Healthful Foods that Reduce Inflammation
Regarding foods that reduce inflammation, there’s been quite a bit of chatter surrounding anti-inflammatory diets, which propose consuming specific foods purported to reduce inflammation. But the burning question remains: do they genuinely deliver results?
Our bodies are amazing at healing themselves. Inflammation is a natural part of this process, triggered by injuries, toxins, or even illness. It’s like a built-in alarm system, sending white blood cells and other defenders to fight off invaders and repair damage.
According to MedlinePlus, these injured cells release chemicals that cause swelling – a telltale sign of inflammation. This inflammation is crucial for healing, but just like a fire alarm, if it’s constantly blaring, it can become a problem.
Chronic, uncontrolled inflammation has been linked to serious health issues down the line, including obesity, heart disease, and even cancer.
To delve into the realm of how dietary choices can impact inflammation, it’s essential to grasp the very nature of inflammation itself.
In essence, inflammation embodies your body’s defense mechanism triggered by various stimuli, spanning from microbial invasions like common cold viruses to physical traumas such as a twisted joint, and virtually anything in the spectrum between these extremes.
“Inflammation essentially signifies your body’s reaction to stimuli,” explains Dr. Robert Hutchins, MD, MPH, an internal medicine expert at UNC Health. “And sometimes, this response is beneficial, like when your immune system kicks into gear to combat an infection or initiates healing in response to an injury.”
Understanding the Dual Nature of Inflammation
Imagine you’re outdoors playing tag with your kids, and suddenly, you twist your ankle. Within moments or perhaps hours, you notice swelling setting in. Similarly, when the flu virus strikes, your body often responds with a fever, an attempt to eradicate the intruder.
Both scenarios exemplify acute inflammation in action—a swift reaction of your inflammatory cells mobilizing to combat potential harm inflicted by injury or invasion. In such instances, the immune system dispatches white blood cells to shield and mend the vulnerable body part.
“The symptoms people experience, like fever, skin redness, headaches, or an accelerated heart rate, are typically attributed to the activity of inflammatory cells responding to stimuli,” explains Dr. Hutchins.
However, there are instances when the body’s inflammatory response veers into overdrive, despite the absence of any imminent threat or injury to heal. Factors such as an unhealthy diet, smoking, stress, and insufficient sleep and exercise can stoke the flames of inflammation.
Studies reveal that chronic inflammation is intricately linked to severe health conditions like cancer, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis.
The silver lining amidst this inflammatory cloud lies in the realm of lifestyle modifications capable of thwarting and mitigating chronic inflammation.
Dr. Hutchins underscores the importance of regular exercise, encompassing both cardiovascular workouts and strength training, along with adopting a nourishing dietary regimen.
Indeed, according to Elizabeth Watt, a registered dietitian at UNC Health, tweaking your dietary habits could potentially yield better results in lowering inflammation levels compared to relying solely on over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications like Advil.
The good news is that what we eat can play a big role in managing inflammation. Research published in a 2018 review in the journal Nutrients found that sugary foods, especially sugary drinks, can actually worsen inflammation.
Dr. Scott Zashin, a clinical professor at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, explained to Health magazine that these sugary culprits can overwork our immune system, leading to uncomfortable symptoms like joint pain and fatigue, and even damage our blood vessels.
But fear not! There’s a silver lining. Plenty of delicious and nutritious foods have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. We’ll explore these wonder foods next!
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Disregard the allure of marketed meal plans promoting specific anti-inflammatory foods. There’s no one-size-fits-all diet regimen to adhere to; once you grasp the essence of inflammation-fighting foods, you can seamlessly incorporate them into your dietary repertoire at your discretion.
At the heart of foods that combat inflammation lie antioxidants. These compounds, whether synthetic or naturally occurring, act as guardians of your body’s tissues, shielding them from the detrimental effects of free radicals—those volatile atoms that wreak havoc on cells, contributing to various illnesses and the aging process.
By fortifying tissues against damage, antioxidants preemptively thwart unwarranted inflammatory responses.
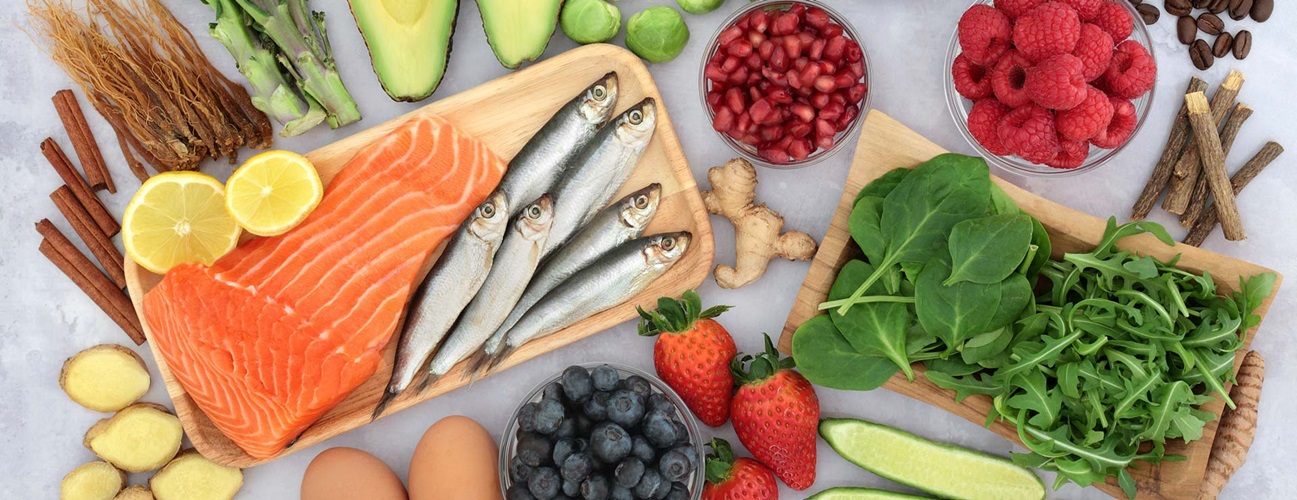
Here are some dietary staples to consider (foods that reduce inflammation):
- Fruits: Particularly rich in vitamin C, berries, oranges, and cherries stand out for their immune-boosting properties. Laden with antioxidants, these fruits aid in neutralizing free radicals, thereby quelling inflammation.
- Tart Cherry Juice: This beverage has garnered favor among athletes for its potent anti-inflammatory effects. In the aftermath of rigorous physical exertion, such as a long run, muscle breakdown and inflammation typically ensue. Tart cherry juice has been shown to mitigate such inflammation in athletes who consume it post-exercise.
- Nuts: Renowned for their antioxidant and omega-3 content, nuts emerge as a stellar choice for inflammation control. Omega-3 fatty acids possess remarkable antioxidant properties, inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX), an enzyme responsible for producing prostaglandin hormones that trigger inflammation. While walnuts reign supreme in omega-3 content, all varieties of nuts confer anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Olive Oil: Esteemed as another antioxidant powerhouse, olive oil deserves a prominent place in your dietary arsenal, as highlighted by Watt.
- Fatty Fish: Rich sources of EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids, fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel exert notable anti-inflammatory effects, aiding in the reduction of inflammation.
- Leafy Greens: Abundant in vitamins A, C, and K, leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collards boast formidable antioxidant credentials.
Watt emphasizes, “Many foods integral to diets like the Mediterranean or DASH diets possess inherent anti-inflammatory properties.”
Foods that Reduce Inflammation in Details

Anti-Inflammatory Fatty Fish!
Swimming with health benefits are fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines. These superstars of the sea are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, known for their anti-inflammatory superpowers.
A 2017 review in Biomedical Society Transactions revealed that omega-3s can actually dampen the body’s inflammatory processes.
Even the American Heart Association (AHA) gives fatty fish a thumbs up as a great source of omega-3s. They’re protein powerhouses too, but light on saturated fat, making them a heart-healthy choice.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends aiming for 8 ounces of fish per week. For the healthiest preparation, go for grilled or baked instead of fried or breaded options.
Not a fish fanatic? Fear not! A 2019 study published in Circulation Research suggests fish oil supplements might be just as effective.
There’s one more thing to keep in mind: balance is key. Our bodies need a healthy balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Since omega-6s are more common in processed foods and some vegetable oils, consider reducing your intake of those to create a more omega-3 friendly environment in your body.
Whole Grains: Filling Fibers for Fewer Flames!
Did you know switching your grains to whole-wheat options can actually help reduce inflammation? Unlike their refined cousins (white bread, cereal, rice, and pasta), whole grains are packed with fiber.
A 2018 study in the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology Journal suggests this fiber might be linked to lower levels of C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation in your blood.
Ready to add some fire-fighting fiber to your meals? Here are some easy tips:
- Mornings: Fuel your day with a bowl of oatmeal or overnight oats.
- Smoothies: Blend in some rolled oats for an extra dose of goodness.
- Lunch: Liven up your salad or grain bowl with chilled quinoa.
- Snacks: Pop some popcorn using heart-healthy olive or avocado oil.
- Dinner: Serve your stir-fry over a bed of brown rice for a satisfying base.
- Soups and Chilies: Add a touch of wild rice for extra depth.
Dark Leafy Greens: Nature’s Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouses!
Leafy greens like spinach, Swiss chard, kale, and broccoli are more than just salad fillers. A 2020 study in Molecular Nutrition & Food Research points to vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant in these greens, as a key player in protecting your body from inflammatory molecules called cytokines.
Plus, according to a 2017 study in Foods, they’re loaded with essential nutrients like iron and vitamin A.
Nuts: Nature’s Mighty Munchies for Inflammation Defense!
Looking for another tasty way to fight inflammation? Nuts are here to save the day! A 2016 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that people who ate five one-ounce servings of nuts each week had lower C-reactive protein levels compared to those who ate fewer nuts.
Almonds, in particular, are superstars when it comes to battling inflammation. A 2018 review in Nutrients highlights their richness in fiber, calcium, and vitamin E. Walnuts are another great choice, packing a powerful punch of alpha-linolenic acid, a type of omega-3 fat, according to a 2020 study in Nutrients.
No matter your nut preference, all nuts are loaded with antioxidants that can help your body fight off and repair damage caused by inflammation.
Here’s a bonus fact: Nuts, along with fish, leafy greens, and whole grains, are all key components of the heart-healthy Mediterranean diet. Following this delicious dietary pattern is a great way to meet the American Heart Association’s recommendations for a healthy way of eating!
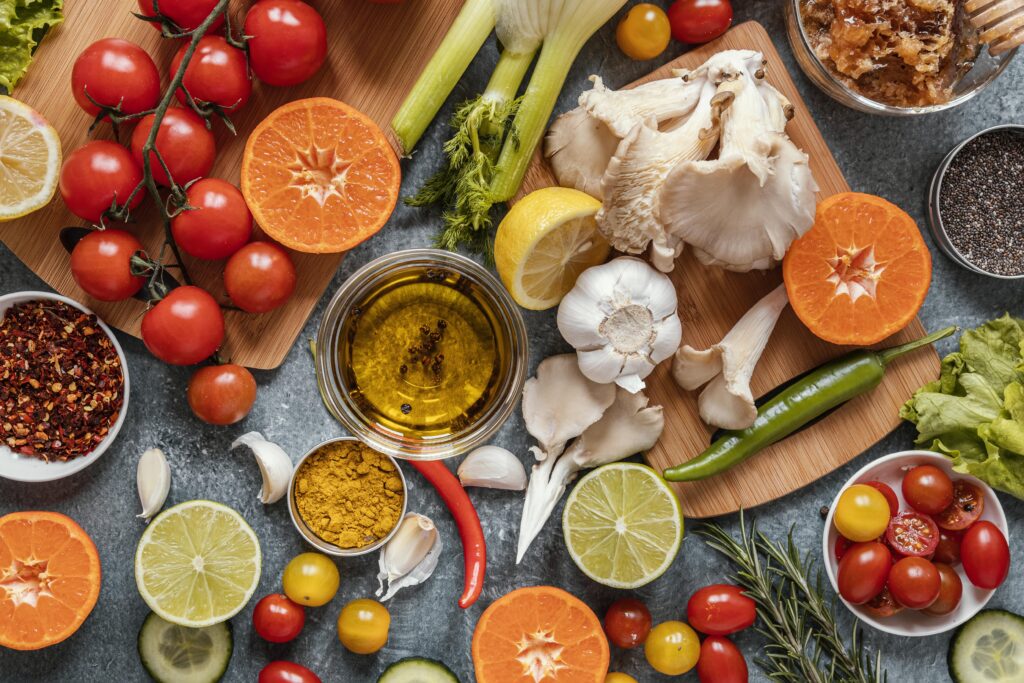
Bell Peppers: A Rainbow of Anti-Inflammatory Power!
Dr. Karen H. Costenbader, a Harvard Medical School professor of medicine and rheumatoid arthritis specialist, emphasizes the importance of colorful vegetables for a healthy diet in general. She highlights bell peppers, tomatoes, squash, and leafy greens for being packed with antioxidant vitamins and lower in starch.
Bell peppers come in a vibrant array of colors, while hot peppers (including chili and cayenne) are rich in capsaicin. Capsaicin is the chemical used in topical creams to reduce pain and inflammation, according to a 2016 review in Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology.
Tomatoes: A Lycopene Powerhouse That Fights Inflammation
Tomatoes may help reduce inflammation for some people. They’re a great source of lycopene, an antioxidant. A 2020 review in Molecules found that low blood levels of lycopene may be linked to increased inflammation in people with health conditions like chronic hepatitis, heart disease, and breast cancer.
The good news is that cooked tomatoes provide even more lycopene than raw ones, so tomato sauce is a great option too! A 2013 study in the British Journal of Nutrition even found that tomato juice consumption was beneficial for reducing systemic inflammation.
Beets: A Vibrant Weapon Against Inflammation (and More!)
On foods that reduce inflammation, the deep red color of beets is a clue to their impressive health benefits. According to a 2017 study in Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, beets are loaded with fiber, folate, and powerful plant pigments called betalains. These betalains offer both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Beets may not only reduce inflammation but also protect against cancer and heart disease, according to a 2015 study in Nutrients. Research on the potential health benefits of beets is ongoing, with some studies suggesting they may be a promising therapeutic treatment for various conditions associated with oxidative stress and inflammation.
Additional Strategies for Inflammation Reduction
- Steer Clear of Processed Foods and Sugar: Ditching or at least limiting your intake of processed snacks, sugary treats, sodas, and chips can yield significant reductions in inflammation. These dietary culprits are notorious for triggering inflammatory responses in the body.
- Bypass the Drive-Thru: Trans fats, prevalent in fast food and deep-fried delicacies, have been implicated in elevating inflammation levels according to research findings. Opting out of fast-food indulgences can serve as a proactive measure in curbing inflammation.
- Exercise Alcohol Moderation: While indulging in alcoholic beverages, it’s prudent to exercise moderation. Studies have established a correlation between alcohol consumption and heightened inflammation. As a guideline, women should cap their intake at one drink per day, while men should limit themselves to no more than two drinks daily.
- Say No to Smoking: Tobacco usage is a prime catalyst for inflammation escalation. Steering clear of smoking or seeking assistance to quit can effectively mitigate inflammation levels.
- Prioritize Quality Sleep: Striking a balance in sleep duration is crucial—most adults require seven to nine hours of nightly rest. Both inadequate and excessive sleep can incite inflammatory responses in the body. Therefore, ensuring sufficient but not excessive sleep is paramount for inflammation management.
- Mitigate Stress: Prolonged stress serves as a breeding ground for chronic inflammation. Adopting stress management techniques is pivotal in mitigating inflammation. Consider embracing mindfulness-based practices to equip your body with effective coping mechanisms against stressors.
By implementing these additional measures alongside dietary adjustments, you can bolster your arsenal against inflammation, paving the way for improved overall health and well-being.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.