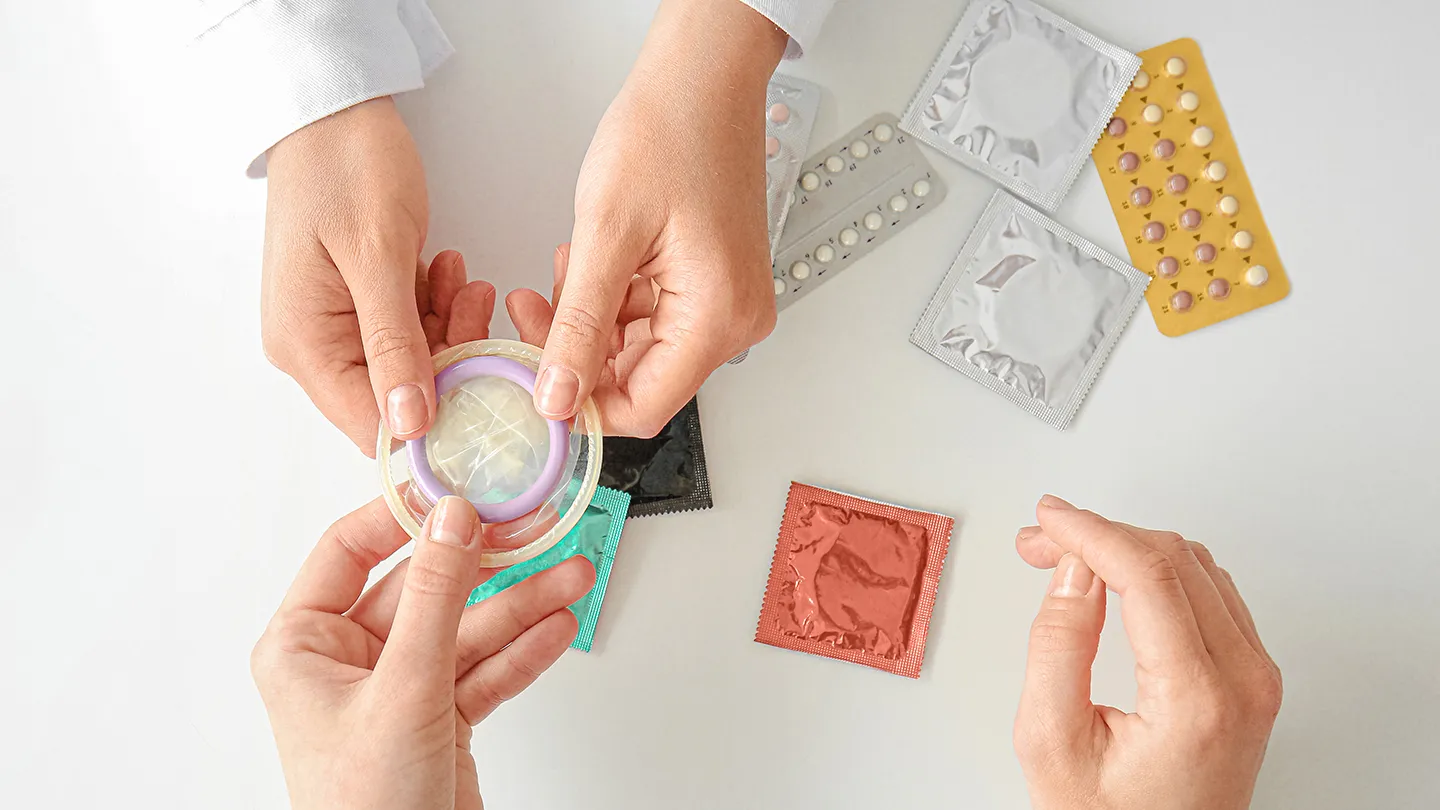
Types of Birth Control: A Complete Guide for Men and Women
Understanding types of birth control is an essential part of taking control of your reproductive health. Birth control isn’t just about preventing pregnancy — it’s also about empowering you to make choices that support your personal goals, lifestyle, and overall well-being.
Using the right birth control method allows individuals and couples to plan their families, reduce stress, and maintain a healthy sexual life. Moreover, some methods provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), which is an important consideration for anyone who is sexually active.
It’s also important to recognize that birth control choices are highly personal. What works well for one person may not be suitable for another. Factors like age, health history, lifestyle, and long-term family planning goals play a significant role in selecting the right method. That’s why exploring the types of birth control available, and consulting with a healthcare professional, is critical.
Types of Birth Control for Women
Women have a wide array of birth control options, ranging from temporary hormonal methods to permanent surgical procedures. Understanding the benefits, potential side effects, and effectiveness of each method will help you make an informed choice.
- Birth Control Pills
How They Work:
Birth control pills are oral contraceptives that contain synthetic hormones — usually a combination of estrogen and progestin. These hormones prevent the ovaries from releasing an egg each month, making fertilization impossible. Some pills are “progestin-only,” which work by thickening cervical mucus to block sperm and thinning the uterine lining.
Effectiveness:
When taken exactly as prescribed, birth control pills are over 99% effective. However, missing doses can reduce their effectiveness, so consistency is key.
Pros:
- Regulates menstrual cycles, making periods more predictable
- Reduces menstrual cramps and heavy bleeding
- Can improve acne and skin health
- May reduce the risk of ovarian cysts and certain cancers
Cons:
- Must be taken daily at the same time
- Can cause nausea, breast tenderness, or mild weight fluctuations
- Does not protect against STIs
Tips for Use:
- Use a reminder app to take your pill on time
- If you miss a dose, follow the instructions on your pill packet carefully
- Pair with condoms if STI protection is needed
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
How They Work:
IUDs are small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus by a healthcare professional. They can be hormonal, releasing progestin, or non-hormonal, made of copper, which is toxic to sperm.
Effectiveness:
IUDs are among the most effective forms of birth control, with over 99% success in preventing pregnancy.
Pros:
- Long-lasting: 3–10 years depending on type
- Low maintenance once inserted
- Hormonal IUDs may reduce menstrual bleeding and cramps
- Reversible — fertility returns quickly after removal
Cons:
- Insertion can be uncomfortable or slightly painful
- Initial cramping or irregular bleeding may occur
- Rarely, the IUD can become dislodged or cause infection
Tips for Use:
- Have a follow-up check after insertion to ensure it’s properly placed
- Learn to check the strings regularly to confirm it’s still in place
- Birth Control Implants
How They Work:
The implant is a small, flexible rod placed under the skin of the upper arm. It releases a steady dose of progestin, which prevents ovulation and thickens cervical mucus.
Effectiveness:
Implants are over 99% effective, making them one of the most reliable types of birth control available.
Pros:
- Long-lasting (up to 3 years)
- No daily attention required
- Can reduce menstrual bleeding and cramps
Cons:
- Minor surgical procedure needed for insertion and removal
- May cause irregular bleeding or spotting
- Some users may experience hormonal side effects such as mood changes
Tips for Use:
- Monitor your menstrual cycle for the first few months
- Report any severe side effects to your healthcare provider
- Birth Control Patch
How They Work:
The patch is a small adhesive square that sticks to your skin, releasing estrogen and progestin into your bloodstream. You apply a new patch once a week for three weeks, followed by a patch-free week.
Effectiveness:
With perfect use, the patch is over 99% effective, though real-world effectiveness is slightly lower due to missed applications or patch detachment.
Pros:
- Weekly application is more convenient than a daily pill
- Hormonal benefits similar to the pill
- Can regulate menstrual cycles and reduce cramps
Cons:
- Possible skin irritation or rash at the application site
- Less effective in individuals over a certain weight
- Does not protect against STIs
Tips for Use:
- Apply the patch to clean, dry skin on the abdomen, back, buttocks, or upper arm
- Rotate placement to reduce irritation
- Vaginal Ring
How They Work:
The vaginal ring is a flexible, hormonal device inserted into the vagina. It releases estrogen and progestin directly to prevent ovulation. The ring is typically worn for three weeks, followed by a one-week break.
Effectiveness:
The ring is over 99% effective with perfect use, and slightly less in typical use.
Pros:
- Only needs monthly attention
- Hormones can improve period symptoms
- Convenient for those who dislike daily pills
Cons:
- Must remember to remove and replace on schedule
- May cause mild vaginal irritation or discharge
- Does not protect against STIs
Tips for Use:
- Wash hands before insertion
- Remove during the scheduled break week, then insert a new ring
- Injectable Contraceptives
How They Work:
Injectable contraceptives like Depo-Provera are shots given every three months. They contain progestin, which prevents ovulation and thickens cervical mucus.
Effectiveness:
Injectables are over 99% effective with proper administration, though effectiveness decreases if shots are delayed.
Pros:
- Administered only every three months
- Highly effective
- Can reduce heavy periods and menstrual pain
Cons:
- Temporary side effects may include weight gain, mood swings, and irregular bleeding
- Fertility may take several months to return after discontinuing
Tips for Use:
- Set reminders for the next injection date
- Discuss with your healthcare provider about managing side effects
- Permanent Methods for Women
How They Work:
Permanent birth control involves surgical procedures like tubal ligation (closing or blocking the fallopian tubes). It is ideal for women who are certain they do not want future pregnancies.
Effectiveness:
Tubal ligation is over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy permanently.
Pros:
- Permanent solution requiring no ongoing maintenance
- Very reliable
Cons:
- Surgery required
- Generally irreversible
- May have surgical risks like infection or bleeding
Tips for Use:
- Only consider if you are certain you do not want future pregnancies
- Discuss risks and recovery thoroughly with your healthcare provider
Expanded Women’s Methods
- Birth Control Pills
Global Usage:
Birth control pills are one of the most commonly used contraceptives worldwide. According to the United Nations, over 150 million women globally rely on oral contraceptives.
Real-Life Example:
Sarah, a 28-year-old teacher, uses birth control pills not only to prevent pregnancy but also to regulate her irregular cycles. She sets a daily phone reminder to ensure she doesn’t miss a dose.
Additional Tips:
- Pair pills with condoms if STI protection is needed
- Track your cycle in a journal or app to notice any changes
- If experiencing side effects, consult your doctor — sometimes switching pill types resolves issues
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Global Usage:
IUDs are highly popular, especially for long-term contraception. Studies show that over 160 million women worldwide rely on IUDs for effective, low-maintenance birth control.
Real-Life Example:
Maria, a 32-year-old nurse, chose a hormonal IUD after deciding she didn’t want more children in the next decade. She appreciates that it’s maintenance-free and significantly reduced her menstrual cramps.
Additional Tips:
- Learn to check the strings to ensure the IUD is in place
- Schedule follow-ups with your healthcare provider
- Understand possible side effects like temporary spotting
- Birth Control Implants
Global Usage:
Implants are increasing in popularity, particularly in countries where long-term contraception is preferred. According to WHO, implants are over 99% effective, with millions of women worldwide using them.
Real-Life Example:
Aisha, a busy entrepreneur, chose the implant for stress-free, long-term protection. She appreciates not needing to remember daily pills while managing her business.
Additional Tips:
- Regularly monitor your cycle for initial irregularities
- Discuss any hormonal side effects with your provider
- Implants can be removed early if you decide to conceive
- Birth Control Patch
Global Usage:
While less common than pills or IUDs, the patch is widely used in North America and Europe, with many women appreciating its weekly convenience.
Real-Life Example:
Emma, a university student, prefers the patch because she often forgets pills. She applies a patch every Sunday and enjoys the freedom from daily dosing.
Additional Tips:
- Rotate patch sites to avoid skin irritation
- Be mindful of the patch’s schedule during travel
- Combine with condoms for STI protection
- Vaginal Ring
Global Usage:
The vaginal ring is gaining popularity, particularly in urban areas where convenience is valued. Usage statistics indicate millions of women globally opt for this monthly method.
Real-Life Example:
Nina, a marketing professional, finds the ring perfect for her busy lifestyle. She only needs to remember monthly insertion and removal, making it much easier than daily pills.
Additional Tips:
- Wash hands before insertion
- Monitor for mild irritation or unusual discharge
- Set a reminder for the one-week ring-free interval
- Injectable Contraceptives
Global Usage:
Injectables like Depo-Provera are used by over 40 million women worldwide, especially in regions where regular access to pills may be limited.
Real-Life Example:
Lydia, a mother of two, uses injections for reliable, three-month protection while balancing work and family life.
Additional Tips:
- Set calendar reminders for your next injection
- Discuss side effects like weight gain or irregular bleeding
- Combine with barrier methods if STI protection is needed
- Permanent Methods for Women
Global Usage:
Tubal ligation is a commonly chosen permanent solution, especially for women over 35 who have completed their families. In some countries, up to 20% of women use tubal ligation as their primary method.
Real-Life Example:
Clara, 38, opted for tubal ligation after having three children. She values the permanent, worry-free protection and no longer needs to manage daily or monthly contraceptives.
Additional Tips:
- Only consider if you are certain you do not want future pregnancies
- Discuss recovery and surgical risks thoroughly
- Continue using other methods until full recovery

Types of Birth Control for Men
Although historically men have had fewer contraceptive options than women, there are still several effective methods available. Understanding these options helps men take an active role in family planning and reproductive health.
- Condoms
How They Work:
Condoms are barrier methods that physically prevent sperm from entering the vagina. They can be made of latex, polyurethane, or polyisoprene. Condoms are the only male contraceptive method that also protects against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Effectiveness:
- Perfect use: 98% effective
- Typical use: 85% effective
Pros:
- Protects against both pregnancy and STIs
- Widely available over-the-counter
- Affordable and easy to use
- No hormones involved
Cons:
- Can break or slip if not used properly
- Some people experience reduced sensation or irritation
- Requires correct use every time
Tips for Use:
- Check the expiration date before use
- Store in a cool, dry place to avoid damage
- Use a new condom for each sexual encounter
- Consider pairing with another method for extra protection
- Withdrawal Method (Pulling Out)
How It Works:
The withdrawal method involves removing the penis from the vagina before ejaculation to prevent sperm from entering the reproductive tract.
Effectiveness:
- Perfect use: 96% effective
- Typical use: 78% effective
Pros:
- No cost or devices needed
- No hormones or side effects
- Can be used spontaneously
Cons:
- Requires self-control and accurate timing
- Less effective than other methods
- Does not protect against STIs
Tips for Use:
- Communication between partners is crucial
- Combine with condoms for added STI protection
- Not recommended as a primary method if reliable contraception is critical
- Vasectomy
How It Works:
Vasectomy is a surgical procedure in which the vas deferens — the tubes that carry sperm — are cut or sealed. This prevents sperm from mixing with semen during ejaculation.
Effectiveness:
- Over 99% effective as a permanent form of birth control
Pros:
- Permanent solution for men who do not want children
- Quick procedure, often done under local anesthesia
- Very low failure rate
Cons:
- Surgical procedure with small risks (infection, bleeding)
- Generally irreversible
- Does not protect against STIs
Tips for Use:
- Consider only if certain you do not want future children
- Use an alternative method until sperm counts confirm sterility
- Developing Male Contraceptives
Emerging Options:
Research is underway for new male contraceptives, including hormonal pills, gels, and reversible injections. These methods aim to suppress sperm production temporarily.
Pros:
- Could provide men with more control over contraception
- Potentially reversible
- May complement existing female methods
Cons:
- Not yet widely available
- Possible side effects (hormonal changes, mood alterations)
Wellness Tip:
Even though options are limited now, staying informed about new types of birth control for men can help couples make more equitable decisions about family planning.
Expanded Types of Birth Control for Men
While men historically have had fewer options than women, there are still several effective methods that allow men to actively participate in family planning and sexual health.
- Condoms
How They Work:
Condoms act as a physical barrier, preventing sperm from reaching the egg. They are also the only male birth control method that protects against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Global Usage:
Condoms are the most widely used male contraceptive worldwide. According to the United Nations, over 150 million men use condoms regularly.
Real-Life Example:
James, a 25-year-old software developer, always uses condoms with new partners. He values the dual protection against pregnancy and STIs, and carries a small travel kit with him to stay prepared.
Pros:
- Protects against both pregnancy and STIs
- Affordable and widely available
- Hormone-free and non-invasive
Cons:
- Can break or slip if used incorrectly
- May reduce sensitivity for some men
Practical Tips:
- Check the expiration date and packaging integrity before use
- Store condoms in a cool, dry place
- Use a new condom for every sexual encounter
- Combine with another method, such as hormonal or female contraception, for added protection
- Withdrawal Method (Pulling Out)
How It Works:
The withdrawal method involves removing the penis before ejaculation, preventing sperm from entering the reproductive tract.
Effectiveness:
- Perfect use: 96% effective
- Typical use: 78% effective
Global Usage:
While harder to quantify, surveys indicate that the withdrawal method is commonly used in North America and Europe, particularly among young adults.
Real-Life Example:
Alex, a college student, occasionally uses the withdrawal method with his long-term partner. They also track her fertility cycle to maximize effectiveness, though they acknowledge it is less reliable than other methods.
Pros:
- No cost or devices needed
- No hormonal side effects
- Can be used spontaneously
Cons:
- Requires discipline and timing
- Less reliable than other methods
- No protection against STIs
Practical Tips:
- Communicate openly with your partner
- Use alongside condoms for STI protection
- Track fertility signs for better reliability
- Vasectomy
How It Works:
A vasectomy is a surgical procedure that cuts or seals the vas deferens, preventing sperm from being released during ejaculation.
Effectiveness:
- Over 99% effective, making it one of the most reliable permanent male birth control methods.
Global Usage:
Vasectomy is widely used in countries like Canada, the United States, and Australia, where long-term family planning is a priority. Statistics show that about 15% of men in these countries opt for vasectomy after completing their families.
Real-Life Example:
Mark, a 40-year-old father of three, chose a vasectomy after deciding he did not want more children. He appreciates the permanent, low-maintenance protection, allowing him and his partner peace of mind.
Pros:
- Highly effective and permanent
- Quick procedure with low complication risk
- Cost-effective over time
Cons:
- Surgery required
- Generally irreversible
- No protection against STIs
Practical Tips:
- Use alternative contraception until sterility is confirmed
- Discuss surgical risks and recovery time with your doctor
- Plan for post-procedure follow-ups to ensure effectiveness
- Emerging Male Contraceptives
How They Work:
Research is ongoing into hormonal pills, gels, and injections for men. These methods aim to suppress sperm production temporarily, providing reversible contraception options.
Global Usage:
While not yet widely available, clinical trials are promising. Experts predict that male hormonal contraceptives could be commercially available within the next decade, giving men more autonomy in family planning.
Real-Life Example:
Although not yet accessible, men participating in trials report minimal side effects and appreciate having a method under their control.
Pros:
- Provides men with more control over contraception
- Reversible and temporary
- Complements female methods for shared responsibility
Cons:
- Limited availability currently
- Possible side effects like mood changes or hormonal imbalance
Practical Tips:
- Stay informed about new developments in male contraception
- Discuss options with your healthcare provider when available
- Consider combining with barrier methods until fully reliable
Wellness Tip for Men
Men play a crucial role in family planning, yet many underestimate their impact. Understanding types of birth control available for men encourages shared responsibility, reduces unintended pregnancies, and promotes healthier sexual relationships.
Natural Methods of Birth Control
Natural methods appeal to those who prefer non-hormonal, chemical-free approaches. While these methods can be effective, they often require careful monitoring and discipline.
- Fertility Awareness
How It Works:
Fertility awareness involves tracking the menstrual cycle to determine fertile days and avoiding unprotected sex during this time. Methods include:
- Basal body temperature tracking
- Cervical mucus monitoring
- Calendar-based calculations
Effectiveness:
- Perfect use: 95–99% effective
- Typical use: 76–88% effective
Pros:
- No hormones or devices
- Increases understanding of your body
- Can be used to plan or avoid pregnancy naturally
Cons:
- Requires daily monitoring and record-keeping
- Less reliable for irregular cycles
- Does not protect against STIs
Tips for Use:
- Use fertility apps or charts to track ovulation
- Combine with barrier methods for extra protection
- Educate both partners for accurate use
- Abstinence
How It Works:
Abstinence means completely refraining from sexual activity. This is the only method that guarantees 100% protection from pregnancy and STIs.
Pros:
- No side effects
- Fully effective against pregnancy and STIs
- No devices or medications required
Cons:
- Not practical for many sexually active adults
- Requires self-discipline and mutual agreement with partners
Tips for Use:
- Abstinence can be a temporary or long-term choice
- Use this method alongside sexual education and awareness for maximum benefit
- Lactational Amenorrhea
How It Works:
Breastfeeding exclusively can naturally suppress ovulation in the first six months postpartum. This is known as lactational amenorrhea.
Effectiveness:
- Highly effective if all conditions are met: exclusive breastfeeding, within six months postpartum, and no return of menstruation
Pros:
- Free and natural
- Temporary postpartum contraception
- Promotes bonding and infant nutrition
Cons:
- Only effective under strict conditions
- Effectiveness decreases with mixed feeding or the return of menstruation
Tips for Use:
- Monitor breastfeeding frequency and menstruation carefully
- Consider additional contraceptive methods as your cycle returns
How to Choose the Right Birth Control Method
Choosing the right birth control method can feel overwhelming, but it’s important to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Every person’s body, lifestyle, and reproductive goals are different. Understanding the factors that influence your choice can help you make an informed, confident decision.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Age and Fertility Goals
Your age and plans for future pregnancy play a significant role. For example:
- Younger individuals or those who may want children soon might prefer temporary methods like pills, condoms, or IUDs.
- Those who are certain they do not want future pregnancies may consider permanent methods like tubal ligation or vasectomy.
- Health History
Certain health conditions may influence which methods are safest:
- People with a history of blood clots may avoid estrogen-containing pills.
- Those with allergies to latex may need non-latex condoms or alternative barrier methods.
- Women with irregular menstrual cycles may benefit from hormonal options like the implant or IUD.
- Lifestyle and Convenience
Your daily routine and comfort with certain methods matter:
- Busy schedules might favor long-acting methods like IUDs or implants.
- People who travel frequently or have unpredictable routines may prefer condoms or monthly rings.
- Protection Against STIs
- If STI protection is important, condoms are essential.
- Combining condoms with another method can offer both pregnancy prevention and STI protection.
- Side Effects and Hormonal Sensitivity
- Some people experience side effects from hormonal methods, such as mood changes, weight fluctuations, or nausea.
- Non-hormonal methods like IUDs (copper), condoms, or natural fertility awareness avoid hormonal side effects.
Wellness Tip:
Always discuss your options with a healthcare provider. They can help you evaluate the types of birth control based on your health history, lifestyle, and reproductive goals, ensuring the method you choose is safe and effective.
Common Myths About Birth Control
There are many misconceptions about birth control that can lead to confusion or misuse. Let’s debunk some of the most common myths:
Myth 1: Birth Control Causes Infertility
Reality: Most birth control methods are fully reversible. Fertility generally returns quickly after stopping hormonal methods, IUDs, or barrier methods. Only permanent methods like tubal ligation or vasectomy are irreversible.
Myth 2: Only Women Need Birth Control
Reality: Men play a critical role in family planning. Options like condoms, vasectomy, and emerging male contraceptives allow men to actively participate in preventing unplanned pregnancies.
Myth 3: Condoms Are 100% Effective
Reality: Condoms are highly effective when used correctly, but they can break, slip, or be used incorrectly, which lowers effectiveness. Always use condoms consistently and consider pairing them with another method.
Myth 4: Hormonal Birth Control is Unsafe
Reality: For most healthy adults, hormonal birth control is safe. Side effects exist but are usually mild and manageable. Your healthcare provider can guide you to the safest option based on your personal health.
Myth 5: Natural Methods Don’t Work
Reality: Fertility awareness and abstinence can be effective if practiced correctly, but they require discipline and accurate monitoring. They may be less reliable than other types of birth control if used inconsistently.
Wellness Tip:
Educating yourself about types of birth control and understanding the facts versus myths helps you make informed choices without unnecessary fear or anxiety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can birth control protect against STIs?
A: Only barrier methods, such as condoms, protect against STIs. Other methods prevent pregnancy but do not provide STI protection.
Q2: How soon can I get pregnant after stopping birth control?
A: Fertility usually returns quickly after stopping most methods. Pills and condoms allow immediate fertility, while injections may take a few months for fertility to return.
Q3: Are all birth control methods reversible?
A: Most methods are reversible, but permanent procedures like tubal ligation and vasectomy are intended to be irreversible.
Q4: Can men use hormonal birth control?
A: Currently, hormonal birth control is only available for women. Research is ongoing for male contraceptives like pills, gels, and injections.
Q5: What if I forget to take my birth control pill?
A: Follow the instructions on your pill packet carefully. Many pills have guidelines for missed doses, and using condoms in the meantime can provide extra protection.
Q6: Is it safe to use multiple birth control methods at the same time?
A: Yes! Using multiple methods, like combining condoms with hormonal birth control, can increase effectiveness and provide STI protection.
Q7: How do I know which birth control is best for me?
A: Speak with a healthcare provider who can evaluate your health history, lifestyle, and reproductive goals. They can guide you through the types of birth control that suit your needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of birth control empowers individuals and couples to take control of their reproductive health. With options for both men and women, from temporary hormonal methods to permanent surgical solutions, everyone can find a method that fits their body, lifestyle, and long-term goals.
Choosing the right method involves considering health history, convenience, STI protection, and personal preferences. Always consult a healthcare professional before making a decision to ensure safety and effectiveness.
With accurate knowledge and proactive planning, birth control becomes a tool for wellness, empowerment, and peace of mind.
Benefits of Eating Strawberries
Benefits of Eating Pomegranate

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.