What is autoimmune disease?
Here’s how we can understand autoimmune disease really is. The immune system is made up of organs and cells designed to defend the body against bacteria, parasites, viruses, and cancer cells. Autoimmune diseases are the result of the immune system mistakenly attacking the body instead of protecting it.
It is unclear why the immune system does this.
A healthy immune system protects the body from disease and infection. However, when the immune system fails, it mistakenly attacks healthy cells, tissues and organs. These attacks, called autoimmune diseases, can affect every part of the body, weakening bodily functions and even being life threatening.
Scientists know of over 100 autoimmune diseases. Some are well-known, such as type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis, while others are rare and difficult to diagnose.
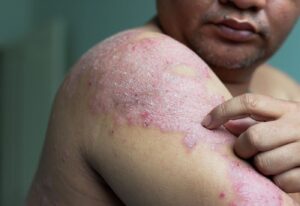
With abnormal autoimmune diseases, patients can suffer for years before receiving a proper diagnosis. Most of these diseases are incurable. Some people need lifelong treatment to relieve symptoms.
Over 100 autoimmune diseases are known. Common ones include lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Autoimmune diseases can affect many types of tissues and almost any organ in the body.
They can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, fatigue (fatigue), rashes, nausea, headaches, dizziness, etc. Specific symptoms depend on the exact disease.
How do autoimmune diseases work?
Experts don’t know why the immune system is turning its back on you. There are several theories as to why this happens, but experts aren’t entirely sure.
What is the list of autoimmune disease?
Some common autoimmune diseases are:
Diseases of joints and muscles
- Psoriatic
- Sjögren’s syndrome
- Rheumatoid arthritis(RA)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus,SLE)
Gastrointestinal diseases
- Crohn’s disease
- Celiac disease
- Ulcerative colitis
Diseases of the endocrine system
- Addison’s disease
- Grave’s disease
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
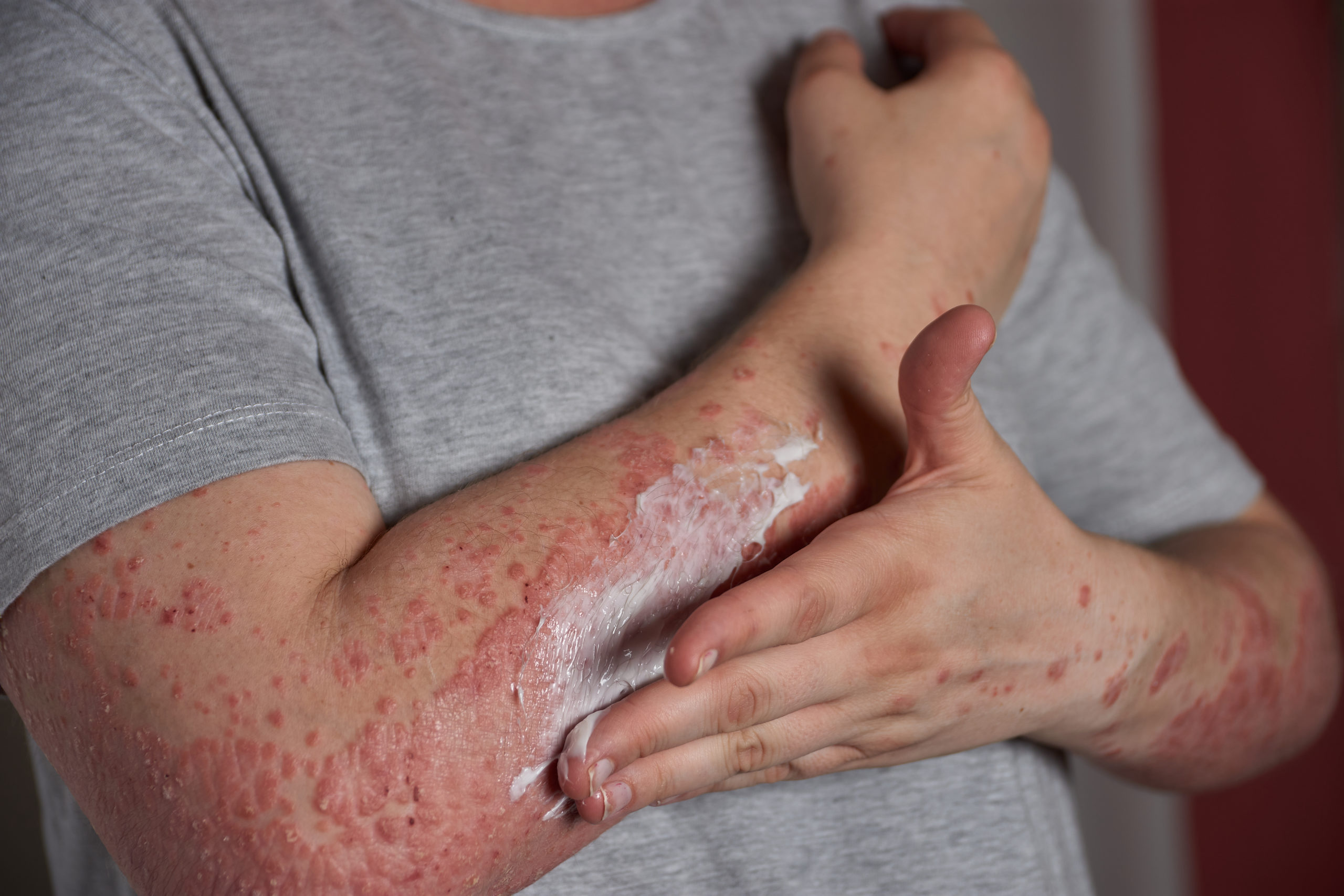
Skin diseases
- Dermatomyositis
- Psoriasis
Diseases of the nervous system
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Multiple sclerosis(MS)
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy(CIDP)
Other diseases
- Myasthenia gravis
- Vasculitis
- Autoimmune vasculitis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Pernicious anemia
Are autoimmune diseases common?
Many autoimmune diseases are more common in women than in men. The disease is prevalent, with 1 in 15 in the United States having an autoimmune disease.
One million people in the United States have lupus and 1.4 million have Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
Are autoimmune diseases hereditary?
Yes. Some autoimmune diseases tend to run in families
Are autoimmune diseases contagious?
No.
Are autoimmune diseases fatal?
Autoimmune diseases are among the top 10 causes of death for women of all ages (up to age 64).
How does an autoimmune disease affect you when trying to conceive?
Some autoimmune diseases affect the ability to conceive, while others adversely affect pregnancy. You can also wait until the disease is in remission before trying to conceive.
Having lupus increases the risk of stillbirth or premature birth. People with myasthenia gravis may have difficulty breathing.
Symptoms and causes
What are the Causes of Autoimmune Diseases?
The exact cause of autoimmune disease is unknown. However, there are risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing an autoimmune disease. Risk factors include:
- Some drugs: Talk to your doctor about side effects of blood pressure medications, statins, and
- Relative with an autoimmune; some diseases are hereditary and run within families.
- Smoking
You already have an autoimmune. Increased risk of developing another disease. - Exposure to toxins
- Being female – 78% of her autoimmune disease patients are female
- Obesity
- Infection
What are the symptoms of autoimmune disease?
Symptoms, grouped by type of disease, include:
Diseases of joints and muscles:
- Muscle aches and pains
- Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
- Weakness of the muscles
- Inflammation
Gastrointestinal diseases:
- Gas (Bloating)
- Constipation
Stomach - Pain
Acid reflux - Nausea
Food - Blood or mucus in stool(poop).
Skin diseases:
- Dry eyes
- Skin rash itch
Dryness of the mouth - Inflammation
Dry skin - Hair loss
Diseases of the nervous system:
– Dizzy
– Anxiety and depression
– Headache
– Blurry vision
– Confusion and difficulty thinking
– Insomnia
– Memory problem
– Migraine
– Sleepiness
– Numbness and tingling.
Other diseases:
Malaise
Pain
Heat
Chest pain.
Swollen glands
Weight gain or loss.
A fast or irregular heartbeat
Difficulty breathing.
Temperature sensitivity.
How long do autoimmune diseases last?
It’s different. Some are easy to handle and some are not. Some autoimmune diseases can be lifelong.
DIAGNOSTICS AND TESTS
How are autoimmune diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases usually takes longer than diagnosing other diseases. This is because many autoimmune diseases share similar symptoms with each other and with others. Bringing the following items with you to your appointment can help your doctor make the diagnosis:
- A detailed list of all symptoms and how long those symptoms
- A record of your family’s health. Please be careful if you have an autoimmune disease in your family.
In addition to asking about your symptoms, your doctor may do some blood tests to check for autoimmune diseases.
- Antinuclear antibody test(ANA).
- Complete blood count(CBC).
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR).
Certain symptoms combined with certain blood markers can prove that you have an autoimmune disease.
Which healthcare providers diagnose autoimmune diseases?
If your GP cannot make a diagnosis, you should see a specialist, such as a gastroenterologist or rheumatologist.
What questions might a healthcare provider ask to help diagnose an autoimmune disease?
When health care providers interview you, they may ask you one or more of the following questions:
- What medications do you take?
- What are your symptoms
- How severe are your symptoms?
- Did you have to go to the emergency room because of your symptoms?
- How long have these symptoms been present?
- How are your symptoms affecting your quality of life?
- Is there any thing that is”triggering”your symptoms?
- Is there anything that makes them worse?
- Do you have a history of autoimmune disease in your family?
- What autoimmune diseases does your family have?
- Have you tried over-the-counter or alternative medicines?
ADMINISTRATION AND TREATMENT
How are autoimmune diseases treated?
There is no cure for autoimmune diseases, but symptoms can be treated. Everyone’s immune system, genetics, and environment are unique. This means your treatment must be unique. Examples of drugs used to treat autoimmune diseases include:
1. Pain reliever
2. Anti-inflammatory
3. Depression and anxiety medicine.
4. Insulin injection
5. Sleeping pills
- Plasma exchange
7. Corticosteroid
8. Rash creams and pills
9. Intravenous immunoglobulin.
10. A drug that suppresses (suppresses) the immune system.
Some people try complementary (alternative) drugs or treatments. For example:
- Hypnosis
- Herb
- Acupuncture
- Chiropractic
What health care providers treat autoimmune diseases?
Which specialist is needed depends on the type of autoimmune disease. Your healthcare provider may refer you to:
1. Gastroenterologist
2. Endocrinologist
- Dermatologist
4. Rheumatologist
Does diet play a role in treating autoimmune diseases?
Some experts say what you eat influences autoimmune diseases. Consult your doctor or dietitian for the ideal meal plan.
Can exercise help with autoimmune diseases?
Yes. However, talk to your doctor about what type and amount of exercise is right for you.
PREVENTION
Can autoimmune diseases be prevented?
Autoimmune diseases may not be preventable. However, some experts recommend trying the following:
1. Avoid toxins
2. Train consistently
3. Eat healthy
4. Stay away from cigarettes
- Limit processed foods from your diet.
Health Benefits of Blueberries

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.