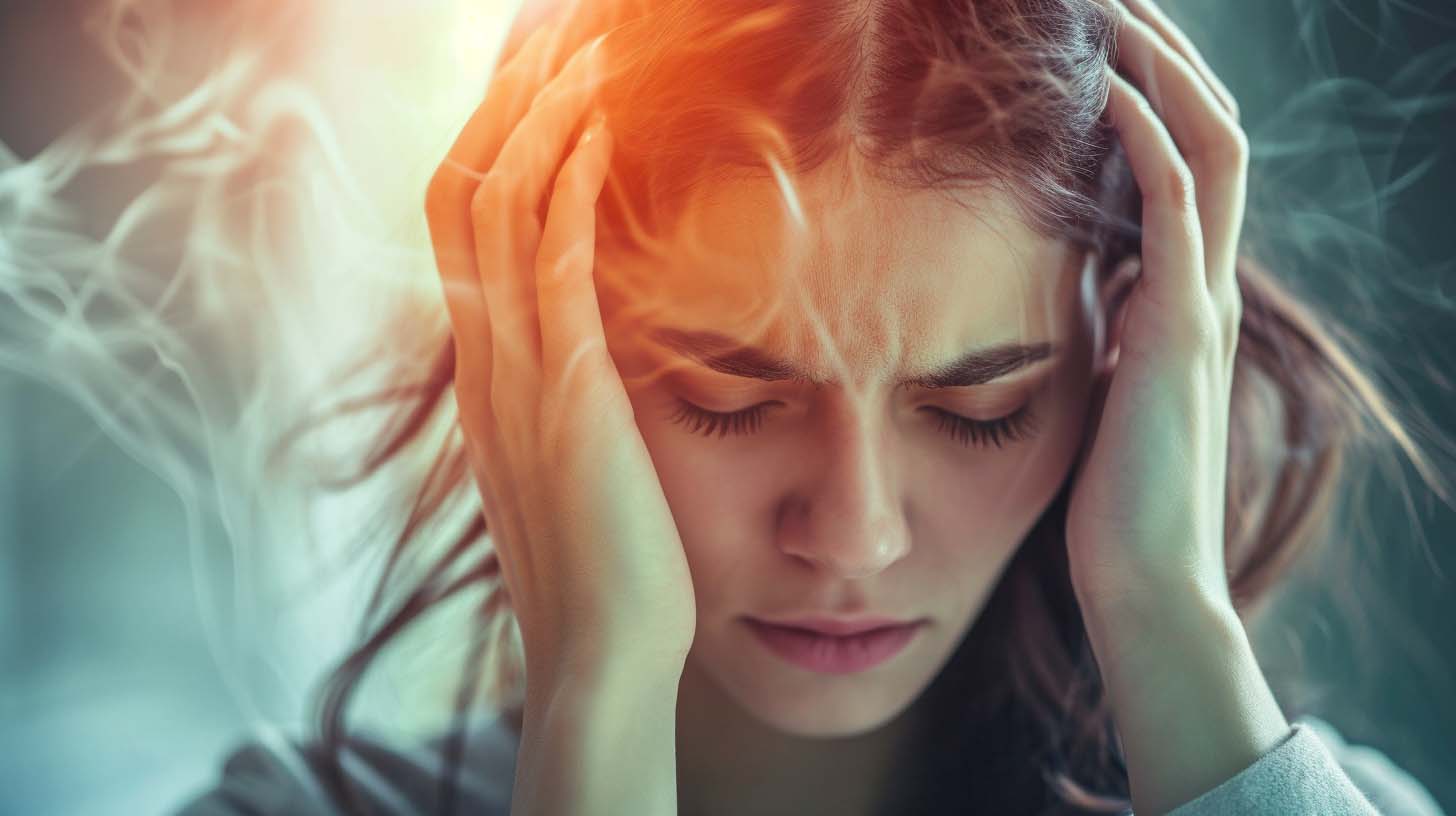
Extreme Fatigue and Brain Fog
Before we delve into extreme fatigue and brain fog, let’s take a look at what brain fog really is. Brain fog is a term often used to describe a set of cognitive symptoms that make mental processes feel clouded or muddled, impacting how clearly you think, focus, and remember.
People experiencing brain fog may find it challenging to concentrate on everyday tasks, recall information, or follow through with activities without feeling mentally drained or distracted.
The sensation is often described as a “fog” because it can make your mind feel cluttered or unclear, interfering with even routine tasks such as holding conversations, listening to instructions, or following a sequence of steps.
This mental haze, also known as “mental fog,” can arise for various reasons. It may occur after an illness, appear as a side effect of certain medications (like chemotherapy drugs), or signal an underlying health condition. Brain fog can be frustrating and disruptive, but in most cases, it’s temporary.
However, the duration and intensity can vary significantly from person to person, depending on the root cause. Consulting a healthcare provider can help identify the reason behind brain fog and guide you toward appropriate treatments or lifestyle adjustments to help you feel more mentally alert and clear-headed.
What does brain fog feel like?
The experience of brain fog can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Difficulty concentrating and staying focused
- Feelings of confusion or mental disorientation
- Persistent fatigue or low energy levels
- Forgetfulness or trouble recalling information
- Frequently losing your train of thought mid-conversation
- Mental exhaustion, even with minor tasks
- Struggling to find the right words during conversations
- Slowed thought processes and reaction times
- Difficulty paying attention or being easily distracted
In short, brain fog can feel like your mind is wading through thick mental “clouds,” making daily activities harder and often leaving you feeling mentally drained.
Possible Causes of Brain Fog
Brain fog can stem from various factors, affecting both mental clarity and cognitive function. Here are some common causes:
- Lack of Sleep: Poor sleep quality or insufficient rest can disrupt mental clarity and lead to cognitive fatigue.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Diseases like lupus, multiple sclerosis, and fibromyalgia often involve inflammation, which can affect the brain and lead to cognitive difficulties.
- Blood Sugar Imbalances: Conditions like diabetes or low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can impact brain function, leading to symptoms of brain fog.
- Mental Health Issues: Anxiety, depression, and chronic stress can reduce cognitive sharpness, making it harder to focus and think clearly.
- Neurodivergent Conditions: ADHD and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can cause challenges with attention, memory, and focus, often contributing to brain fog.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can affect mental clarity and focus.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor nutrition, including a lack of essential vitamins and minerals, can impair brain function.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger brain fog by releasing stress hormones that affect the brain’s ability to function optimally.
Brain fog can also develop after specific events or conditions, including:
- COVID-19 Infection (Long COVID): Many people experience lingering cognitive symptoms post-COVID. Research suggests the virus may alter the gut microbiome, reducing serotonin production, which can impair cognitive function.
- Chemotherapy: Often referred to as “chemo brain,” this type of brain fog can occur during or after cancer treatment.
- Long Hospital Stays: Extended hospitalizations, especially those involving critical illness, can lead to cognitive fatigue and mental sluggishness.
Some studies indicate that immune system activity might provoke inflammation in the brain (neuroinflammation), temporarily disrupting information processing and memory.
Extreme Fatigue and Brain Fog
Extreme fatigue is a debilitating condition that goes beyond ordinary tiredness, leaving individuals feeling physically and mentally drained, even after rest. It’s a sense of overwhelming exhaustion that seems unrelenting, no matter how much sleep or relaxation you get.
When combined with brain fog, extreme fatigue can create a vicious cycle that significantly impacts your daily life. The two conditions are often linked, with one exacerbating the other, leading to an ongoing struggle to function both mentally and physically.
What is Extreme Fatigue?
Extreme fatigue is a profound sense of tiredness or lack of energy that goes beyond the usual weariness people experience after a long day or period of stress. It can persist for weeks or even months and is often accompanied by other symptoms like muscle weakness, difficulty concentrating, and a general sense of heaviness or sluggishness.
Unlike typical tiredness, extreme fatigue doesn’t improve after sleep or rest. In fact, it can make ordinary activities feel like monumental tasks, draining your energy and leaving you feeling defeated before even starting the day.
The Connection Between Extreme Fatigue and Brain Fog
Brain fog, which causes cognitive symptoms like confusion, forgetfulness, lack of focus, and mental exhaustion, is frequently accompanied by extreme fatigue. These two conditions are often intertwined, creating a compounding effect that makes both feel far more intense and debilitating.
When you’re extremely fatigued, your brain struggles to function at full capacity, and the mental clarity required to perform even basic tasks begins to deteriorate.
The constant wear on your body can interfere with brain processes, leading to difficulty concentrating, remembering, and processing information—hallmarks of brain fog. Conversely, the mental cloudiness and confusion of brain fog can make even the simplest decisions or activities feel mentally exhausting, contributing to the feeling of fatigue.
The mechanisms behind both brain fog and extreme fatigue are thought to be related to physical and chemical changes within the body. Fatigue can result from stress, lack of sleep, illness, or underlying health conditions like autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, or chronic conditions like fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome. These same conditions can also cause or exacerbate brain fog, creating a dual problem of mental and physical exhaustion.
How They Amplify Each Other
When you experience both extreme fatigue and brain fog together, it can be overwhelming. Extreme fatigue can impair your ability to focus, leading to an increase in mental confusion and forgetfulness. This, in turn, can make everyday tasks feel impossible to complete, intensifying feelings of frustration, helplessness, and anxiety.
As you struggle to concentrate or remember basic things, you may push yourself harder, trying to power through, which only worsens both your physical exhaustion and mental fatigue. The cycle becomes self-perpetuating, with each symptom feeding off the other.
Additionally, when your brain isn’t functioning optimally due to brain fog, it becomes harder to follow through on healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining proper nutrition, exercise, or good sleep hygiene. This lack of self-care can worsen both brain fog and fatigue, leading to further cognitive impairment and physical exhaustion.
Managing Extreme Fatigue and Brain Fog
Addressing extreme fatigue and brain fog often requires a multi-faceted approach to identify and treat the underlying causes. Here are some strategies that can help break the cycle:
- Prioritize Rest and Sleep: Both brain fog and fatigue can be mitigated with improved sleep hygiene. Ensuring adequate, restorative sleep is critical for both physical recovery and cognitive function.
- Nutritional Support: A well-balanced diet that includes key nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants can support brain health and energy levels. Nutritional deficiencies can exacerbate both fatigue and cognitive symptoms.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular, moderate exercise can improve circulation and boost energy levels, while also promoting cognitive clarity. Even a short walk each day can help clear the mind and reduce feelings of fatigue.
- Stress Management: Since stress is a major contributor to both brain fog and extreme fatigue, incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce its impact on the body and mind.
- Medical Evaluation: If brain fog and extreme fatigue persist, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome, autoimmune disorders, or depression may be contributing to the symptoms. A healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation and recommend treatments or therapies to address the root causes.
Extreme fatigue and brain fog often go hand in hand, creating a cycle that can severely disrupt daily life. Understanding how these two conditions are connected and taking steps to address them can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Whether through lifestyle adjustments, medical intervention, or a combination of both, breaking the cycle of fatigue and brain fog is essential for regaining mental clarity and physical energy.
Care and Treatment for Brain Fog
Currently, there is no single treatment for brain fog, as approaches depend on addressing underlying causes and managing symptoms. Here are some commonly recommended strategies:
- Improving Sleep: Developing better sleep habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful sleep environment, can enhance mental clarity.
- Eating Nutritious Meals: Consuming balanced meals rich in essential nutrients supports brain health.
- Staying Physically Active: Engaging in 30 minutes of daily exercise can boost blood flow to the brain and improve cognitive function.
- Organizing Information: Writing down important details or tasks can help reduce the strain on memory.
- Taking Regular Breaks: Brief 30-minute breaks throughout the day can help reduce mental fatigue.
- Psychotherapy: Techniques like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can improve mental resilience, especially when brain fog is linked to stress or anxiety.
If lifestyle adjustments don’t fully alleviate brain fog, a healthcare provider may recommend specific medications for related symptoms. For instance, antidepressants can help manage mood-related symptoms, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may reduce inflammation. Providers will discuss potential side effects and monitor your response to any new medication.
By addressing underlying causes and using targeted strategies, many people find their cognitive clarity gradually improves over time.
How Long Does Brain Fog Last?
The duration of brain fog can vary dramatically, and there is no definitive timeframe to predict how long it will persist. For some individuals, the fog may linger for just a few days or weeks, causing mild disruption to daily activities. For others, however, the effects can extend far beyond the immediate period, potentially lingering for months or even years.
The intensity and duration of brain fog can be influenced by several factors, including the underlying cause, individual health conditions, and lifestyle choices. If brain fog becomes extreme or continues unabated, severely impacting your ability to function, it is essential to seek medical advice.
A healthcare provider can help you identify potential causes and recommend strategies to minimize its disruptive effects, offering relief from this often overwhelming experience.
Can Brain Fog Be Prevented?
While it’s not possible to completely prevent brain fog from occurring, there are proactive steps you can take to drastically reduce the chances of it becoming a persistent issue. By focusing on both mental and physical health, you can minimize the severity and frequency of brain fog episodes.
For example, regular sleep hygiene, maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and staying active can all contribute to clearer thinking and better cognitive function.
Given that brain fog has become a well-documented symptom following COVID-19 infections, one of the best preventative measures is to get vaccinated against the virus. The COVID-19 vaccine helps reduce the likelihood of severe infection and, consequently, the risk of long-term cognitive issues such as brain fog, offering an extra layer of protection.
While you can’t entirely eliminate the possibility of experiencing brain fog, these preventive steps can significantly reduce your risk of experiencing debilitating symptoms.
When to Call the Doctor
If brain fog becomes severe or starts to interfere with your daily life, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider. This is particularly true if you find yourself forgetting important appointments, struggling to complete routine tasks, or feeling utterly lost in conversations, unable to focus on what others are saying.
When cognitive difficulties become extreme, making it hard to function in everyday situations, it’s a sign that medical intervention may be necessary. Brain fog is common and often temporary, but it can indicate underlying health concerns that require attention.
A healthcare provider can help pinpoint the root cause of your symptoms and guide you toward appropriate treatment options. With professional guidance, you can begin to address the issue and regain your mental clarity, reducing the long-term impact on your quality of life.
Benefits of Eating Strawberries
Benefits of Eating Pomegranate

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.