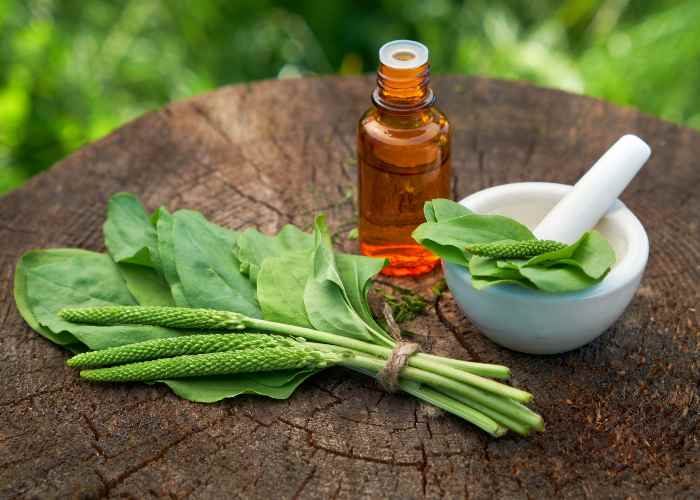
Helpful Plantain Leaves Benefits
As a plant for the respiratory system, plantain leaves benefits lie on their pectoral and cicatrizant properties.
The botanical genus Plantago Comprises about 200 species, among which the most outstanding in regard to their phytotherapeutical applications are psyllium and all three species of plantain (lance- leaf plantain common plantain, and hoary plantain), have been used as medicinal herbs since the times of the ancient Greeks.
The name Plantago refers to the footprint-like shape of their leaves.
PROPERTIES AND INDICATIONS.
All three species of plantain contain a huge amount of mucilage, which gives them emollient, expectorant, antitussive, and bechic properties; tannin, to which they owe their astringent, hemostatic, and cicatrizant (healing) properties; pectin; and chromogenic glycosides (aucubine and catalpol), with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties.
The Common Plantain contains as well phenolic acids, flavonoids, choline, and noscapine, an alkaloid with antispasmodic and antitussive properties.

Plantain soothes and dries at the same time due to the combined action of mucilage (emollient, soothing) and tannin (astringent, which produce desiccation and constriction).
This fact gives plantain a wide anti-inflammatory effect which is very useful in order to heal many respiratory and digestive mucous membrane afflictions. These are their principal applications:
Respiratory afflictions: Acute or chronic bronchitis, bronchial catarrh, asthma. The plantain thins secretions, easing their elimination, as well as reducing the inflammation of the bronchial mucous membrane and ease coughs.
The plantain has been used against pulmonary tuberculosis and pneumonia as a complement to their specific treatment. Among these plants, the common plantain is the one with stronger antitussive properties.
Mouth and throat afflictions, applied in gargles and mouth rinses. The plantain is recommended in the case of stomatitis (inflammation of the oral mucous membrane), gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and laryngitis).
The active components of the plant reduce the inflammation, heal itching and throat irritation, and alleviate coughing from whooping cough (bechic action).
- Digestive afflictions: colitis, aerocolia (gas in the colon), abdominal distension caused by an excess of gas or by bad digestion, intestinal putrefaction, diarrhea, dysentery, chronic constipation with inflammation of the large intestine
- Hemorrhoids: Sitz baths and enemas with a plantain decoction are very effective in reducing the inflammation of hemorrhoids
- Eye ailment: In the form of irrigation, a decoction of plantain alleviates eye diseases such as conjunctivitis and blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids)
- Varicose ulcers, bleeding or suppurating wounds, burns. In these cases you can apply compresses with a plantain decoction, or plantain leaves directly, previously blanched in boiling water.
- Insects and reptile bites: Dr. Leclerc states that weasels rub themselves on the plantain plants before fighting snakes in order to become protected against reptile poison.
In the case of bites of insects, spiders, bees, or scorpions, vigorously rub the affected area with plantain leaves, then apply a dressing or poultice made with plantain leaves.
In the case of snake bites, the usual emergency treatment is required (cut the area, tourniquet, anti-poisonous serum), then a lotion and a dressing or poultice with plantain leaves.
Common Plantain (Plantago major) and Lance-leaf Plantain (plantago lanceolata).
Parts of the plant used:
- Leaves
- Seeds
Properties Include:
- Diuretic
- Emollient
- Alterative
- Astringent
- Deobstruent
- Expectorant
- Vulnerary
- Antiseptic
Plantain leaves affect the following:
- Veins
- Kidneys
- Intestine
- Externally on the skin
Plantain Leaves Benefits and Purposes
There are several plantains, but they all have the same properties. The two primary ones are common plantain (plantago major), which has an almost circular leaf, and the lesser-used lance-leaf plantain (plantago lanceolata), which has very narrow leaves. The wider the leaf, the greater the diuretic effect.
Internally, plantain has soothing, cooling properties which make it effective in a wide range of maladies, including infections, inflammations, diarrhea, ulcers, bronchitis, and excessive menstrual discharge. Make an infusion using an ounce of the herb in a pint of water. It acts as a diuretic and is soothing to the lungs and urinary tract.
It is excellent for acute neuralgia; for this, take 2-5 drops of tincture every 20 minutes.

Regarding plantain leaves benefits, it is a good remedy for cough irritations, hoarseness, gastritis, and enteritis. It is helpful for all respiratory problems, especially those involving mucous congestion. It is useful for indigestion and heart-burn.
It is useful in the treatment of water retention and kidney and bladder infections. It will neutralize stomach acids and normalize all stomach secretions.
Another on plantain leaves benefits is that, it may slow the growth of tuberculosis bacteria.
The seeds are similar to psyllium seeds. And, if taken in amounts of 1 tsp. of powdered juice 3 times a day, it will provide an excellent bulk laxative. Soaked overnight in water, this will produce a gel. Then bring it to a boil, turn off the fire, and let it steep for 10 minutes.
Press the gel through a strainer and use for ulcers, intestinal pains, and spitting up of blood. Inject a cup of the tea several times a day into the colon for hemorrhoids. Use it as a douche for vaginal difficulties. The fresh juice, pressed from the whole plant, is good for chronic catarrhal problems, gastro-intestinal difficulties, and worms.
Externally:
Plantain has a healing, antibiotic, and styptic (blood stanching) effect when applied to sores and wounds. It is commonly known to neutralize the toxins of insect and snakebites.
Put freshly ground leaves (or chewed slightly) onto the bites of snakes, insects, and bees. A decoction of the dried leaves promotes coagulation of blood. Place a salve of it on boils, carbuncles, and eczema. The fresh juice extract is good for itchy skin. At the same time, swallow a tablespoon of the fresh juice.
Plantain is an excellent remedy for skin infections, cuts, scratches, and chronic skin problems. It is used in a variety of salves and ointments, alone or in combination with other herbs (such as chickweed, comfrey, mugwort, and angelica).
Apply the fresh leaves to wounds, sores, insect bites, ringworm, and even hemorrhoids. Chewing the rootstock will give temporary relief from toothache.
Preparation and Use
Internal Use
- Decoction with 20 – 30 g of leaves and/or root per liter of water, boiling for 3 to 5 minutes. Drink from 3 to 5 five cups daily.
External Use
- The same decoction, however more concentrated (50 – 100 g per liter) is used in gargles, compresses on the skin, eye irrigations, sitz baths, or enemas.
- Leaf dressing: Previously wash the leaves, and blanch them in boiling water for 1 minute in order to sterilize them. Then, put them on the wounds and ulcers with the help of a pair of sterilized forceps. Fix them with a bandage and change 2 or 3 times daily.
- Poultices of boiled and mashed leaves.
The following preparation, use and amount are culled from natural remedies encyclopaedia and Healthy Plant Book as written by Dr. George P.
SEE ALSO: Home Remedies for Cystitis
Preparation and Amount
- Infusion (leaf): Steep 5-15 min. 3 0z. 3 – 4 times daily.
- Decoction (seed): Simmer 1 oz. seeds in 1 ½ pints of water; reduce to 1 pint, sweeten with honey. Take 1 Tbsp. 3-4 times daily.
- Tincture: Take 2 – 60 drops 3-4 times daily.
- Fluid extract: Take ½ – 1 tsp. 3 – 4 times daily.
- Powder: Take up to 10 #0 capsules (up to 60 grains) 3-4 times daily.
Oligospermia Natural Treatment
Home Remedies for Motion Sickness
How To Live With HIV-Positive Person

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.