Helpful Bronchial Asthma Treatment
Before delving into bronchial asthma treatment, have you ever heard the term “bronchial asthma” and wondered what it means?
When people talk about bronchial asthma, they are actually talking about asthma.
Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that causes periodic “attacks” of coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and chest tightness.
According to the CDC, more than 25 million Americans now have asthma, 6.8 million of whom are children under the age of 18.
Allergies are closely related to asthma and other respiratory diseases such as chronic sinusitis, otitis media and nasal polyps.
Of particular interest is a recent analysis of asthma patients that found that those with both allergies and asthma were more likely to wake up in the middle of the night due to asthma, miss work due to asthma, or take more medications to control their symptoms.
It turns out that you are more likely to take more medications. It turns out that they are much more likely to need stronger drugs.
However, with proper management and treatment, people with bronchial asthma can lead fulfilling lives. The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive overview of various treatment options for asthma, ranging from medications to lifestyle changes.
Bronchial asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, resulting in recurrent symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and chest tightness. Symptoms range from mild to severe, and vary in frequency and intensity from person to person.
Type Of Asthma
Pediatric Asthma: Asthma in infants and young children often has a paroxysmal form with fever.
If breathing difficulties persist: This type of asthma with persistent dyspnea (dyspnea) is a serious condition that usually affects people with long-term asthma and leads to respiratory failure.
Exercise-induced asthma: Physical exertion causes a shortness of breath crisis.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of bronchial asthma are:
Gasping: Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs as air passes through a narrowed airway. This is a classic asthma symptom often heard when exhaling.
Cough: A persistent dry cough is a common symptom of bronchial asthma. Cough may be worse at night or early in the morning.
Difficulty breathing: People with asthma often feel shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. This sensation can range from mild to severe, depending on the degree of airway obstruction.
Chest tightness: Many people with bronchial asthma feel a tightness or tightness in their chest. This symptom may accompany other asthma symptoms or may occur independently.
Increased respiratory rate: During an asthma attack or attack, people may breathe faster to compensate for the restricted airflow.
Causes of Bronchial Asthma
The exact cause of bronchial asthma is not fully understood, but is thought to be the result of complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Common triggers and underlying causes associated with bronchial asthma include:
Allergen: Exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, and certain foods can trigger asthma symptoms in people with allergic asthma. Environmental factors:
– Irritants such as smoke (cigarette smoke, wood smoke), air pollution, strong odors, and chemical fumes can trigger asthma symptoms.
Respiratory infections: Viral respiratory infections, such as the common cold, can trigger asthma symptoms or exacerbate existing asthma.
Practice: Physical activity or exercise-induced asthma can cause symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath during or after physical activity.
Professional elements: Some people develop work-related asthma as a result of exposure to substances such as chemicals, dust, and fumes at work.
Genetic factors: If you have asthma or allergies in your family, you are more likely to develop bronchial asthma.
Airway Hyperresponsiveness: Individuals with asthma have airways that are more sensitive and react strongly to various stimuli, leading to airway inflammation, constriction, and symptoms.
It is important to note that asthma triggers can vary from person to person, and identifying and avoiding individual triggers is an essential part of managing bronchial asthma effectively.
Proper diagnosis and regular monitoring by a healthcare professional are crucial for understanding specific triggers and developing a personalized treatment plan to control symptoms and prevent exacerbations.
Bronchial Asthma Treatment
Medications for Bronchial Asthma Treatment
- Short-acting Beta2-Agonists (SABAs): These are quick-relief medications used to provide immediate relief during asthma attacks by relaxing the muscles in the airways.
- Long-acting Beta2-Agonists (LABAs): Typically used in combination with inhaled corticosteroids, LABAs help control and prevent asthma symptoms by relaxing the airway muscles for an extended period.
- Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS): The most commonly prescribed long-term controller medication, ICS work by reducing airway inflammation and preventing asthma symptoms from occurring.
- Leukotriene Modifiers: These oral medications help decrease inflammation and open up the airways by blocking the actions of leukotrienes, substances involved in the allergic response.
- Mast Cell Stabilizers: These medications prevent the release of histamine and other chemicals that contribute to airway inflammation, thus reducing asthma symptoms.
- Oral Corticosteroids: Reserved for severe cases or acute exacerbations, oral corticosteroids help reduce inflammation and improve lung function, but they are typically used for short durations due to potential side effects.
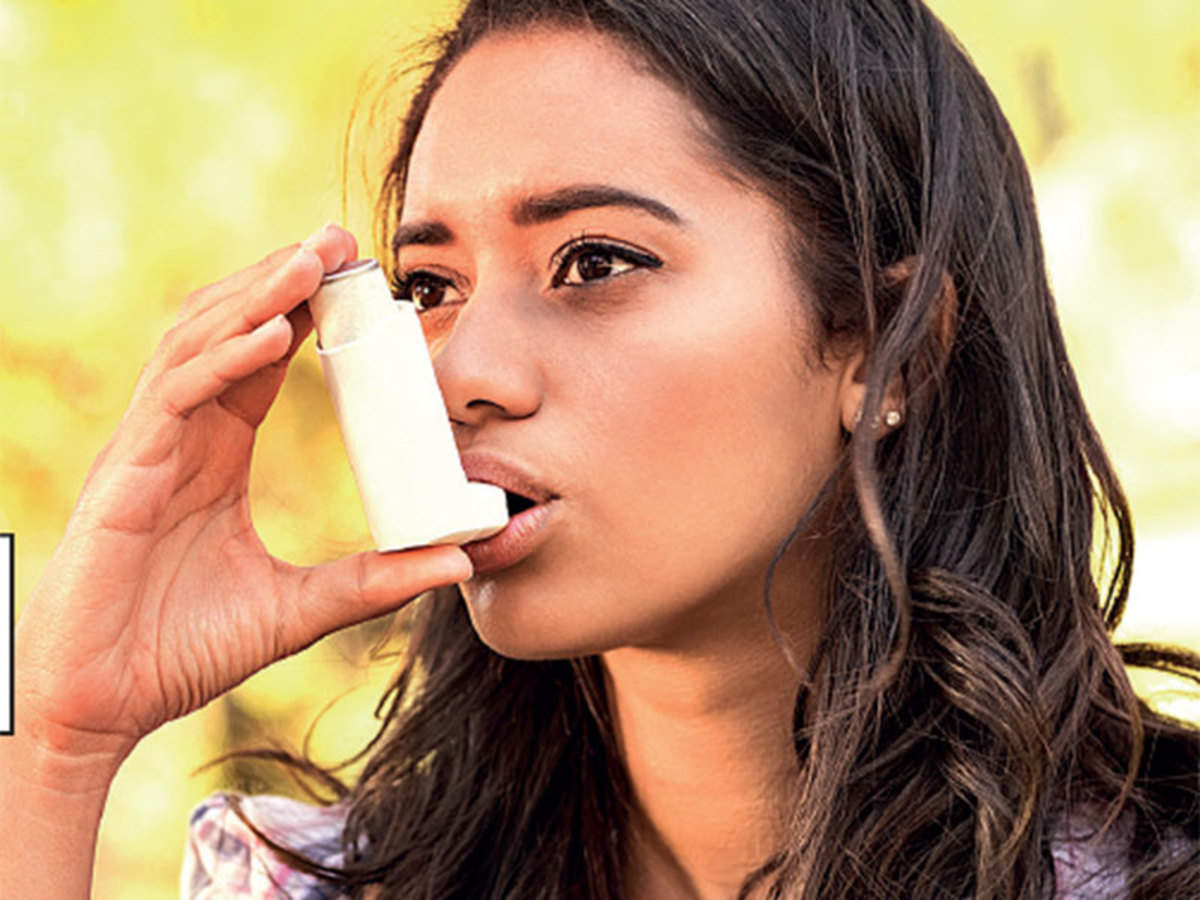
Inhalers and Devices:
- Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs): These portable devices deliver medication directly into the lungs in a spray form and require proper technique for effective use.
- Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs): These inhalers deliver medication in a powdered form, activated by the user’s breath, making them suitable for individuals who struggle with the coordination required for MDIs.
- Nebulizers: Particularly useful for children and individuals who have difficulty using inhalers, nebulizers convert liquid medication into a fine mist that can be inhaled through a mask or mouthpiece.
Allergen Immunotherapy
Allergen immunotherapy, commonly known as allergy shots, involves gradually exposing individuals to increasing amounts of specific allergens to desensitize their immune systems. This treatment can be beneficial for people with allergic asthma, as it helps reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as dust mites, pollen, pet dander, and cigarette smoke can significantly reduce the frequency of asthma attacks.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can help improve lung function and overall fitness.
- Managing Stress: Stress can trigger asthma symptoms, so adopting stress management techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can be beneficial.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation and support overall respiratory health.
Emergency Treatment:
For severe asthma attacks that do not respond to regular medication, immediate medical attention is crucial. Emergency treatments may include short-acting bronchodilators administered through nebulizers, intravenous corticosteroids, and oxygen therapy.
Natural Remedies for Bronchial Asthma Treatment
Although pharmacotherapy plays an important role in managing bronchial asthma, some consider naturopathic options as a complementary or alternative approach.
It is important to note that natural remedies do not replace prescription medications, but can be used in conjunction with them under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Here are some natural treatment approaches that people with bronchial asthma can consider.
Breathing method:
Practicing certain breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing, improves lung function, increases oxygen uptake, and reduces shortness of breath. These exercises are intended to promote relaxation, strengthen respiratory muscle strength, and improve overall breathing control.
Herbs:

Certain herbal medicines may have potential benefits for people with bronchial asthma, but it is important to consult a doctor before use, as they may interact with medications and have different effects. Herbal medicines commonly used to treat asthma include:
Boswellia:
Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, Boswellia extract may reduce airway inflammation and improve symptoms.
Ginger:
Traditionally used to treat respiratory ailments, ginger may have bronchodilatory and anti-inflammatory properties.
Turmeric:
Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory properties and may reduce airway inflammation.
Essential oil:
Certain essential oils, when used with caution and diluted properly, can provide temporary relief from asthma symptoms. Eucalyptus, peppermint and lavender oils are commonly used due to their potential bronchodilatory, anti-inflammatory and soothing properties.
Inhalation methods such as vapor inhalation or using a diffuser are usually recommended.
Acupuncture:
Acupuncture, the traditional Chinese medical practice of inserting fine needles into specific areas of the body, can help reduce asthma symptoms in some people.
It is believed to improve energy flow and balance in the body, reduce inflammation, and potentially improve overall health.
Dietary changes:
There is no specific diet for asthma, but eating a healthy, balanced diet can support overall respiratory health. Eating antioxidant-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation.

Additionally, the omega-3 fatty acids found in oily fish, flax-seed, and walnuts may have anti-inflammatory properties. However, individual food triggers should be identified and avoided if they exacerbate asthma symptoms.
It is important to emphasize that natural treatments for bronchial asthma should be performed under the guidance of a medical professional.
What works for one person may not work for another, and some natural remedies may have limited scientific evidence of their effectiveness. Therefore, it is important to consult a physician who can provide individualized advice and can safely integrate natural remedies with conventional asthma treatment.
Conclusion
Effective treatment and management of bronchial asthma require a comprehensive approach that includes appropriate medication, proper inhaler technique, avoidance of triggers, and lifestyle modifications.
By working closely with healthcare professionals and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals with bronchial asthma can achieve better control of their symptoms, minimize exacerbations, and improve their overall quality of life.
It is important to note that asthma is a highly variable condition and treatment regimens may vary from person to person. Health care providers consider factors such as asthma severity, symptom frequency, response to medications, and personal preferences when developing treatment strategies.
Regular monitoring of lung function B. Spirometry tests help the health care professional assess the effectiveness of treatment and make any necessary adjustments. It is important for people with asthma to maintain open communication with their healthcare team and report any changes in symptoms, side effects of medications, or concerns.
In summary, treatment of bronchial asthma aims to achieve optimal symptom control and improve quality of life for people with this condition.
A combination of drugs, proper inhalation technique, allergen avoidance, lifestyle changes, and regular follow-up by a health care professional can help people with asthma to effectively manage their symptoms and lead active, fulfilling lives.
Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen are key to successful asthma management.
Worst Foods for Erectile Dysfunction
How To Manage High Cholesterol
How To Treat Heartburn Naturally

A graduate of Computer Science and Information Management Technology. Diploma – Caregiving, Certificates – Dementia and Diabetes Awareness and Management. A researcher, blogger, songwriter, singer and acoustic guitarist. Born in an environment where natural talents such as healing are imparted at our natural birth. This natural talents of healing is the result of our genetic inheritance and the training from family environment.