Breadfruit Benefits: A Nutritious Superfood
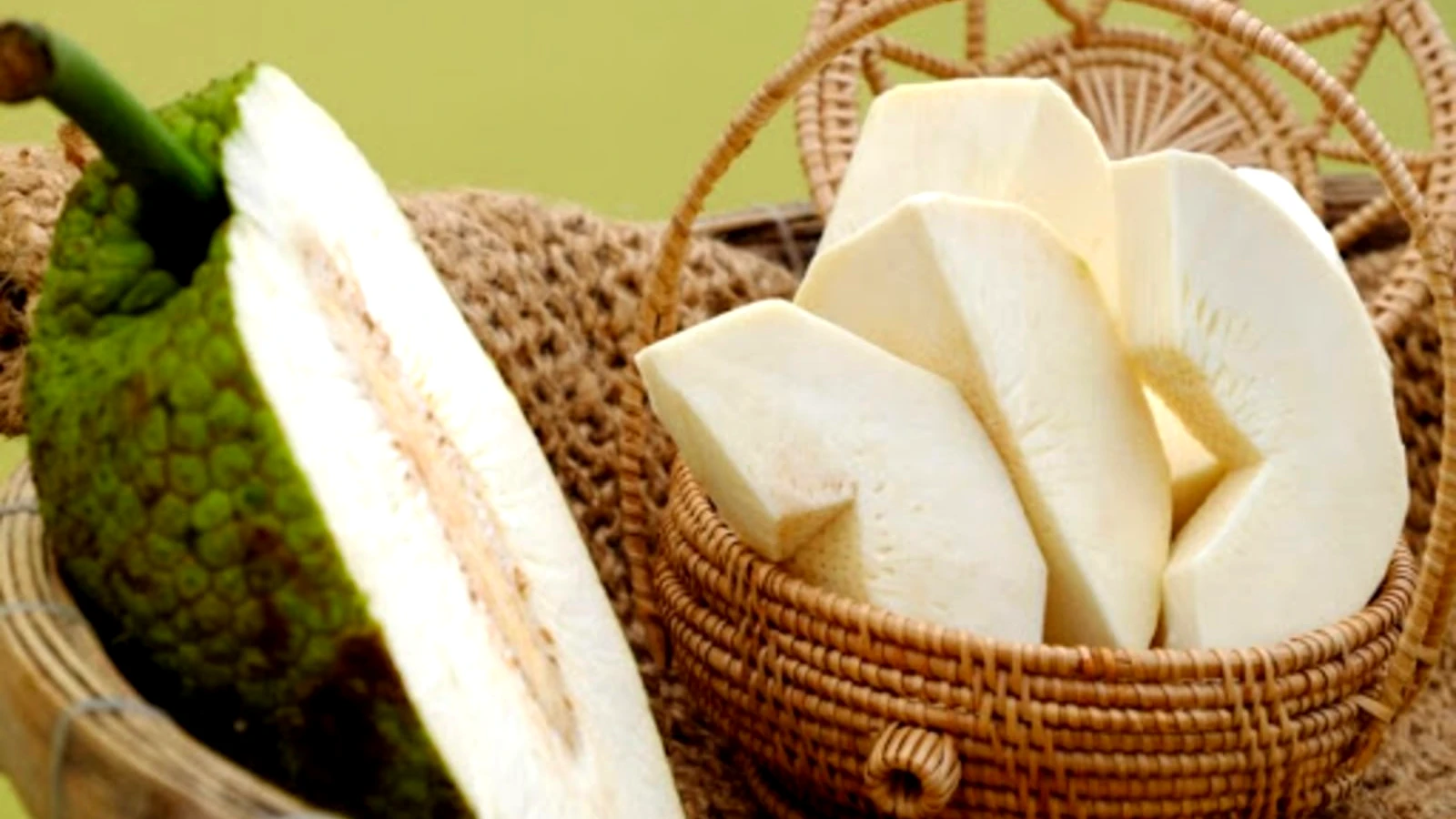
Breadfruit benefits are quite enormous. Scientifically known as Artocarpus altilis, is a flowering tree belonging to the Moraceae family, which also includes jackfruit and mulberry trees. Native to South America, this highly nutritious crop has a variety of health benefits.
Both the fruit and seeds are commonly consumed as food, while the roots and leaves are often used for medicinal purposes.
Breadfruit has a rough, green exterior and a white, fibrous interior. It is rich in complex carbohydrates and low in fat and cholesterol, making it a nutrient-dense fruit.
Its abundance of vitamins and minerals provides numerous health benefits, including support for joint and eye health, as well as anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
Relieves Joint and Muscle Pain
Breadfruit may support joint health and relieve muscle pain due to its rich content of prenylated phenolic compounds, such as flavonoids, which help combat inflammation associated with rheumatic pain.
Rheumatic pain is typically characterized by chronic joint inflammation resulting from the gradual breakdown of the tissue between joints.
Although dietary patterns alone cannot cure muscle and joint pain, nutrition can significantly help alleviate symptoms. Consuming foods like breadfruit, which are rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, can help reduce inflammation caused by oxidative stress.
Provides All Essential Amino Acids
Protein is essential for the body to repair and grow cells. While protein-dense foods like meat are known for their high protein content, breadfruit also provides a valuable source of amino acids—the building blocks of protein.
The human body can produce most amino acids, but there are nine essential ones that must be obtained through food. Breadfruit contains all nine essential amino acids, particularly phenylalanine, leucine, isoleucine, and valine.
Phenylalanine is a precursor for neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation and cognitive function, while leucine, isoleucine, and valine support muscle repair.
Including breadfruit in a well-balanced diet can be especially beneficial for vegans, vegetarians, or anyone falling short of their essential amino acid needs.
Supports Eye Health
Breadfruit is a rich source of carotenoids and lutein, both of which are crucial for eye health. It contains beta-carotene, a precursor for vitamin A, an essential nutrient for eye function. Vitamin A is necessary for the production of pigments in the retina and maintaining moisture throughout the eye.
A deficiency in vitamin A can lead to night blindness and other vision issues. Including breadfruit in your diet may help prevent eye diseases and maintain vision over time. However, for personalized advice, consulting an eye health specialist like an ophthalmologist or optometrist is recommended.
Prevents Bacterial Infections
Another one among breadfruit benefits is that, it possesses antimicrobial properties that can help fight bacterial infections. This tropical fruit contains bioactive compounds, such as ethyl acetate and methanolic extracts, which have been linked to antibacterial activities.
Research indicates that consuming breadfruit may protect against pathogenic organisms like Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus mutans, and Enterococcus faecalis.
While more research is needed to fully understand its antibacterial capabilities, incorporating breadfruit into a balanced diet can support the body’s natural defenses against foodborne illnesses, skin infections, and other bacterial ailments.
YOU MAY LIKE:Turmeric Milk Benefits
Offers a Nutrient-Dense Flour Alternative
Breadfruit is naturally gluten-free, making it an excellent flour alternative for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities.
Studies have shown that breadfruit flour is more easily digested compared to wheat flour, although these studies were not conducted on humans. Cooked breadfruit is also a great source of fiber and other nutrients.
One cup of cooked breadfruit contains 8 grams of fiber, which can help meet daily fiber needs and promote gut health. A healthy gut microflora is essential for regulating appetite, supporting metabolic processes, and protecting against chronic inflammation.
Regarding breadfruit benefits, it is a versatile and nutrient-dense fruit with a multitude of health benefits. Its anti-inflammatory properties can help relieve joint and muscle pain, while its essential amino acids support overall protein needs.
The fruit’s rich carotenoid content aids in eye health, and its antimicrobial properties help protect against bacterial infections.
Furthermore, breadfruit offers a gluten-free flour alternative and a high-fiber food option to support gut health. Including breadfruit in a well-balanced diet can contribute significantly to overall health and well-being.
Nutrition of Breadfruit
Breadfruit is a highly nutritious fruit, with most of its calories derived from carbohydrates. Despite this, it is considered a low-glycemic index fruit, meaning it does not cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, but rather provides a steady source of energy. This makes it a good option for maintaining balanced energy levels throughout the day.

The fruit is low in fat and protein but remarkably provides all nine essential amino acids, which are crucial for protein synthesis in the body.
SEE ALSO:Types of Stomach Infections
Additionally, breadfruit contains a variety of vitamins and minerals, contributing significantly to the recommended Daily Value (DV) for several nutrients.
Here’s a nutritional breakdown for one cup of raw breadfruit (220 g):
- Calories: 227
- Fat: 0.5 g
- Sodium: 4.4 milligrams (mg)
- Carbohydrates: 59.6 g
- Fiber: 10.8 g
- Protein: 2.4 g
- Vitamin C: 63.8 mg, or 71% of the DV
- Potassium: 1,080 mg, or 32% of the DV
- Magnesium: 55 mg, or 13% of the DV
Risks of Breadfruit
While breadfruit is generally safe for healthy adults, there are specific considerations for certain populations:
- Interactions with Medications: Breadfruit may exhibit 5-alpha reductase inhibitory activity, similar to medications used to treat conditions like enlarged prostate and male pattern baldness. Individuals taking these medications should be cautious when consuming breadfruit to avoid potential interactions.
- Kidney Conditions: People with a history of kidney issues should be wary of consuming large amounts of breadfruit. The fruit is high in potassium and magnesium, which are filtered by the kidneys. Excessive intake could lead to a buildup of these nutrients in individuals with compromised kidney function. It is advisable for those with kidney conditions to consult their healthcare provider before adding breadfruit to their diet.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, allergic reactions to breadfruit can occur. As breadfruit belongs to the mulberry family, those who are allergic to mulberries or figs should approach breadfruit with caution. If an allergic reaction is suspected, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional.
In conclusion, breadfruit is a nutrient-dense food that offers various health benefits, but individuals with specific health conditions or on certain medications should consume it with caution and seek medical advice if necessary.
Tips for Consuming Breadfruit
While breadfruit is gaining recognition for its rich nutritional profile and versatility in the kitchen, it may not be readily available in all regions. If you’re new to incorporating breadfruit into your diet, here are some tips to help you make the most of this nutritious fruit:
- Ensure Ripeness: Choose breadfruit that is firm with a fragrant aroma, indicating ripeness. Unripe breadfruit can be too starchy and hard to digest.
- Preparation: Start by peeling the outer skin and removing the core. The core is tough and should be discarded. Once peeled and cored, cut the breadfruit into your desired shape for cooking.
- Cooking Methods: Breadfruit can be prepared in a variety of ways. You can boil, steam, fry, roast, or grill it. Each method offers a different texture and flavor profile, making breadfruit suitable for both sweet and savory dishes.
- Explore Traditional Recipes: Breadfruit has been a staple in the South Pacific for centuries. Consider trying traditional dishes from this region to experience authentic flavors and cooking methods.
- Smoothies: Blend breadfruit with coconut milk and other nutritious ingredients to create a refreshing and healthy smoothie. This is a great way to enjoy breadfruit’s benefits in a liquid form.
- Preservation: Breadfruit is highly perishable. To avoid waste, consider freezing or canning any unused portions. This allows you to enjoy breadfruit out of season and reduces food waste.
A Quick Review on Breadfruit Benefits
Breadfruit, originating from the South Pacific, is a highly nutritious fruit with a variety of health benefits. It boasts anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties and may support joint health and eye function.
Nutritionally, breadfruit is a fantastic source of fiber, vitamin C, and potassium. It’s generally safe to consume but should be eaten in moderation by individuals with kidney disease due to its high potassium content.
Breadfruit’s versatility in the kitchen allows it to be used in a wide range of dishes, both sweet and savory, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
How to Prepare Breadfruit
Breadfruit, a versatile and nutritious tropical fruit, can be prepared in a variety of ways. Whether you’re cooking it for the first time or looking for new methods to try, these steps will help you make the most of breadfruit’s unique flavor and texture.
- Selecting the Right Breadfruit
- Ripeness: Choose a breadfruit that is firm but gives slightly under pressure. It should have a fragrant aroma. Overripe breadfruit will be too soft, while unripe breadfruit will be too starchy.
- Appearance: Look for a breadfruit with a green or slightly yellow skin. Avoid fruit with large brown spots or a mushy texture.
- Preparing the Breadfruit
- Washing: Rinse the breadfruit under cool running water to remove any dirt or debris.
- Peeling: Use a sharp knife to peel the tough, green skin off the breadfruit. Start by cutting off both ends to create a stable base, then carefully slice down the sides to remove the peel.
- Corning: Cut the breadfruit in half lengthwise, then into quarters. Remove the core from each quarter. The core is tough and inedible, so be sure to cut it out completely.
- Cutting: Depending on your recipe, you can slice, dice, or leave the breadfruit in larger chunks.
- Cooking Methods
- Boiling: Place breadfruit pieces in a pot of salted boiling water. Cook for about 30-40 minutes, or until tender. Boiled breadfruit can be mashed or used in soups and stews.
- Steaming: Steam breadfruit pieces in a steamer basket over boiling water for about 20-30 minutes, or until tender. Steamed breadfruit retains more nutrients and has a softer texture.
- Frying: Slice breadfruit into thin pieces or wedges. Heat oil in a frying pan and fry the slices until golden brown and crispy. Fried breadfruit can be enjoyed as a snack or side dish.
- Roasting: Preheat your oven to 375°F (190°C). Place breadfruit pieces on a baking sheet and roast for 45-60 minutes, or until tender and lightly browned. Roasted breadfruit has a rich, caramelized flavor.
- Grilling: Brush breadfruit pieces with oil and place them on a preheated grill. Cook for about 10-15 minutes on each side, or until grill marks appear and the breadfruit is tender.
- Incorporating Breadfruit into Dishes
- Traditional Recipes: Explore traditional South Pacific dishes like breadfruit curry, breadfruit salad, or breadfruit chips to appreciate its authentic flavors.
- Smoothies: Blend cooked breadfruit with coconut milk, fruits, and other ingredients for a nutritious and refreshing smoothie.
- Soups and Stews: Add boiled or steamed breadfruit to soups and stews for a hearty and nutritious addition.
- Side Dishes: Serve roasted or fried breadfruit as a side dish with your favorite meals. It pairs well with both sweet and savory flavors.
- Preserving Breadfruit
- Freezing: Cooked breadfruit can be frozen for later use. Place the cooked pieces in an airtight container or freezer bag and store them in the freezer for up to six months.
- Canning: Breadfruit can be canned in syrup or brine. Follow proper canning procedures to ensure safety and quality.
Tips for Enjoying Breadfruit
- Experiment with Spices: Breadfruit has a mild flavor that pairs well with a variety of spices and seasonings. Experiment with different herbs and spices to find your favorite combinations.
- Mix with Other Ingredients: Breadfruit can be combined with other fruits, vegetables, and proteins to create diverse and balanced meals.
- Healthy Preparation: Opt for healthier cooking methods like steaming, boiling, and roasting to retain the most nutrients and keep the dish low in fat and calories.
By following these steps and tips, you can enjoy the delicious and nutritious benefits of breadfruit in many different ways. Whether you’re new to this tropical fruit or looking to expand your culinary repertoire, breadfruit offers a versatile and healthy addition to your diet.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.