What are the pros and cons of a vegan diet?
But, really, What are the pros and cons of a vegan diet? An again have you noticed how many people around the world are embracing veganism?
Just look at the growing list of celebrities who have adopted a vegan lifestyle: Bill Clinton, Madonna, Stevie Wonder, the Williams sisters, Russell Brand, and many more. Yet, you might be wondering about the advantages and disadvantages of a vegan diet.
The Essentials of Veganism
Veganism involves abstaining from foods that contribute to animal cruelty. This lifestyle choice is not only beneficial for the planet but also for your health. However, it may lead to nutrient deficiencies.
Additionally, the increased demand for certain crops can affect their supply and raise prices. There’s also the often-overlooked issue of labor exploitation in the agricultural industry.
Pros and Cons of a Vegan Diet
If you’re curious about the pros and cons of going vegan, keep reading. This information will help you decide whether this lifestyle change is right for you.
Key Takeaways
- Veganism as a Lifestyle: Adopting a vegan diet influences your health and habits while also affecting animal and environmental welfare.
- Challenges: This diet plan is linked to issues like labor exploitation and the strain on Earth’s resources.
- Nutritional Considerations: While nutritional deficiencies associated with a vegan diet can be managed, it is important to consider the broader impacts of veganism.
What Is a Vegan Diet?
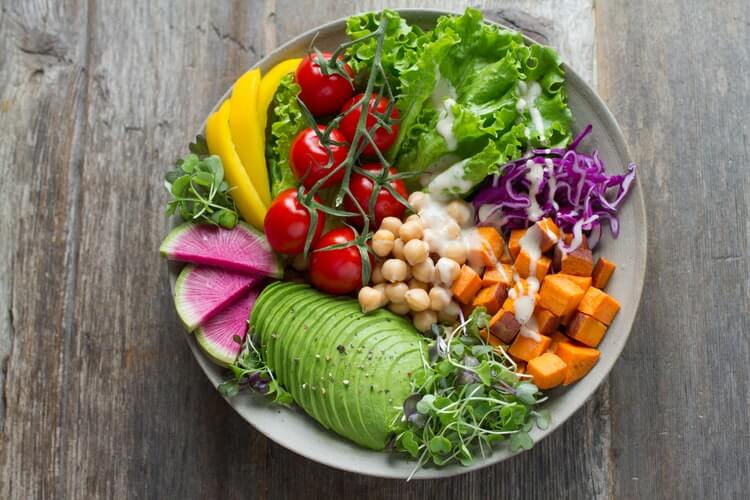
A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, and eggs. It focuses on plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds. This diet is often chosen for health benefits, ethical reasons, or environmental concerns.
However, it requires careful planning to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients such as protein, vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Why Are People Choosing Veganism?
- Health Benefits: Many adopt a vegan diet to improve their health. Research suggests that vegan diets can help with weight loss, reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure and cholesterol, stabilize blood sugar levels, and potentially reduce the risk of certain cancers.
- Animal Welfare: Veganism is rooted in the ethical belief that animals should not be exploited for food. By avoiding animal products, vegans aim to reduce animal suffering and cruelty.
- Environmental Impact: A plant-based diet is considered more sustainable and environmentally friendly. It requires fewer natural resources and generates lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to animal-based diets.
Potential Drawbacks of Veganism
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Without careful planning, a vegan diet can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. Vegans need to ensure they get these nutrients from fortified foods or supplements.
- Economic Impact: The rising demand for plant-based foods can strain the supply of certain crops, leading to higher prices. This economic pressure can affect both consumers and farmers.
- Labor Exploitation: Increased demand for vegan products can lead to labor exploitation in the agricultural sector. Workers may face poor working conditions and low wages.
Choosing to go vegan is a significant lifestyle change that comes with both benefits and challenges. By understanding the full impact of this diet on health, animal welfare, and the environment, you can make an informed decision about whether veganism is right for you.
What Are the Advantages of a Vegan Diet?
With the growing number of vegans worldwide, let’s explore the reasons behind this significant lifestyle shift.
Animal Welfare The primary motivation for veganism is to oppose animal cruelty. By eliminating all animal foods, vegans avoid the slaughter of animals and the cruel treatment they endure in slaughterhouses and farms.
Vegans also aim to reduce inhumane practices in dairy and poultry farms, hatcheries, and apiaries. These practices include stunning, mutilation, genetic manipulation, separating offspring from lactating mothers, and poor hygiene conditions.
Lower Negative Impact on Environment Animal agriculture is highly wasteful, requiring 10 pounds of grains to produce just 1 pound of meat. This demand for land leads to deforestation, animal displacement, water pollution, and scarcity, among other environmental issues.
The animal industry significantly impacts the planet negatively, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and global warming. Veganism offers an eco-friendly lifestyle choice.
Growing Mindful, Healthy Food Habits A vegan diet encourages selective eating by eliminating certain food groups. This mindfulness improves one’s relationship with food, leading to healthier choices.
Vegans often get creative with plant-based sources of fats and proteins, discovering new ways to appreciate nature’s bounty. They tend to choose wholesome foods over fast, frozen, or packaged foods laden with sodium, additives, and preservatives.
Enhanced Weight Loss Veganism is often linked to weight loss. A vegan diet is rich in fiber, which keeps you full longer and curbs hunger pangs. It also reduces the intake of unhealthy fats that contribute to weight gain.
Plant-based foods promote healthy gut flora. Additionally, vegans tend to count calories and monitor their food intake, leading to faster weight loss.
Reduced Health Risks A plant-based diet is associated with numerous health benefits, primarily due to healthier eating habits.
Here’s how a vegan diet can enhance your health:
- Lower blood sugar, higher insulin sensitivity, and reduced risk of Type-II diabetes
- Decreased risk of kidney problems, particularly those related to diabetes
- Reduced risk of breast, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancer
- Improved cardiovascular health with lower risks of hypertension and bad cholesterol
- Fewer arthritis symptoms, such as joint swelling, pain, mobility issues, and stiffness
Maintaining a healthy BMI through veganism can prevent obesity-related health conditions.
Development of Discipline and Control Veganism fosters self-restraint, as restricting certain foods becomes a daily habit, enhancing willpower and discipline.
By monitoring food intake, portion size, macronutrients, and calories, vegans maintain control over their diet. When the motivation for veganism extends beyond personal health to animal welfare and environmental conservation, it strengthens the commitment to this lifestyle.
What Are the Disadvantages of a Vegan Diet?
While the advantages of veganism are often highlighted, there are some downsides that you might be unaware of or overlooking.
Labor Exploitation in Agriculture Plant-based agriculture in some countries that supply vegan staples globally may involve forced labor, child labor, poor and unstable wages, and unsafe working conditions.
Although these issues can be found in animal agriculture as well, they are also linked with certain vegan staples such as soy, rice, cashews, and avocados.
While veganism advocates for animal rights, it is not entirely free of cruelty. The rising demand for these products can contribute to labor abuse.
Higher Demand and Prices with Low Supply As the number of vegans increases, so does the demand for plant-based foods. This increased production can strain the earth’s resources, leading to pressure on the food supply chain. Shortages of popular vegan items like soy or almonds may occur.
Additionally, increased demand and potential supply reductions can lead to higher food prices. The cost of vegan supplies has already seen inflation rates of 7.8% to 10.5%.
Agricultural and Environmental Footprint New farming practices and overproduction of plant-sourced foods may affect the earth’s ability to produce crops sustainably in the long run. This can increase our environmental footprint.
The use of fertilizers and other farming practices can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the reliance on imported exotic crops can lead to environmental pollution due to transportation.
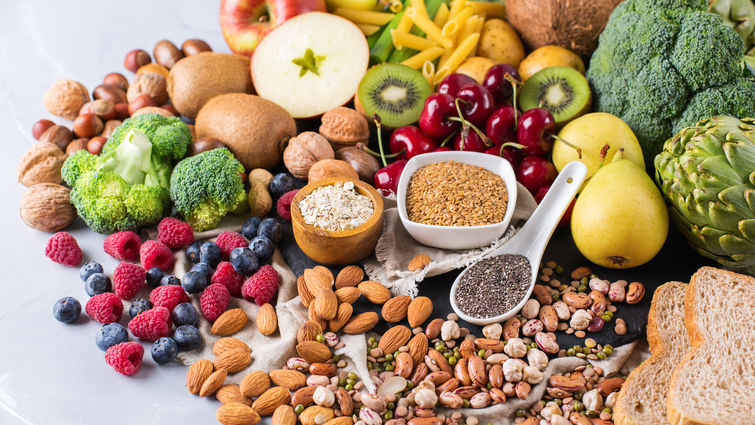
Lack of Certain Nutrients Certain nutrients are primarily available in animal-sourced foods. Without supplements and fortified foods, vegans may miss out on essential vitamins, minerals, and other micronutrients. Some key nutrients that can be deficient in a vegan diet include:
- Zinc
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin D
- Taurine
- Selenium
- Riboflavin
- Retinol
- Pyridoxine
- Iron
- Iodine
- DHA and EPA (Omega-3 Fatty Acids)
- Creatine
- Carnosine
- Carnitine
- Calcium
Digestive Issues and Stomach Discomfort Transitioning to a vegan diet can lead to digestive problems, especially if the diet is not well-planned. A complete change in diet can affect the digestive system, particularly if hydration is not maintained.
High fiber intake from a plant-based diet can be harder to process, and proteins from grains and legumes are 10%-20% harder for the body to absorb, leading to digestive discomfort.
Limited Food and Medicine Options A restrictive vegan diet can make it challenging to find suitable options for foods, desserts, and beverages. Additionally, finding vegan-friendly medicines can require significant effort and research, though more brands are starting to focus on this.
The limited availability of vegan-only restaurants and eateries can also make socializing with friends, family, and colleagues difficult due to restricted menu options.
While veganism offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. From labor exploitation in agriculture to nutrient deficiencies and limited food options, it is essential to consider these disadvantages when deciding if a vegan lifestyle is right for you.
How to Avoid Nutritional Deficiencies on a Vegan Diet
One of the most significant challenges of a vegan diet is the risk of nutritional deficiencies, as some essential nutrients, like vitamin B12 and taurine, are not present in plant-based foods. Your body, accustomed to animal-sourced nutrients, must adapt to absorbing nutrients differently on a vegan diet.
A survey revealed that 28% of vegans suffer from nutrient deficiencies. However, with proper planning and adjustments, you can maintain a healthy vegan lifestyle. Here are some strategies to ensure you get all the necessary nutrients:
- Take Supplements: Incorporate supplements to address nutrient deficiencies. Consult your nutritionist to identify which supplements you need, and speak to your doctor about prebiotics, probiotics, and enzymes to aid nutrient absorption.
- Choose Fortified Foods: Include foods fortified with essential micronutrients, such as almond milk, nut butter, and cereals.
- Opt for Whole Foods: Avoid packaged and processed foods, opting for whole foods instead.
- Plan Meals Carefully: Avoid resorting to fast food, even if it’s labeled vegan. Prepare a shopping list full of nutritious staples and stick to it.
- Ease Into Veganism: Transition slowly to give your body time to adapt to absorbing nutrients from plant-based foods.
The Vegan Diet: Advantages and Disadvantages – FAQs
Q: Is vegan always healthier? A: No, veganism isn’t automatically healthier just because it includes plant-based foods. Many vegan options are processed or contain sodium, sugar, and other unhealthy ingredients.
Plus, they may contain preservatives or chemicals. Don’t forget that vegan foods naturally lack some key vitamins and minerals.
Q: Who should avoid being vegan? A: You may want to reconsider going vegan if you have IBS, nut or soy allergies, or conditions like celiac disease, diabetes, Crohn’s disease, or cancer, which can increase your chances of zinc deficiency. Additionally, alcoholism and following a low-carb diet or disliking vegetables may make veganism challenging.
Q: What is an unhealthy plant-based diet? A: An unhealthy plant-based diet includes processed or fried foods, sugary items, refined grains, or pre-cooked and packaged foods with preservatives. A vegan diet that excludes fresh produce, whole foods, and healthy nutrient sources, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains, is considered detrimental to your health.
Q: Is it more expensive to be vegan? A: The rising demand for plant-based foods can increase their prices, making veganism more expensive.
However, you can manage costs by planning meals and purchasing supplies according to your budget. Buying fresh, seasonal products from local markets and farmers can help reduce expenses.
Benefits of Eating Pomegranate
Foods to help with Constipation

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.