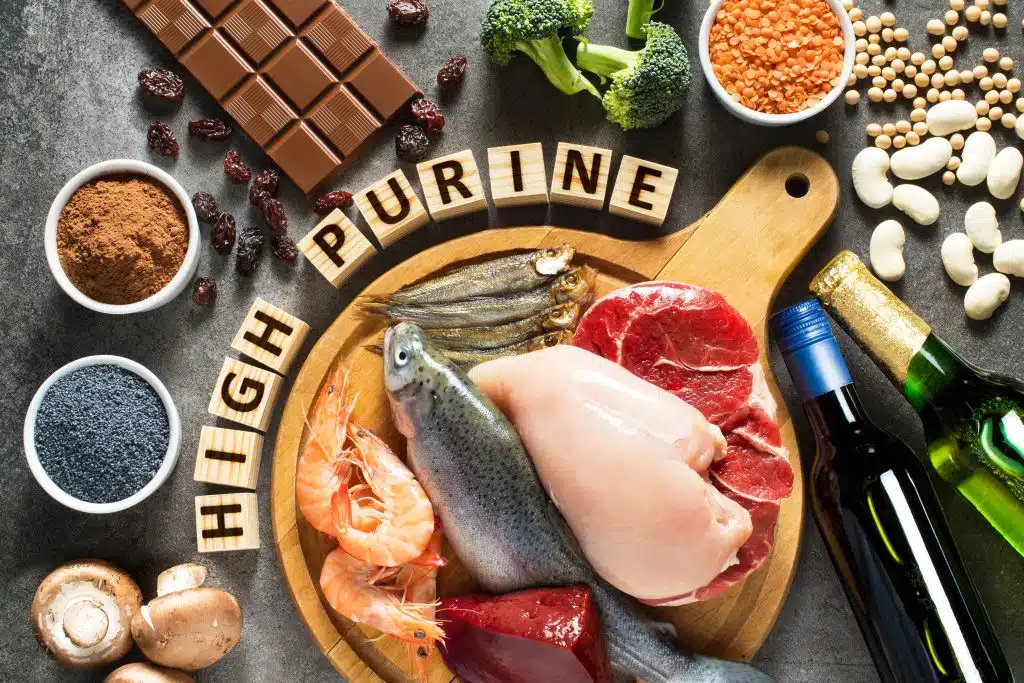
These are Food that Cause Gout
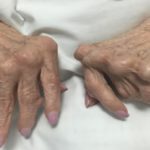
First of all on the foods that cause gout, If you have hyperuricemia, it means there’s too much uric acid in your blood. This excess uric acid can form sharp crystals in your joints, leading to painful gout attacks.
It can also cause kidney stones, which are very painful. Purine is a natural substance found in many foods, especially in meat, fish, and certain vegetables.
Regarding foods that cause gout, when you eat foods high in purine, your body breaks it down into uric acid. To help manage your uric acid levels, doctors advise eating fewer purine-rich foods. This dietary change can make a big difference in preventing gout and kidney stones.
What is the Gout Diet?
Gout is a condition caused by high levels of uric acid in your blood. When there’s too much uric acid, it can form sharp crystals that settle in your joints, causing swelling and intense pain. This is where the gout diet comes in.
A gout diet focuses on eating foods that are low in purine. Purine is a substance found in many foods, and when your body breaks it down, it produces uric acid.
By eating fewer purine-rich foods, you can help lower the amount of uric acid in your body. This can prevent new crystals from forming and reduce the frequency of painful gout attacks.
Key Components of a Gout Diet:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables: Most fruits and vegetables are low in purine and high in nutrients. Cherries, in particular, may help reduce uric acid levels and inflammation.
- Choose whole grains: Whole grain bread, pasta, and rice are better choices compared to refined grains.
- Limit meat and seafood: Red meat, organ meats, and certain fish like sardines and anchovies are high in purine. Try to limit these in your diet.
- Cut down on alcohol: Alcohol, especially beer, can raise uric acid levels. Reducing or avoiding alcohol can help manage gout.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps your body remove uric acid more efficiently.
- Dairy can be beneficial: Low-fat dairy products like milk and yogurt can actually help lower uric acid levels.
By following these guidelines and making smart food choices, you can help manage your gout and reduce the risk of painful attacks. Always consult with a healthcare professional to tailor the diet to your specific needs.
What is a Low Purine Diet?
A low purine diet is designed to help manage the levels of uric acid in your body. Purines are chemicals found naturally in certain foods and drinks. When your body breaks down these purines, it produces uric acid.
By reducing the intake of high-purine foods, you can lower the uric acid levels in your blood and reduce the risk of gout and kidney stones.
Key Aspects of a Low Purine Diet:
- Avoid High-Purine Foods:
-
- Red Meat and Organ Meats: Liver, kidneys, and other organ meats are high in purines.
- Certain Seafood: Anchovies, sardines, mackerel, and scallops have high purine content.
- Certain Vegetables: Asparagus, spinach, and mushrooms have moderate levels of purines but are generally considered safe in moderation.
- Limit Alcohol:
-
- Beer and liquor can increase uric acid levels, so it’s best to reduce or avoid these drinks.
- Choose Low-Purine Foods:
-
- Fruits and Vegetables: Most fruits and vegetables are low in purines. Cherries, for instance, may help lower uric acid.
- Whole Grains: Whole grain breads, pasta, and rice are better choices than refined grains.
- Low-Fat Dairy: Milk, cheese, and yogurt can help lower uric acid levels.
- Stay Hydrated:
-
- Drinking plenty of water helps your body flush out uric acid more effectively.
- Encourage Certain Foods:
-
- Cherries: May help reduce uric acid levels.
- Coffee: Some studies suggest coffee may lower uric acid levels.
- Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Foods high in vitamin C can help lower uric acid levels.
By following a low purine diet, you can manage your uric acid levels more effectively and reduce the risk of gout attacks and kidney stones. Always consult with a healthcare professional to ensure the diet meets your individual health needs.
Who Can Benefit from a Low Purine Diet?
A low purine diet can be particularly beneficial for individuals with high levels of uric acid in their blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. This diet can help:
- Prevent Gout:
-
- People with hyperuricemia who haven’t developed gout yet can lower their risk by reducing high-purine foods.
- Manage Existing Gout:
-
- For those already suffering from gout, a low purine diet can help prevent further gout attacks and alleviate symptoms.
- Prevent Kidney Stones:
-
- High uric acid levels can lead to the formation of kidney stones. A low purine diet can help reduce this risk.
- General Health Maintenance:
-
- Even if you don’t have hyperuricemia, adopting some principles of a low purine diet, such as eating more fruits and vegetables and staying hydrated, can contribute to overall health and well-being.
By cutting down on foods high in purines, individuals can manage their uric acid levels more effectively, reducing the risk of painful gout attacks and other complications associated with hyperuricemia. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
Foods that Cause Gout
Here’s a more detailed look at the top 10 foods that cause gout and drinks that can trigger gout attacks by increasing uric acid levels in the blood:
- Sugary Drinks and Sweets:
-
- Why They’re Bad: Sugary beverages like soda, fruit juices, and sweetened drinks contain high levels of fructose. Fructose is a type of sugar that the body breaks down into uric acid. The rapid absorption of fructose can lead to spikes in uric acid levels, triggering gout attacks.
- Examples: Soft drinks, fruit-flavored drinks, candies, pastries, and desserts.
- High Fructose Corn Syrup:
-
- Why It’s Bad: High fructose corn syrup (HFCS) is a highly concentrated form of fructose often used in processed foods and beverages as a sweetener. HFCS can significantly elevate uric acid levels.
- Examples: Sodas, some fruit juices, candies, baked goods, and many packaged snacks.
- Alcohol:
-
- Why It’s Bad: Alcohol interferes with the kidneys’ ability to filter out uric acid, leading to higher levels in the bloodstream. Beer is particularly bad because it also contains purines from brewer’s yeast.
- Examples: Beer, wine, spirits, and cocktails.
- Organ Meats:
-
- Why They’re Bad: Organ meats are exceptionally high in purines, which the body breaks down into uric acid. Regular consumption of these meats can lead to elevated uric acid levels.
- Examples: Liver, tripe, sweetbreads, brains, kidneys, and heart.
- Game Meats:
-
- Why They’re Bad: Game meats are rich in purines. Historically, these meats were associated with the wealthy, who were more likely to suffer from gout.
- Examples: Goose, veal, venison, and wild boar.
- Certain Seafood:
-
- Why It’s Bad: Many types of seafood are high in purines, contributing to increased uric acid production in the body.
- Examples: Herring, scallops, mussels, codfish, tuna, trout, haddock, and anchovies.
- Red Meats:
-
- Why They’re Bad: Red meats, including beef, lamb, and pork, contain significant amounts of purines. Consuming these meats frequently can raise uric acid levels.
- Examples: Steak, ground beef, lamb chops, pork ribs, and bacon.
- Turkey:
-
- Why It’s Bad: Turkey, although leaner than other meats, still has a high purine content. Processed turkey products, such as deli turkey, are particularly problematic.
- Examples: Roast turkey, deli turkey slices, and turkey bacon.
- Gravy and Meat Sauces:
-
- Why They’re Bad: Gravies and meat sauces are made from meat drippings, which are rich in purines. These sauces concentrate the purines and can lead to increased uric acid levels.
- Examples: Traditional gravy, meat-based sauces like Bolognese, and jus.
- Yeast and Yeast Extract:
-
- Why They’re Bad: Yeast and yeast extracts contain high levels of purines. These ingredients are often used in baking and as flavor enhancers.
- Examples: Bread, certain types of beer, Vegemite, Marmite, and nutritional yeast.
By understanding which foods and drinks can exacerbate gout symptoms, individuals can make more informed dietary choices to manage their condition effectively. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized dietary advice.
YOU MAY LIKE: Sugarcane Juice Benefits
Best Foods to Eat When You Have Gout
While no single food can cure gout, certain foods and drinks can help reduce uric acid levels and alleviate symptoms. Here are some of the best options:
- Skim Milk:
-
- Benefits: Skim milk may help reduce uric acid levels and prevent gout flare-ups. It speeds up the excretion of uric acid in your urine and reduces the inflammatory response to uric acid crystals in your joints.
- How to Use: Drink a glass of skim milk daily or incorporate it into smoothies and cereal.
- Cherries:
-
- Benefits: Cherries and cherry juice have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce uric acid levels. Studies suggest they can be beneficial in managing gout symptoms.
- How to Use: Eat fresh cherries or drink cherry juice. Dried cherries or cherry extract supplements are also options.
- Coffee:
-
- Benefits: Coffee can lower uric acid levels by slowing the breakdown of purines and increasing the rate of uric acid excretion. Regular coffee consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of gout.
- How to Use: Drink one to two cups of coffee daily, but avoid excessive amounts which may have other health impacts.
- Water:
-
- Benefits: Staying well-hydrated helps your kidneys excrete uric acid more efficiently. Drinking water also supports overall kidney health, which is crucial for managing gout.
- How to Use: Aim to drink five to eight glasses of water a day. Carry a water bottle to help you remember to stay hydrated.
General Dietary Guidelines for Managing Gout
- Vary Your Protein Sources:
-
- Guideline: Avoid high-purine meats like organ meats, certain seafood, and game meats. Opt for low-purine protein sources such as legumes, tofu, and lean poultry.
- Examples: Chicken, turkey (in moderation), beans, lentils, and dairy products.
- Enjoy Fruits and Vegetables:
- Incorporate Whole Grains:
-
- Guideline: Whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat pasta, and quinoa are gout-friendly. Avoid grains that may contribute to higher uric acid levels, such as oats.
- Examples: Whole grain bread, brown rice, barley, and quinoa.
- Be Cautious with Added Sugars:
-
- Guideline: Avoid foods and drinks with high fructose corn syrup, as they can increase uric acid levels.
- Examples: Opt for natural sweeteners and read labels to avoid high fructose corn syrup in packaged products.
By following these dietary guidelines and incorporating specific foods that help reduce uric acid levels, you can better manage gout symptoms and reduce the frequency of attacks. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice tailored to your health needs.
Risks and Benefits of a Low-Purine Diet
Advantages of a Low-Purine Diet
- Reducing Uric Acid:
-
- Benefit: A low-purine diet helps manage hyperuricemia, reducing the risk of developing complications like gout and kidney stones.
- Impact: For those already diagnosed with gout or kidney stones, this diet can prevent new uric acid crystals from forming in the joints or kidneys, or at least slow down the formation process.
- Reducing Weight:
-
- Benefit: Avoiding high-purine foods such as red meats and sweets can aid in weight loss.
- Impact: Weight loss lowers the risk of developing gout and helps relieve symptoms by reducing stress on the joints. It also mitigates associated conditions like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
- Reducing Medication:
-
- Benefit: While diet is not a substitute for medication, it can complement medical treatment, potentially reducing the need for medications.
- Impact: By carefully managing their diet, individuals may need fewer medications to control their uric acid levels and manage gout symptoms.
Disadvantages of a Low-Purine Diet
- It’s Limiting:
-
- Challenge: A low-purine diet requires long-term lifestyle changes and the avoidance of many favorite indulgences, including sugar, sweets, and alcohol.
- Impact: For some, adhering to this diet indefinitely may seem unrealistic, especially since it is only a complementary therapy.
- It Limits Omega-3 Sources:
-
- Challenge: Seafood, an important source of omega-3 fatty acids, is limited on a low-purine diet. Omega-3s are beneficial for reducing inflammation and joint pain, especially in arthritis.
- Impact: Many people already don’t get enough omega-3s, and limiting seafood can exacerbate this issue. Fish-oil supplements are an alternative, but they may not completely replace the benefits of dietary omega-3s.
- It’s Not a Cure:
-
- Challenge: Diet alone may not significantly reduce uric acid levels compared to medications.
- Impact: While diet can help, it should be combined with medication for the best results. Some people might find the dietary restrictions burdensome compared to the benefits, but others appreciate having proactive measures to reduce symptoms.
Conclusion on foods that cause gout
A low-purine diet offers several advantages, particularly in managing uric acid levels, reducing weight, and potentially minimizing the need for medications.
However, it comes with limitations, including dietary restrictions that can be challenging to maintain and the potential reduction of omega-3 fatty acids intake.
While not a cure, combining dietary changes with medication can provide a comprehensive approach to managing gout and hyperuricemia. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice is recommended.

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.