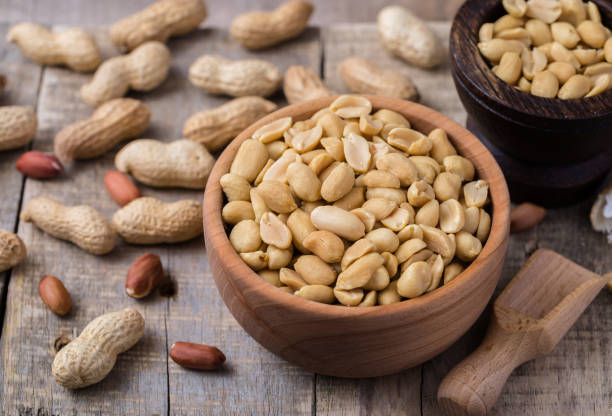
Health benefits of eating peanut
One of the outstanding benefits of eating peanut is the fact that it nourishes and fortifies the skin. Therefore, peanut is one of the foods for the skin, whether eaten roasted, raw or made as peanut butter, it contains more nutrients especially vitamin B3 and also brings down cholesterol levels.
It is quite uncommon that in the vegetable kingdom, the fruit of a plant develops underground. As it is, this is the case of groundnut (peanut). This happens when the flower ovary is fertilized; it goes straight underground and develops to maturity.
Some people believe that peanut is a root or a tuber; however, it is a legume, a subterranean fruit. The fruit is a pod housing the seeds which is also the edible portion.
Common names remain:
Groundnut, Goober (pea), Mani, Spanish peanut, Runner peanut
French: Cacahuète
Spanish: Cacahuete, cacahuate, Mani
German: ErdnuB.

Peanut plant (‘Arachis hypogea’ L.) is an herbaceous plant belonging to the botanical family Leguminosea which grows from 30 to 40 cm high. It is cultivated mostly in tropical and subtropical regions of the globe.
Some people believe that peanut is native to Brazil and East Asia, however it has been the staples in the diet of native Americans, in particular Central Americans. This is before the arrival of the Europeans. Today, peanut is one of the oil-bearing nuts, regarding its taste and nutritional values.
READ ALSO: Winter Savory
Peanut Composition
Energy = 567 kcal = 2,374 kj
Carbohydrates = 7.64 g
Protein = 25.8 g
Fiber = 8.50 g
Vitamin A = ___
Vitamin B1 = 0.640 mg
Vitamin B2 = 0.135 mg
Niacin = 16.2 mg NE
Vitamin B6 = 0.348 mg
Folate = 240 µg
Vitamin B12 = ____
Vitamin C = ____
Vitamin E = 9.13 mg α-TE
Potassium = 705 mg
Calcium = 92.0 mg
Magnesium = 168 mg
Iron = 4.58 mg
Phosphorus = 376 mg
Zinc = 3.27 mg
Saturated Fat = 6.83 g
Total Fat = 49.2 g
Cholesterol = ____
Sodium = 18.0 mg
This is based on percentage (%) daily value which is also based on a 2,000 calorie diet given by 100 grams of peanut.
Below is the percentage composition of groundnut (peanut)
Fat = 49.2%
Fiber = 8.50%
Minerals = 2.33%
Carbohydrates = 7.64%
Water = 6.50%
Properties and Some Indications of Peanut
Peanuts are quite nutritious and their nutrient concentration or nutrients surpass any animal-based food such as meat and fish. It is only the walnut and almond that can compare with peanut in terms of nutritional properties or richness.

In proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins B1, C, E and niacin, peanut exceeds fish and eggs. Their mineral content in calcium, potassium, and magnesium are superior. Honey and oil surpass peanut in some nutrients such as fats and carbohydrates but oil-bearing nut like peanut holds all the basis nutritional values in high concentration.
The following are some its detailed nutrient properties in which benefits of eating peanuts are derived from.
Protein
Proteins in peanut reaches 26% of their weight and are rather poor in amino acids (lysine, methionine and threonine) and in order to get the benefits of eating it, it is recommended to have peanut eaten with the following:
- Legumes (which are rich in lysine and threonine)
- Whole grains (which is highly rich in methionine)
- Brewer’s Yeats (highly rich in methionine and threonine)
YOU MAY LIKE: Echinacea Benefits for Skin
Carbohydrates
Peanut holds a significant amount of carbohydrates (about 10%), in particular maltose and starch. As it is, it is important to chew and properly salivate peanut well so as to enable ptyline in the saliva to start off digestion process.
Fats
The fat contained in peanut can be extracted as oil. Here, they formed of a balanced combination of polyunsaturated, saturated and monounsaturated. The least abundant here is saturated fatty acids.
One of the benefits of eating peanut is its vital role played in the formation and restoration of the skin and the brain as well.
Peanut percentage distribution of fatty acids
Monounsaturated = 24.4 g
Polyunsaturated = 15.6 g
Saturated = 6.83 g
Among the benefits of eating peanut is the involvement in the immune system and in the heart metabolism. This is because; they are seen as one of the primary source of energy for muscle of the heart. Another benefit is that the brain needs all glucose so as to maintain all of its activities; like burning the fatty acids to get energy needed for it beats.
Vitamins
They hold some amounts of B complex vitamins B1, B2 and B6) and also a small amount of vitamin A and C.
Niacin in peanuts acts as a coenzymes which helps to facilitate various chemical reactions necessary for the metabolism of carbohydrate and fat thereby making way for these nutrients to provide adequate energy for the cells. This is an awesome benefit of eating peanut.

It is noteworthy that lack of niacin displays itself by red, dry and cracked skin as well as dyspepsia and weakness of the muscles. Niacin deficiency that is somewhat serious results to a disease called pellagra which is characterized by what is commonly known as three “D’s” (diarrhea, dermatitis and dementia).
Minerals
Peanuts contain about 670 mg of potassium per 100 grams and quite low in sodium, that’s when salt has not been added. They also contain calcium, phosphorus and iron and other trace elements such as copper, manganese and zinc.
Vegetable Fiber
Groundnuts are quite poor in cellulose fiber (vegetable fiber) and this can trigger constipation especially when consumed in large amount without combining them with whole grains or fruit.
SEE ALSO: Cypress Benefits
Applications for the benefits of eating peanut
The benefits of eating peanut are quite helpful in the following:
- Cardiac conditions
- Skin conditions
- Cardiac conditions
Cardiac conditions
Since peanuts are rich in essential fatty acid content, it is therefore recommended for individuals with heart conditions. This is because the fatty acids are the essential source of energy for the cells of the heart. They help in lowering cholesterol levels thereby promoting blood circulation of the coronary arteries.
Another benefit of eating peanut is that they help protect against high blood pressure and fluid retention especially in the tissues. Keep in mind that these benefits are assumed when the groundnuts are not salted.
Skin conditions
The regular eating of peanut facilitates the skin’s good health and also the mucosa due to its unsaturated fatty acids and niacin content which is quite high. These substances are helpful for regeneration of the skin and overall health.
Preparation and Use of Peanut
- Fried in oil: Fried groundnuts are quite tasty, if somewhat indigestible
- Raw: There are varieties which have unpleasant flavor and again, they are difficult to digest.
- Peanut flour: In some places, it is mixed with wheat flour to obtain nutritious bread. Peanut flour is very rich in protein.
- Roasted: If they have been shelled, it is recommended to not roast them beyond 5 to 10 minutes; 15 to 20 minutes if they have not been shelled.
- Peanut butter: Peanuts are roasted, lightly and then grinding them to a homogenous paste. It may be substituted for diary butter.
Peanut Oil

The cold-pressed groundnut oil, that is, the first and second extraction is always fluid, clear and also with a delicate flavor. Groundnut oils that are not fluid should not be accepted because it shows that the unsaturated fatty acids have now become hydrogenated (saturated) and thereby losing their dietetics importance.
Original peanut oil does not go smoking except when the temperature is quite high and since it is used as kitchen oil, it is only used for frying and other forms of cooking.
Groundnut oils are quite rich in unsaturated fatty acids and therefore recommended as a lotion on the skin in cases of dermatitis, eczema and dry skin. It can also be taken orally and according to pulse.ng, it may also with weight loss These are some of the benefits of eating peanut.
Foods that lower high blood pressure quickly

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.